Abstract
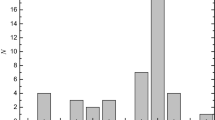
Addition of water to stoichiometric 100% sulfuric acid increases the density untila maximum results near 87 mole% H2SO4. The density and conductivity maximaand viscosity minimum, the latter two near 75 mole%, are direct macroscopicresponses to microscopic quantum mechanical properties of H3O+ and of nearlysymmetric H-bond double-well potentials, as follows: (1) lack of H bonding tothe O atom of H3O+; (2) short, 2.4–2.6 A, O—O distances of nearly symmetricH bonds; and, (3) increased mobility of protons in such short H bonds, give riseto the density maximum via (1) and (2); (1) produces the viscosity minimum;and the conductivity maximum results from (2) and (3). A pronounced minimumnear 1030 cm−1 in the symmetric SO3 stretching Raman frequency of HSO4 −,observed near 45 mole% also results from double-well effects involving the shortH bonds of direct hydronium ion—bisulfate ion pair interactions. Estimates of theconcentrations of the (H3O+)(HSO4 −) and (H2SO4)(HSO4 −) pair interactions weredetermined from Raman intensity data and are given for compositions between42–100 mole%
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
T. F. Young, Rec. Chem. Progr. 12, 81 (1951).
T. F. Young, L. F. Maranville, and H. M. Smith, in The Structure of Electrolytic Solutions, W. J. Hamer, ed. (Wiley, New York, 1959).
I. M. Klotz and C. F. Eckert, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 64, 1878 (1942).
T. F. Young, C. R. Singleterry, and I. M. Klotz, J. Phys. Chem. 82, 671 (1978).
B. S. W. Dawson, D. E. Irish, and G. E. Toogood, J. Phys. Chem. 90, 334 (1986).
E. R. Malinowski, R. A. Cox, and U. L. Haldna, Anal. Chem. 56, 778 (1984).
K. Tomikawa and H. Kanno, J. Phys. Chem. A 102, 6082 (1998).
T. F. Young and G. E. Walrafen, Trans. Faraday Soc. 57, 34 (1960).
W. F. Giauque, E. W. Hornung, J. E. Kunzler, and T. R. Rubin, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 82, 62 (1960).
J. N. Brönsted, Z. Phys. Chem. 68, 693 (1910).
G. N. Lewis and M. Randall, Thermodynamics and the Free Energy of Chemical Substances (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1923), Table 7, p. 95.
P. A. Giguère, J. Chem. Educat. 56, 571 (1979).
M. D. Newton and S. Ehrenson, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 93, 4971 (1971).
G. E. Walrafen, J. Chem. Phys. 40, 2326 (1964).
G. E. Walrafen, M. R. Fisher, M. S. Hokmabadi, and W.-H. Yang, J. Chem. Phys. 85, 6970 (1986).
G. E. Walrafen, W.-H. Yang, Y. C. Chu, and M. S. Hokmabadi, J. Phys. Chem. 100, 1381 (1996).
C. Weast, ed., in Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 67th edn. (CRC, Boca Raton, FL., 1986-87).
G. W. C. Kaye and T. H. Laby, Tables of Physical and Chemical Constants, (Longman, London, 1986), p. 222.
R. Börnstein and W. A. Roth, eds., Physikalisch-Chemische Tabellen, (Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1912).
O. T. Fasullo, Sulfuric Acid Use and Handling (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1965).
L. P. Hammett and A. J. Deyrup, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 55, 1900 (1933).
G. E. Walrafen and R. T. W. Douglas, Ph.D. Thesis, Howard University, 1980.
R. Pascard, C. R. Acad. Sci. 240, 2162 (1955).
R. Triolo and A. Narten, J. Chem. Phys. 63, 3624 (1975).
G. E. Walrafen and Y. C. Chu, J. Phys. Chem. 96, 9127 (1992).
G. E. Walrafen, M. Abebe. F. A. Mauer, S. Block, G. J. Piermarini, and R. G. Munro, J. Chem. Phys. 77, 2166 (1982).
J. C. Speakman, in MTP International Review of Science, Physical Chemistry Series One, J. M. Robertson, ed., Vol. II (Butterworths, Baltimore, Maryland, 1972), pp. 1-31.
F. H. Rhodes and C. B. Barbour, Ind. Eng. Chem. 15, 850 (1923).
A. Das, S. Dev, H. Shangpliang, K. L. Nonglait, and I. Ismail, J. Phys. Chem. 101, 4166 (1997).
M. Catti, G. Ferraris, and G. Ivaldi, Acta Crystallogr. B35, 525 (1979).
G. Ferraris and G. Ivaldi, Acta Crystallogr. B40, 1 (1984).
H. E. Darling, J. Chem. Eng. Data 9, 421 (1964).
M. Eigen, in The Structure of Electrolytic Solutions, W. J. Hamer, ed. (Wiley, New York, 1959).
G. E. Walrafen, unpublished Raman measurements conducted at Bell Telephone Laboratories, Murray Hill, New Jersey, 1961.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walrafen, G.E., Yang, WH., Chu, Y.C. et al. Structures of Concentrated Sulfuric Acid Determined from Density, Conductivity, Viscosity, and Raman Spectroscopic Data. Journal of Solution Chemistry 29, 905–936 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005134717259
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005134717259