Abstract
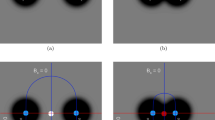
How common are magnetic null points in the highly complex magnetic field of the solar atmosphere? In this work we seek to model the magnetic structure of quiet regions by placing magnetic sources and sinks on a hexagonal network of supergranule cells to represent the intense magnetic fields that occur at the boundaries of these cells. The resulting potential coronal magnetic field is then computed analytically and searched numerically for magnetic null points, which are classified according to their types and spine directions. Two relations from the theory of vector fields relate the numbers of null points to the numbers of sources and sinks and these are used to check the numerical results. Previous results relating these quantities for monopolar and dipolar magnetic fields are described and a new one for a particular class of quadrupolar fields arising in this study is derived. We model a three-cell configuration and study the effects of increasing the strength of a central sink and of moving the central sink. A twelve-cell configuration is studied in lesser detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, D. S. and Priest, E. R.: 1999, Proc. Roy. Soc. London, in press.
Cowley, S. W. H.: 1973, Radio Sci. 8, 903.
Démoulin, P., Hénoux, J. C., and Mandrini, C. H.: 1992, Solar Phys. 139, 105.
Démoulin, P., Hénoux, J. C., and Mandrini, C. H.: 1994, Astron. Astrophys. 285, 1023.
Démoulin, P., Mandrini, C. H., Rovira, M. G., Hénoux J. C., and Machado, M. E.: 1994, Solar Phys. 150, 221.
Démoulin, P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Schmieder, B., Hénoux, J. C., Csepura, G., and Hagyard,M. J.: 1993, Astron. Astrophys. 271, 292.
Dubrovin, B. A., Fomenko, A. T., and Novikov, S. P.: 1990, Modern Geometry-Methods andApplications. Part II. The Geometry and Topology of Manifolds, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Gorbachev, V. S.: 1988, 'The Field Topology and Frozen-In Magnetohydrodynamic Flows of Plasma in the Strong Field Approximation'. PhD thesis, Moscow Institute of Physics and Engineering.
Gorbachev, V. S. and Somov, B. V.: 1989, Soviet Astron. 33, 57.
Gorbachev, V. S., Kel'ner, S. R., Somov, B. V., and Shvarts, A. S.: 1988, Soviet Astron. 32, 308.
Greene, J. M.: 1988, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8583.
Hornig, G. and Rastätter, L.: 1998, Physica Scripta T74, 34.
Inverarity, G. W. and Titov, V. S.: 1997, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 22285.
Lau, Y.-T. and Finn, J. M.: 1990, Astrophys. J. 350, 672.
Longcope, D. W.: 1996, Solar Phys. 169, 91.
Longcope, D. W.: 1998, Astrophys. J. 507, 433.
Mackay, D. H. and Priest, E. R.: 1996, Solar Phys. 167, 281.
Mandrini, C. H., Démoulin, P., Rovira, M. G., de La Beaujardière, J.-F., and Hénoux, J. C.: 1995, Astron. Astrophys. 303, 927.
Molodenskii, M. M. and Syrovatskii, S. I.: 1977, Soviet Astron. 21, 734.
Parnell, C. E., Smith, J. M., Neukirch, T., and Priest, E. R.: 1996, Phys. Plasmas 3, 759.
Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T., and Flannery, B. P.: 1992, Numerical Recipes in Fortran: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd edition, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Priest, E. R. and Démoulin, P.: 1995, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 23443.
Priest, E. R. and Forbes, T. G.: 1989, Solar Phys. 119, 211.
Priest, E. R. and Titov, V. S.: 1996, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A354, 2951.
Priest, E. R., Bungey, T. N., and Titov, V. S.: 1997, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 84, 127.
Schindler, K., Hesse, M., and Birn, J.: 1988, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 5547.
Schrijver, C. J., Title, A. M., Harvey, K. L., Sheeley, Jr., N. R., Wang, Y.-M., van den Oord, G. H. J., Shine, R. A., Tarbell, T. D., and Hurlburt, N. E.: 1998, Nature 394, 152.
Seehafer, N.: 1986, Solar Phys. 105, 223.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inverarity, G., Priest, E. Magnetic Null Points due to Multiple Sources of Solar Photospheric Flux. Solar Physics 186, 99–121 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005129931992
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005129931992