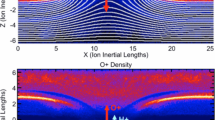
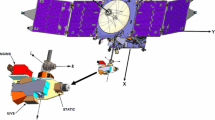
Abstract
The Cluster Ion Spectrometry (CIS) experiment is a comprehensive ionic plasma spectrometry package on-board the four Cluster spacecraft capable of obtaining full three-dimensional ion distributions with good time resolution (one spacecraft spin) with mass per charge composition determination. The requirements to cover the scientific objectives cannot be met with a single instrument. The CIS package therefore consists of two different instruments, a Hot Ion Analyser (HIA) and a time-of-flight ion COmposition and DIstribution Function analyser (CODIF), plus a sophisticated dual-processor-based instrument-control and Data-Processing System (DPS), which permits extensive on-board data-processing. Both analysers use symmetric optics resulting in continuous, uniform, and well-characterised phase space coverage. CODIF measures the distributions of the major ions (H+, He+, He++, and O+) with energies from ~0 to 40 keV/e with medium (22.5°) angular resolution and two different sensitivities. HIA does not offer mass resolution but, also having two different sensitivities, increases the dynamic range, and has an angular resolution capability (5.6° × 5.6°) adequate for ion-beam and solar-wind measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burgess, D.: 1989, ‘Cyclic Behaviour at Quasi-Parallel Collisionless Shocks’, Geophys. Res. Letters 16, 345.
Carlson, C. W. et al.: 1982, ‘An Instrument for Rapidly Measuring Plasma Distribution Functions with High Resolution’, Adv. Space Res. 2 (7), 67.
Escoubet, P. C. and Schmidt, R.: 1997, ‘Cluster Science and Mission Overview’, Space Sci. Rev., this issue.
Giacalone, J. et al.: 1994, ‘Artificial Spacecraft in Hybrid Simulations of the Quasi-parallel Earth's Bow Shock: Analysis of Time Series Versus Spatial Profiles and a Separation Strategy for Cluster’, Ann. Geophys. 12, 591.
Gloeckler, G. et al.: 1993, ‘Detection of Interstellar Pick-up Hydrogen in the Solar System’, Science 261, 70.
Lin, R. P. et al.: 1995, ‘A Three-dimensional Plasma and Energetic Particle Investigation for the Wind Spacecraft’, Space Sci. Rev. 71, 125.
Martz, C.: 1993, ‘Spectrométrie Ionique dans la Magnétosphère et le Vent Solaire. Simulation et Précision des Mesures Coordonnées au Moyen des 4 Satellites de la Mission Cluster’, Thesis, Paul Sabatier Toulouse University.
Martz, C. and Sauvaud, J. A.: 1995, Accuracy of Ion Distribution Measurements and Related Parameters Using Top-hat Ion Spectrometers; Application to the CIS Cluster Experiment, submitted to Rev. Sci. Instruments.
Möbius, E. et al.: 1985, ‘The Time-of-Flight Spectrometer SULEICA for Ions of the Energy Range 5-270 keV/charge on AMPTE IRM’, IEEE Trans. Geosc. Remote Sens. GE-23, 274.
Möbius, E. et al.: 1985, ‘Direct Observation of He+ Pick-up Ions of Interstellar Origin in the Solar Wind’, Nature 318, 426.
Möbius, E. et al.: 1988, ‘Interaction of Interstellar Pick-up Ions with the Solar Wind’, Astrophys. Space Sci. 144, 487.
Paschmann, G. et al.: 1985, ‘The Plasma Instrument for AMPTE IRM’, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. GE-23, 262.
Paschmann, G. et al.: 1986, ‘The Magnetopause for Large Magnetic Shear: AMPTE/IRM Observations’, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 11099.
Quest, K. B.: 1988, ‘Theory and Simulation of Collisionless Parallel Shocks’, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 9649.
Rème, H. et al.: 1987, ‘The Giotto Electron Plasma Experiment’, J. Phys. E: Sci. Instrum. 20, 721.
Ritter, H.: 1985, ‘Sekundärelektronenemission von Kohlenstoffolien beim Durchgang von Ionen im Energiebereich von 40 bis 500 keV’, MPE Report 190.
Scholer, M.: ‘Interaction of Upstream Diffuse Ions with the Solar Wind’, Adv. Space Sci., in press.
Scholer, M. and Terasawa, T.: 1990, ‘Ion Reflection and Dissipation at Quasi-parallel Collisionless Shocks’, Geophys. Res. Letters 17, 119.
Sckopke, N. et al.: 1990, ‘Ion Thermalization in Quasi-perpendicular Shocks Involving Reflected Ions’, J. Geophys. Res. 95, 6337.
Trattner, K. et al.: 1994, ‘Statistical Analysis of Diffuse Ion Events Upstream at the Earth's Bow Shock’, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 13389.
Young, D. et al.: 1988, ‘2π-radian Field-of-View Toroidal Electrostatic Analyzer’, Rev. Sci. Instr. 59, 743.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RÈME, H., Bosqued, J.M., Sauvaud, J.A. et al. THE CLUSTER ION SPECTROMETRY (CIS) EXPERIMENT. Space Science Reviews 79, 303–350 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004929816409
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004929816409