Abstract
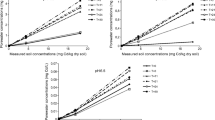
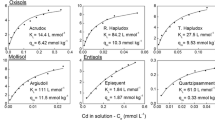
Batch adsorption experiments were carried out with samples from an A-, Bh- and C-horizon of contaminated sandy soil of podzolic character from the Kempen region at the Dutch-Belgian border. Cadmium sorption was studied on 3 soil samples at 3 different pH-levels (3.6, 4.3 and soil buffered pH) and 3 different additions of zinc (0–40 mg l-1).
Adsorption of cadmium by acid sandy soils can be fitted by a Freundlich adsorption isotherm. Although zinc competes with cadmium for the sorption sites, we observe a two to three times stronger competition effect of the proton cation, which is explained by the chemical properties of both ions. The cadmium adsorption coefficient KF decreases considerably by an increase of the proton activity used in the sorption experiments. Organic matter content explains for a large part the variation of KF of te three soil samples. Desorption data do not fit the proposed regression model for adssorption. Not all the cadmium, intitially present in the polluted soil, will fylly desorb reversibly. Thus, part of the cadmium may be irreversible bound.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, P. R. and Christensen, T. H.: 1988, Journal of Soil Science 39, 15.
Barrow, N. J., Gerth, J. and Brümmer, G. W.: 1989, Journal of Soil Science 40, 437.
Benjamin, M. M. and Leckie, J. O.: 1981, Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 79(1), 209.
Black, C. A.: 1965, Methods in Soil Analysis, Part Two, Chemical And Microbiological Properties, American Society of Agronomy.
Boekhold, A. E.: 1992, Field Scale Behaviour of Cadmium in Soil, Thesis, Agricultural University Wageningen, the Netherlands.
Chardon, J.: 1984, Mobiliteit van cadmium in de bodem, Thesis, Agricultural University Wageningen, the Netherlands.
Christensen, T. H.: 1984, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 21, 105.
Christensen, T. H.: 1987, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 34, 305.
Christensen, T. H.: 1989, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 44, 71.
de Haan, F. A. M. van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M. and van Riemsdijk, W. H.: 1987, Netherlands Journal of Agricultural Science 35, 347.
del Castilho, P. and Chardon, W. J.: 1993, Heavy Metals in the Environment, Conference proceeding, Toronto, Canada.
Eriksson, J. E.: 1989, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 48, 317. García.Miragaya, J. and Page, A. L.: 1978, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 9, 289.
Gerritse, R. G. and van Driel, W.: 1984, Journal of Environmental Quality 13(2), 197.
Miller, W. P., McFee, W. W. and Kelly, J. M.: 1983, Journal of Environmental Quality 12(4), 579.
Scokart, P. O., Meeus-Verdinne, K. and de Borger, R.: 1983, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 20, 451.
Sims, J. T.: 1986, Soil Science Society of America Journal 50, 367.
Wilkens, B. J. and Loch, J. P. G.: 1996, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. (submitted for publication).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkins, B.J., Brummel, N. & Loch, J.P.G. Influence of pH and Zinc Concentration on Cadmium Sorption in Acid, Sandy Soils. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 101, 349–362 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004909322206
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004909322206