Abstract
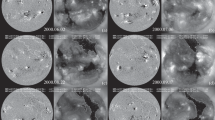
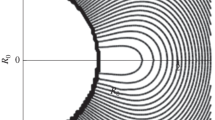
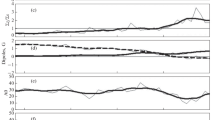
This paper is aimed at establishing the relationship between the large-scale magnetic fields (LSMF), coronal holes (CH), and active regions (AR) in the Sun. The LSMF structure was analyzed by calculating the vector photospheric magnetic field under a potential approximation. Synoptic maps were drawn to study the distribution of the B ⊥ field component and to isolate regions where the open field lines of the unipolar magnetic field are most radial. These are the sites of occurrence of X-ray and Hei 10830 Å coronal holes detected from the SXT/Yohkoh images. It is shown that coronal holes are usually located in LSMF regions with a typical pattern of divergentB ⊥ vectors and a so-called ‘saddle’ configuration.B ⊥ vectors from the ‘conjugate’ (spaced by 90°) coronal holes converge towards the active regions between CH. Variations in AR distort coronal holes and change their boundaries. This implies that the energy regime in CH depends on the energy supply from the active region. The LSMF structure is more stable than coronal holes, remaining practically unchanged during tens of rotations of the Sun. Thus, a peculiar magnetically coupled system of LSMF/CH/AR has been revealed. A model has been suggested to describe the interaction of the emerging toroids in the convection zone and in the photosphere. The cellular convection, that develops at the center of the toroids, is responsible for the occurrence of active regions. The model qualitatively describes the observed particularities of the LSMF/CH/AR system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avrett, E. H., Vernnazza, E. V., and Linsky, J. L.: 1976, Astrophys. J. 207, L199.
Bumba, V., Klvaňna, M., and Sýkora, J.: 1995, Astron. Astrophys. 298, 923.
DeLuca, E. E. and Gilman, P. A.: 1991, in A. N. Cox, W. C. Livingston, and M. S. Matthews (eds), Solar Interior and Atmosphere, Tucson University Arizona Press, p. 304.
Hara, H., Tsuneta, S., Acton, L. W., Bruner, M. E., Lemen, I. R., and Ogawa, J.: 1996, Adv. Space Res. 17, (4-5) 231.
Harvey, J. W., Krieger, A. B., Timothy, A. F. et al.: 1975, Bull. Amer. Astron. Soc. 7, 358.
Hoeksema, J. T.: 1991, Solar Magnetic Fields - 1985 through 1990 2, Report CSSA-ASTRO-91-01.
Hoeksema, J. T. and Scherrer, P. H.: 1986, Solar Magnetic Fields-1976 through 1985, WDCA, UAG Report 94, Boulder, U.S.A.
Kahler, S.W. and Moses, D.: 1990, Astrophys. J. 362, 728.
Kundu, M. R., Strong, K. T., Pick, M. et al.: 1994, Astrophys. J. 427, L59.
Levine, R. H.: 1977, in J. B. Zirker (ed.), Coronal Holes and High-Speed Wind Streams, Skylab Solar Workshop, Colorado Assoc. University Press, p. 103.
McIntosh, P. S.: 1992, in K. Harvey (ed.), The Solar Cycle, p. 14.
Mogilevsky, E. I.: 1995, Geomagn. i Aeron. 35, 11.
Mogilevsky, E. I. and Shilova, N. S.: 1994, Preprints IZMIRAN, Parts 1 and II, Nos. 4. and 4a (1054), Moscow.
Mogilevsky, E. I. and Shilova, N. S.: 1996, Izv. Krym. Astrofiz. Obs. 94, in press.
Moses, D., Cook, J. W., Burtoe, J. F. et al.: 1994, Astrophys. J. 430, 913.
Nikolskaya, K.I.: 1967, Ph.D. Thesis, IZMIRAN, Moscow.
Obridko, V. N. and Shelting, B. D.: 1989, Solar Phys. 124, 73.
Obridko, V. N. and Shelting, B. D.: 1990, Astron. Zh. 67, 890.
Obridko, V. N. et al.: 1997, Solar Phys., in press.
Patron, J., Hill, F., Rhodos, E. I. et al., 1995, Astrophys. J. 455, 746.
Pozhalova, Zh. A.: 1987, Pisma v Astron. Zh. 13, 610.
Shibata, K., Jokoyama, T., and Shimojo, M.: 1994, in Proceedings of Kofu Symposium, NRO, p. 75.
Shine, R., Gerola, H., and Linsky, Z. L.: 1975, Astrophys. J. 202, L101.
Solar Geophysical Data: 1991-1994.
Stepanyan, N. N.: 1995, Izv. RAN, Phys. Ser. 59, 63.
Withbroe, C. L.: 1977, in J. B. Zirker (ed.), Coronal Holes and High-Speed Streams, Colorado Assoc. Univiversity Press, p. 145.
Zirin, H.: 1975, Astrophys. J. 109, L63.
Zirker, J. B. (ed.): 1977, Coronal Holes and High-Speed Wind Streams, Skylab Solar Workshop, Colorado Assoc. University Press, p. 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mogilevsky, E.I., Obridko, V.N. & Shilova, N.S. Large-Scale Magnetic Field Structures and Coronal Holes on the Sun. Solar Physics 176, 107–121 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004908014970
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004908014970