Abstract
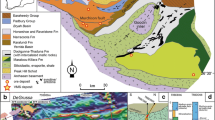
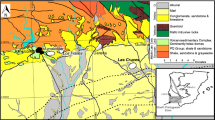
The Semail ophiolite in Oman is one of the few ophiolitic complexes that may display locally magmatic sulphide ores in layer 3 of the crustal section. The ores found in the wadi Haymiliyah plutonic sequence, are composed of low Ni-pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, pyrite and pentlandite. They are located at the bottom of a thick two-pyroxene and noritic gabbro unit, the Main Laminated Noritic Gabbro Unit (MLNGU) that crystallized from evolved tholeiites according to a calc-alkaline liquid line of descent. The MLNGU rests on coarse-grained layered gabbros of the Main Layered Gabbro Unit (MLGU) crystallized from more primitive MORB-like magmas. A detailed mineralogical study coupled with analyses of S, Se, chalcophile transition metals (Cu, Ni, Platinum-group elements, PGE) and Au allows two stages to be distinguished in the precipitation of the sulphides. Sulphide modal abundances start to increase at the top of the MLGU (up to 4%) where orthopyroxene becomes a major phase. Sulphides in the MLGU are only intercumulus and Cu-rich, indicating a S-undersaturated regime. The fine-grained two-pyroxene gabbros at the bottom of the MLNGU contain up to 16% sulphides (monoclinic pyrrhotite, pyrite, chalcopyrite). However, their precious metal contents are very low and far from economic grade (Σ PGE+ Au <15 ppb except one concentration at 230 ppb in the richest layer). Sulphide droplets in cumulus silicates indicate that sulphides precipitated in the fine-grained gabbros from a S-saturated magma. Sulphide liquid immiscibility was likely triggered by a set of unusual circumstances, such as a progressive S enrichment in high fO2 environments resulting from the closure of the Haymiliyah magma subchamber, the lack of a strong Fe-enrichment trend, and possibly a sudden temperature drop. The abundance of disseminated ores suggests that gravity segregation was inefficient; sulphide droplets probably nucleated at the crystallization front of the silicates. This hypothesis (of in-situ crystallization of sulphides) would also account for the very low precious metal contents. All the S present in the magma chamber was mobilized into the ores since the underlying MLNGU and isotropic gabbros are almost devoid of sulphides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alt, J.C. and Anderson, T.F., 1991, Mineralogy and isotopic composition of sulfur in layer 3 gabbros from the Indian ocean, hole 735 B, In R.P. Von Herzen, P.T. Robinson et al. (eds), Proc. ODP., Scien. Results 118: 113–125.
Ballhaus, C. and Ryan, C.G., 1995, Platinum-group elements in the Merensky reef. I. PGE in solid solution in base metal sulphides and the down-temperature equilibration history of Merensky ores, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 122: 241–251.
Ballhaus, C., 1995, Is the upper mantle metal-saturated? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 132: 75–86.
Barnes, S.J., Naldrett, A.J. and Gorton, M.P., 1985, The origin of the fractionation of Pt group elements in terrestrial magmas, Chem. Geology 53: 303–323.
Barnes, Sarah-Jane, Boyd R., Kornellisen, A., Nillsen, L.P., Often, M., Pedersen, R.B. and Robins, B., 1988, The use of mantle normalization and metal ratios in discriminating between the effects of partial melting, crystal fractionation and sulphide segregation on platinum-group elements, gold, nickel and copper: examples from Norway, In H.M. Prichard, P.J. Potts, J.F.W. Bowles and S.J. Cribbs (eds), Geo-Platinum 87, London, Elsevier, pp. 113–143.
Barnes, Sarah-Jane, Zientek M.L. and Severson, M.J., 1997, Ni, Cu, Au, and platinum-group element contents of sulphides associated with intraplate magmatism: a synthesis, Can. J. Earth Sci. 34: 337–351.
Beurrier, M., 1987, Géologie de la nappe ophiolitique de Samail dans les parties orientales et centrales des montagnes d'Oman, thèse Doctorat d'Etat Univ. Paris 6, Paris, France, Documents du BRGM n°128.
Boudier, F., Nicolas, A. and Ildefonse, B. 1996, Magma chambers in the Oman ophiolite: fed from the top and the bottom, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 144: 239–250.
Cabri, L.J., 1973, New data on phase relations in the Cu-Fe-S system, Econ. Geology 68: 443–454.
Campbell, I.H. and Naldrett, A.J., 1979. The influence of silicate: sulfide ratios on the geochemistry of magmatic sulfides, Econ. Geology 74: 1503–1505.
Campbell, I.H., Naldrett, A.J. and Barnes S.J., 1983, A model for the origin of the Pt rich sulfide horizon in the Bushveld and Stillwater complexes, J. Petrol. 24: 133–165.
Caroll, M. R. and Webster, J.D., 1994, Solubilities of sulphur, noble gases, nitrogen, chlorine, and fluorine in magmas, In M.R. Carroll and J.R. Holloway (eds), Volatiles in magmas, Review in Mineralogy, Vol. 30; pp. 231–279.
Craig, J.R., 1973, Pentlandite-pyrrhotite and other low-temperature relations in the Fe-Ni-S systems, Am. J. Sci. 273: 496–510.
Crocket, J.H., Fleet, M.E and Stone, W.E., 1997, Implications of composition for experimental partitioning of platinum-group elements and gold between sulphide liquid and basalt melt: the significance of nickel content, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61: 4139–4149.
Crocket, J.H. 1990, Noble metals in sea floor hydrothermal mineralization from the Juan de Fuca and Mid-Atlantic ridges: a fractionation of gold from platinum metals in hydrothermal fluids, Can. Mineral. 28, 639–648.
Dahl, R., 1984, Etude géométrique, pétrologique et géochimique de la séqeunce crustale de l'ophioite d'Oman, Massif de Rustak (bloc de Haylayn). Un modèle tridimensional de zone d'accrétion, Thèse Université de Clermont Ferrand, France, 264 pages.
Donaldson, C.H. 1979, An experimental investigation of the delay in nucleation of olivine in mafic magmas, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 69, 21–32.
Duke, J.M. and Naldrett, A.J., 1978, A numerical model of the fractionation of olivine and molten sulphides from komatiite magma, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 39: 255–266.
Durazzo, A. and Taylor, L.A., 1982, Exsolution in the mss pentlandite system: textural and genetic implications for Ni sulfides ores, Miner. Deposita, 17: 313–332.
Eckstrand, O.R., 1975, The Dumont serpentinite: a model for control of nickeliferous opaque mineral assemblages by alteration reactions in ultramafic rocks, Econ. Geology 70: 183–201.
Ernewein, M. Pflumio C. and Whitechurch, H., 1988, The death of an accretion zone as evidenced by the magmatic history of the Sumail ophiolite (Oman)? Tectonophysics 151: 247–274.
Ewers, W.L. and Hudson D.R., 1972, An interpretative study of a nickel-iron sulfide ore intersection, Lunon Shoot, Kambalda, Western Australia, Econ. Geology 76: 1075–1092.
Glennie, K.W., Boeuf M.G.A., Highes-Clarke M.W., Moody-Stuart, M., Pilaar, W.F.H. and Reinhardt, B.M., 1974, Geology of the Oman mountains, Part one (Text), Part two (Tables and Illustration), Part three (enclosures), Kon. Nederlands Geol. Mijb. Gen. Ver. Verh., 31, 423 pp.
Greenough, J.D. and Fryer, J.B., 1990, Distribution of gold, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, and iridium in Leg 115 hotspot basalts; implications for magmatic processes, Proc. ODP, Sci. Results 115: 71–84.
Hamlyn, P.R., Keays, R.R., Cameron, W.E., Crawford, A.J. and Waldron, H.M., 1985, Precious metals in magnesian low-Ti lavas: implications for metallogenesis and sulfur saturation in primary magmas, Geochim. Cosmochem. Acta 49: 1797–1811.
Haughton, D.R., Roeder, P.L. and Skinner, B.J., 1974, Solubility of sulfur in mafic magmas, Econ. geology 69: 451–467.
Hébert, R. and Constantin, M., 1991, Petrology of hydrothermal metamorphism of oceanic layer 3: implications for sulphide paragenese and redistribution, Econ. Geol. 86: 472–485.
Hertogen, J., Janssens, M.J. and Palme, H., 1980, Trace elements in ocean ridge basalt glasses; implications for fractionations during mantle evolution and petrogenesis, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 44: 2125–2143.
Jackson, S.E., Fryer, B.J., Gosse, W.D, Healey, C.H., Longerich, P. and Strong D.F., 1990, Determination of the precious metals in the geological materials by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) with nickel-sulfide fire-assay collection and tellurium coprecipitation, Chem. Geol. 83: 119–132.
Jover, O., Rochette, P., Lorand, J.P., Maeder, M. and Bouchez, J.L., 1989, Magnetic mineralogy of some granites from the French Massif Central: inference on magnetic fabric interpretation, Phys. Earth. Planet. Int. 55: 79–92.
Juteau, T., Beurrier, M., Dahl, R. and Nehlig, P., 1988, Magmatic, tectonic and hydrothermal interaction at a dying spreading center: the example of theWadi Haymiliyah section (Haylayn block, Semail nappe, Oman), Tectonophysics 151: 167–198.
Juteau, T., Nehlig, P., Lachise, M. and Lorand, J.P., 1989, Découverte d'une zone à sulfures primaires d'origine magmatique dans la chambre gabbroïque fossile d'Haymiliyah (nappe ophiolitique de Semail, sultanat d'Oman). C.R. Acad. Sci, Paris, t. 309; Série II, pp. 1773–1780.
Kelly, D.P. and Vaughan D.J., 1983, Pyrrhotine-pentlandite ore textures: a mechanistic approach, Mineral. Mag. 47: 453–463.
Kissin, S.A. and Scott, S.D., 1982, Phase relations involving pyrrhotite below 350 °C, Econ. Geology 77: 1739–1755.
Kullerud, G., Yund, R.A. and Moh, G., 1969, Phase relations in the Cu-Fe-S, Cu-Ni-S and Fe-Ni-S systems, in ‘Magmatic ore deposits’, Econ. Geol. Monogr. 4: 323–343.
Lachize, M., 1993, La chambre magmatique fossile d'Haymiliyah (masif de Haylayn, ophiolite de Semail, Sultanat d'Oman; un cas de precipitation de sulfures magmatiques dans la couche 3 de la lithosphère océanique, thèse de Doctorat de l'Univ. Bretagne Occidentale., 314= pp.
Lachize, M., Lorand, J.P. and Juteau T., 1991, Cu-Ni-PGE magmatic sulfide ores and their host layered gabbros in the Haymilyah fossil magma chamber (Haylayn block, Oman ophiolite). In T.J. Peters et al. (eds), “Ophiolite genesis and evolution of Oceanic Lithosphere”, Ministry of Mineral Ressources and Energetics, Sultanate of Oman, pp. 211–231.
Lachize, M., Lorand, J.P and Pattou, L., 1995, Géochimie des métaux nobles (Au et éléments du groupe du platine), cuivre et soufre dans les gabbros lités et les roches ultramafiques intrusives de l'ophiolite d'Oman. Cr. Acad. Sci., t. 320, série II, fascicule A, 23–30.
Lachize, M., Lorand, J.P and Juteau, T., 1996, Calk-alkaline differentiation trend in the plutonic sequence of the Wadi Haymiliyah section, Haylayn massif, Semail ophiolite, Oman, Lithos 38: 207–232.
Li, C., Barnes, S.J., Mackovicky, E., Rose-Hansen, J. and Mackovicky, M., 1996, Partitioning of nickel, copper, iridium, rhenium, platinum, palladium between monosulphide solid solution and sulphide liquid; Effects of composition and temperature, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60: 1231–1238.
Lorand, J.P., 1989, Mineralogy and chemistry of Cu-Fe-Ni sulfides in mantle-derived spinel peridotite bodies from Ariège (Northeastern Pyrenees, France), Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 103: 335–345.
Lorand, J.P., 1990, Are spinel lherzolite xenoliths representative of the sulfur content of the upper mantle? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 54: 1487–1493.
Lorand, J.P., Keays, R.R. and Bodinier, J.L, 1993, Copper-and noble metal enrichment across the asthenosphere-lithosphere mantle diapirs: the Lanzo lherzolite massif, J. Petrology, 34: 1111–1140.
Lorand, J.P., Gros, M. and Pattou, L., 1999, Fractionation of platinum-group element in the upper mantle: a detailed study in Pyrenean orogenic peridotites, J. Petrology 40: 957–981.
Mathez, E.A., 1976, Sulfur solubility and magmatic sulfides in submarine basalt glass. J. Geophys. Res. 81(23), 4269–4276.
Mc Carthy, T.S., Lee, G.A., Fesk, H.W., Kable, D. and Erasmus, C.S., 1984, Sulfur saturation in the Lower and Critical zones of the eastern Bushveld complex, Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 48: 1005–1019.
Mc Queen, K.G., 1979, Experimental heating and diffusion effects in Fe-Ni sulfide ores from Redross, Western Australia. Econ. Geology 74: 140–148.
Misra, K. and Fleet, M.E., 1973, The chemical composition of synthetic and natural pentlandite assemblages, Econ. Geology 68, 518–539.
Morgan, J., 1986, Ultramafic xenoliths: clues to earth's late accretionary history, J. Geophys. Res. 91: 12375–12387.
Morimoto, N., Gyobu, A., Msukuma, K. and Koto, K., 1975, Superstructure and non stoechiometry of intermediate pyrrhotite, Amer. Mineral. 60: 240–248.
Mountain, B.W. and Wood, S.A., 1988, Chemical controls on the solubility, transport and deposition of platinum and palladium in hydrothermal solutions: a thermodynamic approach, Econ. Geology 83: 492–511.
Naldrett, A.J., 1973, Nickel sulfide deposits. Their classification and genesis with special emphasis on deposits of volcanic associations, Can. Inst. Met. Trans. 76: 183–201.
Naldrett, A.J., Craig, J.R. and Kullerud, G., 1967, The central portion of the Fe-Ni-S system and its bearing on pentlandite exsolution in iron-nickel sulfide ores, Econ. Geology 62: 826–847.
Naldrett, A.J., 1989, Sulfide melts-crystallization temperatures, solubilities in silicate melts, and Fe, Ni, and Cu partitioning between basaltic magmas and olivine, In J.A. Whitney and A.J. Naldrett (eds), Ore depositions associated with magmas, Review in Economic Geology, Volume 4, pp. 5–20.
O'Neill, H. St. C., 1991, The origin and the early history of the Earth-A chemical model. Part 2: The Earth, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 55: 1159–1172.
Page, N.J. and Simon, F.O., 1978, Differentiation of the sulfide in the Basal zone of the Stillwater complex, Montana, J. Res. U.S. Geol. Survey 6: 473–482.
Pattou, L., Lorand, J.P. and Gros, M., 1996, Non-chondritic PGE ratios in the terrestrial upper mantle, Nature 379: 712–715.
Peach, C.L., Mathez E.A. and Keays, R.R., 1990, Sulphide meltsilicate melt distribution coefficients for the noble metals and other chalcophile metals as deduced from MORB; implications for partial melting, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 54: 3379–3389.
Peach, C.L., Mathez, E.A., Keays R.R. and Reeves, S.J., 1994, Experimentally-determined sulfide melt-silicate melt partition coefficients for iridium and palladium, Chem. Geology 117: 361–377.
Peck, D.C. and Keays, R.R., 1990, Geology, geochemistry and origin of platinum-group element-chromitite occurrences in the Heazlewood River Complex, Tasmania, Econ. Geol. 85: 765–793.
Poulson, S.R. and Ohmoto, H., 1990, An evaluation of the solubility of sulfide sulfur in silicate melts from experimental data and natural samples, Chem. Geol. 85: 57–75.
Prichard, H.M., Lord, R.A. and Neary, C.R., 1996, A model explaining the occurrence of platinum-and palladium-rich ophiolitic complexes, J. Geol. Soc. London 153: 323–328.
Pflumio, C., 1988, Histoire magmatique et hydrothermale du bloc de Sahali: implcations sur l'origine et l'évolution de l'ophiolite de Sémail (Oman). Thèse de l'Ecole des Mines de Paris, 243 pp.
Rajamani, V. and Naldrett, A.J., 1978, Partitioning of Fe, Co, Ni and Cu between sulfide liquids and basaltic melts and the composition of Ni-Cu sulfide deposists. Econ. geology 73: 82–93.
Rehkämper, M., Halliday, A.N., Lee, D.C., Fitton, JG., Devey, C.W. and Wieneke, 1997, Extreme variability in Ir, Ru, Pt and Pd abundances in Mantle-derived basalts from continental and oceanic settings, AGU Fall Meeting, EOS.
Reuber, I., Nehlig, P. and Juteau, T., 1991, Axial segmentation in a fossil spreading center in the Haylayn block (Semail napper, Oman); off-axis mantle diapir and advancing ridge tip, J. Geodynamics 13: 253–278.
Ripley E., M., Park, Y.R., Li, C. and Naldrett, A.J., 1999, Sulfur and oxygen isotopic evidence of country rock contamination in the Voisey's Bay Ni-Cu-Co deposit, Labrador, Canada. Lithos 47: 53–68.
Sinton, J.M. and Detrick, R.S., 1992, Mid-ocean ridge magma chambers. J. Geophys. Res. 97: 197–216.
Sun, M., Jain, J., Zhou, M.F. and Kerrich, R., 1993, A procedural modification for enhanced recovery of precious metals (Au, PGE) following nickel sulfide assay and tellurium coprecipitation; applications for analyses of geological samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, Canad. J. Appl. Spectroscopy 38: 103–108.
Usselman, T.M., Hodge, D.S., Naldrett, A.J. and Campbell, I.H., 1979, Physical constraint on the characteristics of Ni sulfide ores in ultramafic lavas. Can. Mineral. 17: 361–362.
Vaughan, D.J. and Craig, J.R., 1978, Mineral chemistry of metal sulphides. Cambrid. Earth Sci. Ser., Eds. Harland, W.B., Cook, A.H., and Hughes, N.F., Cambridge Univ. Press, 493 pp.
Wood, S.A., Mountain, B.W. and Fenlon, B, 1993, Thermodynamic constraints on the solubility, transport, and deposition of platinum and palladium in hydrothermal solutions: reassessment of hydroxide, bisulfide and ammonia complexing. Econ. Geol. 84: 2020–2028.
Yund, R.A. and Hall, H.T., 1970, Kinetics and mechanism of pyrite exsolution from pyrrhotite, J. Petrol. 11: 381–404.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lorand, J., Juteau, T. The Haymiliyah Sulphide Ores (Haylayn Massif, Oman Ophiolite): In-situ Segregation of PGE-poor Magmatic Sulphides in a Fossil Oceanic Magma Chamber. Marine Geophysical Researches 21, 327–350 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004887103269
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004887103269