Abstract
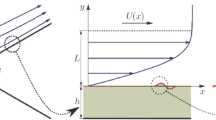
It has been demonstrated experimentally that thin liquid layers may be applied to a solid surface or substrate if a temperature gradient is applied which results in a surface tension gradient and surface traction. Two related problems are considered here by means of the long-wave or lubrication theory. In the first problem, an improved estimate of the applied liquid coating thickness for a liquid being drawn from a bath is found through asymptotic and numerical matching. Secondly, the theory is extended to consider substrates that are not perfectly wetted but exhibit a finite equilibrium contact angle for the coating liquid. This extension incorporates the substrate energetics using a disjoining pressure functional. Unsteady flows are calculated on a substrate of nonuniform wettability. The finite contact angle value required to stop stress-driven flow is predicted and the resulting steady profiles are compared with experimental results for several values of the applied stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Erhard and S. H. Davis, Nonisothermal spreading of liquid drops on horizontal plates. J. Fluid Mech. 229 (1991) 365–388.
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshitz, Fluid Mechanics. Oxford: Pergamon Press (1959).
S. K. Wilson, The effect of an axial temperature gradient on the steady motion of a large droplet in a tube. J. Eng. Math. 29 (1995) 205–217.
M. K. Smith, Thermocapillary migration of a two-dimensional liquid droplet on a solid surface. J. Fluid. Mech. 294 (1995) 209–230.
A. Mazouchi and G. M. Homsy, Thermocapillary migration of long bubbles in cylindrical capillary tubes. Phys. Fluids 12 (2000) 542–549.
T. S. Sammarco and M. A. Burns, Thermocapillary pumping of discrete drops in microfabricated analysis devices. AIChE J. 45 (1999) 350–366.
V. Ludviksson and E. N. Lightfoot, The dynamics of thin liquid films in the presence of surface-tension gradients. AIChE J. 17 (1971 1166–1173.
A. M. Cazabat, F. Heslot, S. M. Troian and P. Carles, Fingering instability of thin spreading films driven by temperature gradients. Nature 346 (1990) 824–826.
A. M. Cazabat, F. Heslot, P. Carles and S. M. Troian, Hydrodynamic fingering instability of driven wetting films. Adv. Coll. Interf. Sci. 39 (1992) 61–75.
X. Fanton, A. M. Cazabat and D. Quere, Thickness and shape of films driven by Marangoni flow. Langmuir 12 (1996) 5875–5880.
V. G. Levich, Physiochemical Hydrodynamics. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall (1962) 700 pp.
S. D. R. Wilson, The drag-out problem in film coating theory. J. Eng. Math. 16 (1982) 209–221.
D. E. Kataoka and S.M. Trojan, A theoretical study of instabilities at the advancing front of thermally driven coating films. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 192 (1997) 350–362.
D. E. Kataoka and S. M. Troian, Stabilizing the advancing front of thermall driven climbing films. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 203 (1998) 335–344.
M. H. Eres, L. W. Schwartz and R. V. Roy, Fingering phenomena for driven coating films. Phys. Fluids 12 (2000) 1278–1295.
P. Carles and A. M. Cazabat, The thickness of surface-tension-gradient-driven spreading films. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 157 (1993) 196–201.
H. Gau, S. Herminghaus, P. Lenz and R. Lipowsky, Liquid morphologies on structured surfaces; from microchannels to microchips. Science 283 (1999) 46–48.
N. V. Churaev and V. D. Sobolev, Prediction of contact angles on the basis of the Frumkin-Derjaguin approach. Adv. Colloid Interf. Science 61 (1995) 1–16.
B. V. Derjaguin, The definition and magnitude of disjoining pressure and its role in the statics and dynamics of thin fluid films. Kolloid Zhurnal 17 (1955) 205–214.
G. F. Teletzke, H. T. Davis and L. E. Scriven, Wetting hydrodynamics. Revue de Physique Appliquee 23 (1988) 989–1007.
V. S. Mitlin and N. V. Petviashvili, Nonlinear dynamics of dewetting: Kinetically stable structures. Phys. Lett. A 192 (1994) 323–326.
L. W. Schwartz, Hysteretic effects in droplet motions on heterogeneous substrates: Direct numerical simulation. Langmuir 14 (1998) 3440–3453.
L. W. Schwartz and R. R Eley, Simulation of droplet motion on low-energy and heterogeneous surfaces. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 202 (1998) 173–188.
A. L. Bertozzi, A. Munch, X. Fanton and A.M. Cazabat, Contact line stability and undercompressive shocks in driven thin film flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 (1998) 5169–5172.
A. L. Bertozzi, A. Munch and M. Shearer, Undercompressive shocks in thin filmflows. Physica D 134 (1999) 431–464.
A. Munch and A. L. Bertozzi, Rarefaction-undercompressive fronts in driven films. Phys. Fluids 11 (1999) 2812–2814.
R.W. Atherton and G.M. Homsy, On the derivation of evolution equations for interfacial waves. Chem. Eng. Comm. 2 (1976) 57–77.
E. O. Tuck and L. W. Schwartz, A numerical and asymptotic study of some third-order ordinary differential equations relevant to draining and coating flows. S.I.A.M. Rev. 32 (1990) 453–469.
M. D. Van Dyke, Perturbation Methods in Fluid Mechanics. Annotated Edition. Stanford: Parabolic Press (1975) 271 pp.
H. M. Princen, The equilibrium shapes of interfaces, drops and bubbles. Surf. Colloid Sci. 11 (1969) 1–84.
C. Huh and L. E. Scriven, Hydrodynamic model of steady movement of a solid liquid fluid contact line. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 35 (1971) 85–101.
J. A. Moriarty and L.W. Schwartz, Effective slip in numerical calculations of moving-contact-line problems. J. Eng. Math. 26 (1992) 81–86.
J. N. Israelachvili, AIntermolecular and Surface Forces, 2nd Ed. London: Academic Press (1992) 450 pp.
J. A. Moriarty and L.W. Schwartz, Dynamic considerations in the closing and opening of holes in thin liquid films. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 161 (1993) 335–342.
D. E. Weidner, L.W. Schwartz and R. R. Eley, Role of surface tension gradients in correcting coating defects in corners. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 179 (1996) 66–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwartz, L.W. On the asymptotic analysis of surface-stress-driven thin-layer flow. Journal of Engineering Mathematics 39, 171–188 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004855022321
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004855022321