Abstract
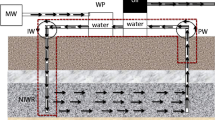
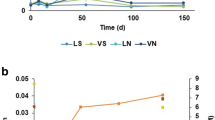
Thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) oxidizing lactate, butyrate, and C12–C16 n-alkanes of oil at a temperature of 90°C were isolated from samples of water and oil originating from oil reservoirs of the White Tiger high-temperature oil field (Vietnam). At the same time, no thermophiles were detected in the injected seawater, which contained mesophilic microorganisms and was the site of low-temperature processes of sulfate reduction and methanogenesis. Thermophilic SRB were also found in samples of liquid taken from various engineering reservoirs used for oil storage, treatment, and transportation. These samples also contained mesophilic SRB, methanogens, aerobic oil-oxidizing bacteria, and heterotrophs. Rates of bacterial production of hydrogen sulfide varied from 0.11 to 2069.63 at 30°C and from 1.18 to 173.86 at 70°C μg S/(l day); and those of methane production, varied from 58.4 to 100 629.8 nl CH4/(l day) (at 30°C). The sulfur isotopic compositions of sulfates contained in reservoir waters and of hydrogen sulfide of the accompanying gas indicate that bacterial sulfate reduction might be effective in the depth of the oil field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rozanova, E., Nazina, T., Mats, A., and Kulik, E., Development of Hydrocarbon-Oxidizing Bacteria in Model Oil Strata and Production of Oil-Releasing Compounds, Doklady po geokhimii i fiziko-khimicheskim voprosam razvedki i dobychi nefti i gaza (Reports Concerning Geochemical and Physicochemical Issues Related to Oil and Gas Prospecting and Extraction), 1988, Solnok (Hungary), vol. III, pp. 426–434.
Nazina, T.N., Rozanova, E.P., and Kuznetsov, S.I., Microbial Oil Transformation by Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Formation, Geomicrobiol. J., 1985, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 103–130.
Rueter, P., Rabus, R., Wilkes, H., Aeckersberg, F., Rainey, F.A., Jannasch, H.W., and Widdel, F., Anaerobic Oxidation of Hydrocarbons in Crude Oil by New Types of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Nature, 1994, vol. 372, pp. 455–458.
Heider, J., Spormann, A.M., Beller, H.R., and Widdel, F., Anaerobic Bacterial Metabolism of Hydrocarbons, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 1999, vol. 22, pp. 459–373.
Mago, M., O llivier, B., and Patel, B.K., Thermophiles from Petroleum Reservoirs, Int. Conf. Thermophiles'98, 6–11 Sept., 1998, Brest, France, B-06.
Belyaev, S.S., Rozanova, E.P., Borzenkov, I.A., Charakhch'yan, I.A., Miller, Yu.M., Sokolov, M. Yu., and Ivanov, M.V., Peculiarities of Microbial Processes in a Water-Flooded Oil Field in the Central Ob Region, Mikrobiologiya, 1990, vol. 59, no. 6, pp. 1075–1082.
Beeder, J., Nilsen, R.K., Rosnes, J.T., Torsvik, T., and Lien, T., Archaeoglobus fulgidus Isolated from Hot North-Sea Oil Field Waters, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1999, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 1227–1237.
Areshev, E.G., Dong, Ch.L., and Kireev, F.A., The Oil and Gas Content of the Base Granitoid Rock by the Example of the White Tiger Field, Neftyanoe Khoz-vo, 1996, no. 8, pp. 50–58.
Widdel, F., Anaerober Abbau von Fettsüren und Benzoesüre durch neu isolierte Arten Sulfat-reduzierender Bakterien, Thesis, Göttingen: Univ. Göttingen, 1980, pp. 7–147.
Trüper, H.G. and Schlegel, H.G., Sulphur Metabolism in Thiorhodaceae: I. Quantitative Measurements on Growing Cells of Chromatium okenii, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 1964, vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 225–238.
Milekhina, E.I., Borzenkov, I.A., Zvyagintseva, I.S., Kostrikina, N.A., and Belyaev, S.S., Characterization of Hydrocarbon-Oxidizing Rhodococcus erythropolis Strain Isolated from an Oil Field, Mikrobiologiya, 1998, vol. 67, no. 3, pp. 328–332.
Balch, W.E., Fox, G.E., Magrum, L.J., Woese, C.R., and Wolf, R.S., Methanogens: Reevaluation of Unique Biological Group, Microbiol. Rev., 1979, vol. 43, pp. 260–296.
Oremland, R.S. and Capone, O.G., Use of Specific Inhibition in Biogeomicrobial Ecology, Adv. Microbiol. Ecol., 1988, vol. 10, pp. 285–384.
Borzenkov, I.A., Belyaev, S.S., Miller, Yu. M., Davydova, I.A., and Ivanov, M.V., Methanogenesis in the Highly Mineralized Stratal Waters of the Bondyuzhskoe Oil Field, Mikrobiologiya, 1997, vol. 66, no. 1, pp. 122–129.
Laurinavichus, K.K. and Belyaev, S.S., Radioisotopic Determination of the Rate of Microbial Production of Methane, Mikrobiologiya, 1978, vol. 47, no. 6, pp. 1115–1117.
Nazina, T.N., Rozanova, E.P., Belyaev, S.S., and Ivanov, M.V., Khimicheskie i mikrobiologicheskie issledovaniya plastovykh zhidkostei i kernov neftyanykh mestorozhdenii (Chemical and Microbiological Investigations of Stratal Fluids and Cores from Oil Fields), Pushchino: 1988.
Reznikov, A.A. and Mulikovskaya, E.P., Metody analiza prirodnykh vod (Methods for the Analysis of Natural Waters), Moscow: Izd. literatury po geologii i okhrane nedr, 1954.
Isaksen, M.F., Bak, F., and Jorgensen, B.B., Thermophilic Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in Cold Marine Sediments, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 1994, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 1–8.
Nilsen, R.K., Beeder, T., Thorstensen, T., and Torsvik, T., Distribution of Thermophilic Marine Sulfate Reduction in North Sea Oil Field Waters and Oil Reservoir, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1996, vol. 63, pp. 1793–1798.
Bluche, E., Rachel, R., Burggraf, S., Hafenbradl, D., Jannasch, H.W., and Stetter, K.O., Pyrolobus fumaris, gen. nov. and sp. nov., Represents a Novel Group of Archaea, Extending the Upper Temperature Limit for Life to 113°C, Extremophiles, 1997, vol. 1, pp. 14–21.
Jorgensen, B.B., Isaksen, M.F., and Jannasch, H.W., Bacterial Sulfate Reduction above 100°C in Deep-Sea Vent Sediments, Science, 1992, vol. 258, pp. 1756–1757.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rozanova, E.P., Borzenkov, I.A., Tarasov, A.L. et al. Microbiological Processes in a High-Temperature Oil Field. Microbiology 70, 102–110 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004809308305
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004809308305