Abstract
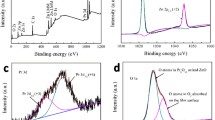
The microstructure, electrical properties, and degradation behavior of Pr-based zinc oxide varistors, which are composed of Zn-Pr-Co-Cr-Y oxides were investigated according to Y2O3 additive content in the range 0.5–4.0 mol%. The majority of the Sadded Y2O3 were segregated at the multiple ZnO grain junctions and grain boundaries. The average grain size was markedly decreased in the range 27.3–8.6 μm with increasing Y2O3 additive content. Y2O3 acted as an inhibitor of grain growth. Additions of Y2O3 increased the varistor voltage in the range 36.90–686.58 V/mm, increased the nonlinear exponent in the range 3.75–87.42, decreased the leakage current in the range 115.48–0.047μA, increased the barrier height in the range 1.06–2.16 eV, and decreased the donor concentration in the rang 1.87 × 1018–0.19 × 1018 cm−3. Y2O3 acted as an acceptor, as a result of the decrease of donor concentration. All Pr-based ZnO varistors doped with Y2O3 exhibited very predominant degradation characteristics, which show a nearly symmetric I-V after the stress. In particular, since 4.0 mol% Y2O3-added ZnO varistor has not only very excellent non-ohmicity, but also very stable degradation behavior, it is estimated to be sufficiently used to various application fields.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Matsuoka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 10 (1971) 736.
L. M. Levinson and H. R. Philipp, Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 65 (1986) 639.
T. K. Gupta, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73 (1990) 1817.
L. K. J. Vanadamme and J. C. Brugman, J. Appl. Phys. 51 (1980) 4240.
S.-N. Bai and T.-Y. Tseng, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 31 (1992) 81.
L. M. Levinson and H. R. Philipp, J. Appl. Phys. 46 (1975) 1332.
M. Fix and J. Soln, Appl. Phys. Lett. 26 (1075) 519.
P. R. Emtage, J. Appl. Phys. 48 (1977) 4372.
K. Eda, ibid. 49 (1978) 2964.
G. D. Mahan, L. M. Levinson and H. R. Philipp, ibid. 50 (1979) 2799.
J. Wong, ibid. 46 (1975) 1653.
M. Inada, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 17 (1978) 1.
Idem., ibid. 17 (1978) 673.
C.-Y. Shen, Y.-C. Chen and L. Wu, ibid. 32 (1993) 2043.
J. Fan and R. Freer, J. Appl. Phys. 77 (1995) 4795.
T. R. Kutty and S. Ezhilvalavan, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 34 (1995) 6125.
S. A. Pianaro, E. C. Pereira, L. O. S. Bulhoes, E. Longe and J. A. Varela, J. Mat. Sci. 30 (1995) 133.
T. K. Gupta and W. G. Carlson, ibid. 20 (1985) 3487.
Y.-S. Lee and T.-Y. Tseng, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75 (1992) 1636.
J. Fan and R. Freer, J. Mat. Sci. 28 (1993) 1391.
C.-S. Chen, C.-T. Kuo and I.-N. Lin, J. Mat. Res. 13 (1998) 1560.
A. B. Alles and V. L. Burdick, J. Appl. Phys. 70 (1991) 6883.
A. B. Alles, R. Puskas, G. Callahan and V. L. Burdick, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76 (1993) 2098.
Y.-S. Lee, K.-S. Liao and T.-Y. Tseng, ibid. 79 (1996) 2379.
M. Mukae, K. Tsuda and I. Nagasawa, J. Appl. Pshys. 50 (1979) 4475.
S. M. Sze, in “Physics of Semiconductor Devices” (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1981) p. 402.
J. C. Wurst and J. A. Nelson, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97–12 (1972) 109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nahm, CW., Park, CH. Microstructure, electrical properties, and degradation behavior of praseodymium oxides-based zinc oxide varistors doped with Y2O3. Journal of Materials Science 35, 3037–3042 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004749214640
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004749214640