Abstract
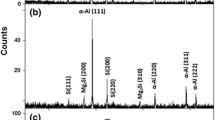
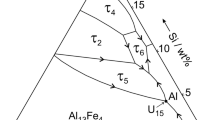
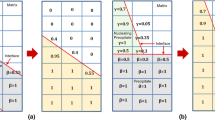
The evolution of microstructure as-spun and during subsequent heat treatment at 200 to 500°C for up to 1000 h has been studied for Al-6.3 Mn-3.3 Si, Al-8.3 Mn-3.7 Si and Al-14.5 Mn-5.8 Si (wt %) alloys, containing 17, 26 and 48 vol % αAlMnSi at equilibrium respectively. Microstructure as-spun ranged from primary icosahedral phase nucleating radial cellular αAl arrays to less regular duplex arrays of αAl and αAlMnSi with decreasing alloy content and decreased section thickness or reduced distance from the chill surface. Heat treatment in the range 200 to 500°C transformed any icosahedral phase present to αAlMnSi along with spheroidization and coarsening/coalescence of αAlMnSi, to produce isolated spheroids when volume fraction f was lower and very stable interlinked chains at higher f. Measured coarsening rates of αAlMnSi were a factor of 10 below predictions of LSW theory at lower f but were within a factor of 2 of prediction at highest f. Hardness was governed by a combination of Hall-Petch and matrix solid solution hardening as-spun supplanted by particle-radius dependent Orowan combined with matrix Hall-Petch hardening for the evolution of hardness during prior long term heat treatment at 425°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. V. Hyattand S. Axter, in “RASELM 91,” ed. K. Hirano et al. (Jap Inst of Light Metals, Tokyo, 1991), pp 273–280.
W. Wei, Metals and Materials 8 (1992) 430.
Y. Barbauxand G. Pons, J. Physique IV, Colloque C7, Supplement III, 3 (1993), 191.
J. Zhou, A. Druzdzeland J. Duszczyk, Proc P/M94 3 (1994) 1587.
T. Koikeand H. Yamagata, ibid., idem. 1627.
C. J. Peel, in “LightWeight Alloys for Aerospace Applications,” eds. E. W. Lee et al; (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1995) pp. 191–205.
A. J. Shakesheffand P. D. Pitcher, Mater Sci. Forum, 217–222 (1996) 1133.
P. Gilman, Metals and Materials 6(8) (1990) 504.
R. E. Frankand J. A. Hawk, Scripta Met, 23 (1989) 113.
H. G. Paris, F. R. Billman, W. S. Cebulakand J. I. Petit, in “Rapid Solidification Processing: Principles and Technologies II,” eds. R. Mehrabian et al. (Claitor's, Baton Rouge, LA, 1980), pp. 331–341.
H. G. Paris, J. W. Mullinsand T. H. SandersJr, in “High Strength P/M Al Alloys,” eds. M. J. Koczak and G. J. Hildeman (The Met. Soc AIME, New York, 1982) pp. 277–296.
G. Terlinde, G. L¨utjering, M. Peters,J. C. Williamsand H. Paris, in “High Strength Materials in Aircraft,” eds. W. Bunk and J. Hansen (D G M, Oberursel, 1982) pp. 95–112.
T. Ahrens, A. Gyslerand G. L¨utjering, Z. Metallkunde 76 (1985) 391.
G. Terlinde, M. Peters, G. L Utjeringand J. C. Williams, Z. Metallkunde, 78 (1987) 607.
B. Saal, J. Albrecht, G. Lutjering, J. Becker and G. Fischer, in “Light Weight Alloys for Aerospace Applications,” eds. E. W. Lee et al. (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989), pp. 3–13.
B. Saal, J. Albrecht, G. L Utjering, J. Beckerand G. Fischer, in “Advanced Aluminium and Magnesium Alloys,” eds. T. Khan and G. Effenberg (ASM, 1990), pp. 299–306.
G. Lutjering, B. Sopartand J. Albrecht, in “Science and Engineering of Light Metals,” eds. K. Hirano et al. (Jap Inst Light Metals, Tokyo, 1991), pp. 27–34.
O. Roder, J. Albrechtand G. L Utjering, Proc Euromat 94, eds. B. Vorsatz and E. Szoke, Vol II, pp. 641–652.
O. Roder, J. Albrechtand G. Lutjering, Proc ICAA4, 1994, eds. T. H. Sanders Jr and E. A. Starke Jr, Vol II, pp. 766–773.
J. A. Hawke, L. M. Angers and H. G. F. Wilsdorf, in “Dispersion Strengthened Aluminium Alloys,” eds. Y. W. Kim and W. M. Griffiths (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1988), pp. 337–354.
H. G. F. Wilsdorf, L. M. A ngers, J. K. Briggs and J. A. Hawk, in “Advances in P/M,” MPIF/APM I, 1989, Vol. 3, pp. 269–283.
J. A. Hawk, J. K. Briggs and H. G. F. Wilsdrof, ibid. pp. 301–315.
H. G. F. Wilsorf, J. K. Briggs and L. M. Angers, Key Eng. Mater., 38, 39 (1989) 318(Proc ICMS-89, Jamshedpur).
E. H. B. Uchler, E. Watanabeand N. S. Kazama, Internat. J. Nupon-equilibrium Processing 10 (1997) 35.
D. M. J. Wilkes, H. Jones and R. W. Gardiner, Mater. Sci. Forum 217–222 (1996) 943.
D. M. J. Wilkesand H. Jones, J. Mater. Sci. 34 (1999) 735.
R. Hambleton, H. Jonesand W. M. Rainforth, Mater. Sci. Eng. A A226/8 (1997) 157.
H. Jones, Mater. Sci. Eng. 5 (1969) 1.
C. G. Leviand R. Mehrabian, Met. Trans. A 13A (1982) 13.
W. J. Boettinger, L. Benderskyand J. G. Early, Met. Trans. A 17A (1986) 781.
P. S. Gilmanand S. K. Das, Metal Powder Report 44 (1989) 617.
G. J. Marshall, J. Mater. Sci. 22 (1987) 3581.
M. A. Zaidi, Mater. Sci. Eng. 98 (1988) 221.
N. J. E. Adkinsand P. Tsakiropoulos, Mater. Sci. Technol. I (1991) 334.
J. Zhon, J. Duszczykand B. M. Korevaar, J. Mater. Sci. 26 (1991) 3292.
G. Shao, P. Tsakiropoulosand A. P. Miodownik, Internat. J. Rapid Solidification 8 (1993) 41.
M. Lieblich, G. Caruana, M. Torralbaand H. Jones, Mater. Sci. Technol. 12 (1996) 25.
V. Radmilovic, G. Thomasand S. K. Das, Mater. Sci. Eng. A A132 (1991) 171.
Z. Y. Mo, N. G. Ning, Y. X. Lu, J. H. Li, J. Biand Y.Z. Zhang, Mater. Lett. 21 (1994) 69.
T. J. Lienert, W. A. Baeslack III, J. Ringnalda and H. L. Fraser, J. Mater. Sci. 31 (1996) 2149.
D. J. Skinner, in “Dispersion Strengthened Aluminium Alloys,” eds. Y. W. Kim and W. M. Griffith (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1988), pp. 181–197.
M. S. Zedalis, J. M. Peltierand P. S. Gilman, in “LightWeight Alloys for Aerospace Applications,” ed. E.W. Lee, E. H. Chia and N. J. Kim (TMS,Warrendale, PA, 1989), pp. 323–334.
M. S. Z edalisand D. J. Skinner, in “LightWeight Alloys for Aerospace Applications,” eds. E. W. Lee, E. H. Chia and N. J. Kim (TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989), pp. 335–344.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkes, D.M.J., Jones, H. Structure and properties of rapidly solidified Al rich Al-Mn-Si alloys Part I Melt spun ribbons. Journal of Materials Science 34, 735–747 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004516728379
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004516728379