Abstract
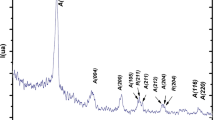
Lead scandium tantalate (PST) thin films have been deposited on a platinized silicon substrate with and without a buffer layer of MgO at the temperature of 525°C. It was found that PST films on the substrate without a buffer layer were strongly (1 1 1) oriented perovskite, whilst films on the substrate with a buffer layer showed the presence of second-phase pyrochlore, and the films were (1 1 1) and (1 1 0) oriented. These structural differences were believed to result from the structural differences between the platinum layers immediately below the respective PST layers. The “lines” which divide PST into “network” of islands were found to be no more than wider grain boundaries, rather than “cracks” as believed previously. Micro-beam diffraction and energy dispersive X-ray analysis showed that grain boundaries were tantalum-rich and lead-deficient compared to perovskite grain centres. Electrical properties, such as relative permittivity and dielectric loss, for the films were also measured.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. W. Whatmore, Rep. Prog. Phys. 49 (1986) 1335.
C. A. Randall, D. J. Barber, R. W. Whatmore and P. Grovers, J. Mater. Sci. 21 (1986) 4456.
N. Setter and L. E. Cross, ibid. 15 (1980) 2478.
G. F. Stenger and A. J. Burgraaf, Phys. Status Solidi (a) 61 (1980) 653.
K. Z. Baba-Kishi and D. J. Barber, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 23 (1990) 43.
K. Z. Baba-Kishi, I. M. Reaney and D. J. Barber, J. Mater. Sci. 25 (1990) 1645.
K. Z. Baba-Kishi, G. Cressey and R. J. Crenik, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 25 (1992) 477.
C. A. Randall, D. J. Barber and R. W. Whatmore, J. Microscop. 145 (1987) 275.
N. Setter and L. E. Cross, J. Appl. Phys. 51 (1980) 4356.
R. Watton, Integr. Ferroelect. 4 (1994) 175.
S. H. Pyke, K. Z. Baba-Kishi, R. Watton and M. A. Todd, ibid. 4 (1994) 25.
C. D. Meekison, K. Z. Baba-Kishi, R. Watton and M. A. Todd, ibid. 8 (1995) 283.
A. Patel, N. Sharrocks and R. Whatmore, Ferroelectrics 134 (1992) 343.
D. Liu and D. Payne, J. Appl. Phys. 77 (1995) 3361.
C. Bjormander, K. Sreenivas, A. M. Grighin and K. V. Rao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 67 (1995) 58.
P. Groves, J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 18 (1985) L1073.
R. W. Whatmore, Z. Huang, M. A. Todd, J. Appl. Phys. (1997), in press.
C. Hsueh and M. McCartney, J. Mater. Res. 6 (1991) 2208.
R. Watton, Ferroelectrics, 184 (1996) 141.
K. G. Brooks, I. M. Reaney, R. Klissurska, Y. Huang, L. Bursill and N. Setter, J. Mater. Res. 9 (1994) 2540.
S. Hirano, T. Yogo, K. Kikuta, Y. Araki, M. Saitoh and S. Ogasahara, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75 (1992) 2785.
L. Reimer, “Scanning Electron Microscopy”, edited by J. N. Chapman and A.J. Craven, (SUSSP 1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Todd, M.A., Watton, R. et al. Sputtered lead scandium tantalate thin films: a microstructural study. Journal of Materials Science 33, 363–370 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004367712774
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004367712774