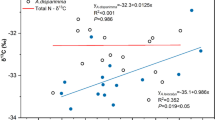
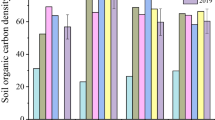
Abstract
Nitrogen deposition in the range of 10–40 kg N ha-1 a-1 is common in large parts of Europe. Substancial amounts are deposited as NH +4 having fertilization and acidification effects in ecosystems. In a long term experiment the reactions of different compartments of a forest ecosystem were studied when the system became N saturated by continuously applying (NH4)2SO4. The experiment was conducted in a beech forest and the application of 10 kmolc N ha-1 a-1 lasted 11 yr from 1983 till 1993.
The results revealed that despite the high soil acidity, the applied NH +4 was quickly oxidized to NO -3 in the surface 10 cm soil layer and leached to deeper depths. The amount of NO -3 leached from the surface soil increased during the initial three years and remained constant on a high level for the rest of the experimental period. Nitrification was associated with acidification of the soil solution, causing high concentrations of Al and Mn2+ in soil solutions. More than 50% of total Al in solution occurred in non-phytotoxic form (Al–SO4 complexes). Moreover, concentration of base cations and dissolved organic carbon increased. Concentrations of SO 2-4 in soil solutions increased during the first few years approaching more or less constant values in the surface 40 cm depth, whereas in 40–100 cm depth it took about 10 yr to reach those levels of sulphate concentrations in soils, indicating its retention in the deeper soil layers. No significant change in the chemistry of throughfall water and leaves was observed, indicating to N-saturation of the trees.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez E, Martínez A and Calvo R 1992 Geochemical aspects of aluminium in forest soils in Galicia (N.W. Spain). Biogeochemistry 16, 167–180.
Beese F, Waraghai A, Wöhler I, Stickan W and Meiwes K J 1991 Phänologie und Inhaltsstoffe von Buchenblättern in Relation zur Acidität von Böden. Ber. Forschungszentrum Waldökosysteme, Göttingen, Reihe B, Vol. 25.
Berggren D 1992 Speciation and mobilization of aluminium and cadmium in Podzols and Cambisols of S. Sweden. Water Air Soil Pollut. 62, 125–156.
Bergkvist B and L Folkeson 1992 Soil acidification and element fluxes of a Fagus sylvatica forest as influenced by simulated nitrogen deposition. Water Air Soil Pollut. 65, 111–133.
Box G E P and Jenkins G M 1976 Time series analysis: Forecasting and Control, 2nd ed. Holden-Day, San Francisco, USA.
Bredemeier M, Matzner E and Ulrich B 1990 Internal and external proton load to forest soils in Northern Germany. J. Environ. Qual. 19, 469–477.
Brumme R and Beese F 1992 Effects of liming and nitrogen fertilization on emissions of CO2 and N2O from temporate forest. J. Geophys. Res. 97, 851–858.
Cronan C S and Grigal D F 1995 Use of calcium/aluminum ratios as indicators of stress in forest ecosystems. J. Environ. Qual. 24, 209–226.
Cronan C S and Aiken G R 1985 Chemistry and transport of soluble humic substances in forested watersheds of the Adirondack Park, New York. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 49, 1697–1705.
David M B, Vance G F, Rissing J M and Stevenson F J 1989 Organic carbon fractions in extracts of O and B horizons from a New England Spodosol: effects of acid treatment. J. Environ. Qual. 18, 212–217.
De Vries W, Van Grinsven J J M, Van Breemen N, Leeters E E J M and Jansen P C. 1995 Impacts of acid deposition on concentrations and fluxes of solutes in acid sandy forest soils in the Netherlands. Geoderma 67, 17–43.
Dietze G and Köning N 1988 Metallspeziierung in Bodenlösungen mittels Dialysen-und Ionenaustauscherverfahren. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 151, 243–250.
Draaijers G P J, Ivens W P M F, Bos M M and Bleuten W 1989 The contribution of ammonia emissions from agriculture to the deposition of acidifying and euthropying compounds onto forests. Environ. Pollut. 60, 55–66.
Driscoll C T 1989 The chemistry of aluminum in surface waters. In The Environmental Chemistry of Aluminum. Ed. G Sposito. pp 242–277. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA.
Ellenberg H, Mayer R and Schauermann J 1986 Oekosystemforschung: Ergebnisse des Sollingprojekts 1966–1986. Ulmer Verlag, Stuttgart, Germany.
Fangmeier A, Hadwiger-Fangmeier A, Van der Eerden L and Jäger H J 1994 Effects of atmospheric ammonia on vegetation. A review. Environ. Pollut. 86, 43–82.
Feger K H 1992 Nitrogen cycling in two Norway spruce (Picea abies) ecosystems and effects of a (NH4)2SO4 addition. Water Air Soil Pollut. 61, 295–307.
Guggerberger G and Zech W 1992 Retention of dissolved organic carbon and sulfate in aggregated acid forest soils. J. Environ. Qual. 21, 643–653.
Gundersen P and Rasmussen L 1990 Nitrification in forest soils: affects from nitrogen deposition on soil acidification and aluminum release. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 113, 1–45.
Hauhs M 1989 Lange Bramke: an ecosystem study of a forested catchment. In Acidic Precipitation. Vol. 1: Case Studies. Eds. D C Adriano and M Havas. pp 275–305. Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
James B R and Riha S J 1984 Soluble aluminum in acified organic horizons of forest soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 64, 637–646.
Johnson D W 1991 Nitrogen retention in forest soils. J. Environ. Qual. 21, 1–12.
Johnson D W and Lindberg S E 1992 Atmospheric deposition and forest nutrient cycling. Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
Khanna P K and Mishra B 1978 Behavior of manganese in some acid soils in Western Germany in relation to pH and air-drying. Geoderma 20, 289–297.
König N and Fortmann H 1996 Probenvorbereitungs-, Untersuchungs-und Elementbestimmungs-methoden des Umweltanalytik-Labors der Niedersächsischen Forstlichen Versuchsanstalt und des Zentrallabor II des Forschungszentrums Waldökosysteme. Teil 1 und 2: Elementbestimmungsmethoden A-M, N-Z. Ber. Forschungszentr. Waldökosysteme, Reihe B, Bd. 46–47.
Lamersdorf N and Meyer M 1993 Nutrient cycling and acidification of a northwest German forest site with high atmospheric nitrogen deposition. For. Ecol. Manage. 62, 323–354.
Lang E 1986 Heterotrophe und autotrophe Nitrifikation untersucht an Bodenproben von drei Buchenstandorten. Göttinger Bodenkundliche Ber. 89, 1–199.
Lang E and Jagnow G 1986 Fungi of forest soil nitrifying at low pH values. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 38, 257–265.
Martikainen P J 1985. Numbers of autotrophic nitrifiers and nitrification in fertilized forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 17, 245–248.
Matzner E 1989 Acidic precipitation: Case study Solling. In Acidic Precipitation. Vol. 1: Case Studies. Eds D C Adriano and M Havas. pp 37–83. Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
Matzner E, Khanna P K, Meiwes K J and Ulrich B 1983 Effects of fertilization on the fluxes of chemical elements through different forest ecosystems. Plant Soil 74, 343–358.
Matzner E and Meiwes K J 1994 Long-term development of element fluxes with bulk precipitation and throughfall in two German forest. J. Environ. Qual. 23, 162–166.
Meesenburg H, Meiwes K J and Rademacher P 1995 Long term trends in atmospheric deposition and seepage output in northwest German forest ecosystems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 85, 611–616.
Meiwes K J, Hauhs M, Gerke H, Asche N, Matzner E and Lamersdorf N 1984 Die Erfassung des Ionenkreislaufs — Konzept und Methodik. Berichte Forschungszentrum Waldökosysteme/Waldsterben Göttingen, Bd. 7, 70–142.
Meiwes K J and Khanna P K 1981 Distribution and cycling of sulphur in the vegetation of two forest ecosystems in an acid rain environment. Plant Soil 60, 369–375.
Meiwes K J, Khanna P K and Ulrich B 1980 Retention of sulphate by an acid brown earth and its relationship with the atmospheric input of sulphur to forest vegetation. Z. Pflanzernernaehr. Bodenkd. 143, 402–411.
Mochoge B O and Beese F 1986 Leaching of plant nutrients from an acid forest soil after nitrogen fertilizer application. Plant Soil 91, 17–29.
Nilsson L O and Wiklund K 1994 Nitrogen uptake in a Norway spruce stand following ammonium sulphate application, fertigation, irrigation, drought and nitrogen-free-fertilization. Plant Soil 164, 221–229.
Nodvin S C, Driscoll C T and Likens G E 1986 Simple partitioning of anions and dissolved organic carbon in a forest soil. Soil Sci. 142, 27–35.
Prenzel J 1990 WAKO — A program for the calculation of complexation equilibria un aqueous solutions. Introductions and example. Ber. d. Forschungsz. Waldökosystem, B-16.
Prietzel J and Feger K H 1992 Dynamics of aqueous aluminum species in a podzol affected by experimental MgSO4 and (NH4)2SO4 treatments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 65, 153–172.
Rapp C 1991 Untersuchung zum Einfluß von Kalkung und Ammoniumsulfat-Düngung auf Feinwurzeln und Ektomykorrhizen eines Buchenaltbestandes im Solling. Berichte d. Forschungszentrums Waldökosysteme d. Univ. Göttingen, Reihe A, Bd. 72.
Stickan W, Schulte M, Kakubari Y, Niederstadt F, Schenk J and Runge M 1991 Ökophysiologische und biometrische Untersuchungen in einem Buchenbestand (Fagus sylvatica L.) des Sollings als ein Beitrag zur Waldschadensforschung. Ber. Forschungszentrum Waldökosysteme, Reihe B, Vol. 18, pp 1–82.
Schulze E D 1989 Air pollution and forest decline in a Spruce (Picea abies) forest. Science (Washington, DC) 244, 776–783.
Smolander A, Kurka A, Kitunen V and Mälkönen E 1994 Microbial biomass C and N, and respiratory activity in soil of repeatedly limed and N-and P-fertilized Norway Spruce stands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 26, 957–962.
Staaf H 1992 Plant nutrient changes in beech leaves during senescence as influenced by site characteristics. Oecol. Plant. 3, 161–170.
Stams A J M, Flameling E M and Marnette E C L 1990 The importance of autotrophic versus heterotrophic oxidation of atmospheric ammonium in forest ecosystems with acid soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 38, 337–344.
Tamm C O 1991 Nitrogen in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Questions of Productivity, Vegetation Changes, and Eecosystem Stability. Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
Ulrich B 1989 Effects of acidic precipitation on forest ecosystems in Europe. In Acidic Precipitation. Vol. 2: Biological and Economical Effects. Ed. D C Adriano and A H Johnson. pp 189–262. Springer-Verlag, New York, USA.
Ulrich B 1994 Nutrient and acid-base budget of Central European forest ecosystems. In Effects of Acid Rain on Forest Processes. Eds D L Godbold and A Hütterman. pp 1–50. Wiley-Liss, New York, USA.
Van Breemen N, Mulder J and Van Grinsven J J M 1987 Impacts of acid deposition on woodland soil in the Netherlands: II. Nitrogen transformation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 51, 1634–1640.
Van den Burg J 1990 Foliar analysis for determination of tree nutrient status — a compilation data. 2. Literature 1985–1989. “De Dorschkamp”, Institute for Forestry and Urban Ecology, Wageningen, Rapport Nr. 591.
Wöhler I 1988 Die Elementverteilung in Blattgeweben und deren Bedeutung für das Pufferverhalten. Ber. des Forschungszentrums Waldökosysteme/Waldsterben, Reihe A, Bd. 41, 1–270.
Wolt JD 1989 Effects of acidic deposition on the chemical form and bioavailability of soil aluminum and manganese. In Mechanisms of Forest Responses to Acidic Deposition. Eds. A A Lucier and S G Haines. pp 62–107. Springer-Verlag. New York, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meiwes, K.J., Merino, A. & Beese, F.O. Chemical composition of throughfall, soil water, leaves and leaf litter in a beech forest receiving long term application of ammonium sulphate. Plant and Soil 201, 217–230 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004315513482
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004315513482