Abstract
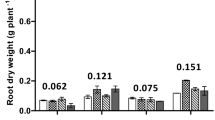
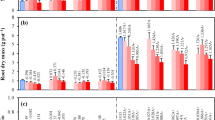
The exudation of certain organic anions and protons by roots which may affect solubility of metals and P and uptake by plants, is affected by nitrogen form and pH. The objective of this work was to study exudation of carboxylates and H+/OH− by tomato plants in response to NH4/NO3 ratio and pH in nutrient solution. Four NH4/(NH4+NO3) ratios (R= 0, 0.33, 0.67 and 1) and constant vs. variable solution pH treatments were investigated. The sum of the exudation rates of all carboxylates tended to decline with increasing R, particularly tri- and dicarboxylates. The molar fraction of the exuded tri- and dicarboxylates, averaged over all treatments and plant ages, increased in the order tartarate ∼2%), malate (∼6%), succinate (∼15%), citrate (∼26%) and fumarate (∼46%). At R=1 the solution pH dropped from 5.2 to ∼3 and at R=0 increased to ∼8. The R corresponding to the pH stat of tomato plant was ∼0.3. For the constant solution pH treatment, the effect of solution pH on carboxylate exudation rate was small as compared to the effect of R. The exudation of citrate and H+ efflux which were initiated when NO3 and NH4 uptake rates per plant exceeded certain threshold values, increased with plant age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-Yosef B 1996 Root excretions and their environmental effects-Influence on availability of phosphorus. InPlant Roots-The Hidden Half, 2nd ed. Eds. Y Waisel, A Eshel and U Kafkafi. pp 581-605. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York.
Bremner J M and Keeney D R 1965 Steam distillation methods for determination of ammonium, nitrate and nitrite. Anal. Chim. Acta 32, 485-495.
Cole C V, Grunes D L, Porter L K and Olsen S R 1963 The effect of nitrogen on short-term phosphorus absorption and translocation in corn. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 27, 671-674.
Epstein E 1972 Mineral Nutrition of Plants: Principles and Perspectives. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York. 412 p.
Feigin A, Zwibel M, Rilski I, Zamir N and Levav N 1980 The effect of ammonium/nitrate ratio in the nutrient solution on tomato yield and quality. Acta Hortic. 98, 149-160.
Fox T R and Comerford N B 1990 Low-molecular weight organic acids in selected forest soils of the Southeastern USA. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 54, 1139-1144.
Gerendas J and Sattelmacher B 1990 Influence of nitrogen form and concentration on growth and ionic balance of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) and potato (Solanum tuberosum). InPlant Nutrition-Physiology and Applications. Ed. M L van Beusichem. pp 33-37. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Hoagland D R and Arnon D J 1938 The water culture method for growing plants without soils. Circ. Calif Agric. Exp. Stn. No. 347.
Kirkby E A and Knight A H 1977 Influence of the level of nitrate nutrition on ion uptake and assimilation, organic acid accumulation, and cation-anion balance in whole tomato plants. Plant Physiol. 60, 349-353.
Kirkby E A and Mengel K 1967 Ionic balance in different tissues of tomato plants in relation to nitrate, urea and ammonium nutrition. Plant Physiol. 42, 6-14.
Kraffczyk I, Trolldenier G and Beringer H 1984 Soluble root exudates of maize, influence of potassium supply and rhizosphere microorganisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 16, 315-322.
Landsberg E 1981 Organic acid synthesis and release of hydrogen ions in response to Fe deficiency stress of mono-and dicotyledoneous plant species. J. Plant Nutr. 3, 579-591.
Marschner H 1995 Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd ed. Academic Press Limited, London. 674 p.
Mengel K and Kirkby E A 1987 Principles of plant nutrition, 4th ed. Potash Institute, Bern. 687 p.
Miller G W, Shigematsu A, Welkie G W, Motoji N and Szlek M 1990 Potassium effect on iron stress in tomato. II. The effect on root CO2-fixation and organic acid formation. J. Plant Nutr. 13, 1353-1370.
Mozafar A, Duss F and Oertli J J 1992 Effect of Pseudomonas fluorescenson the root exudates of two tomato mutants differently sensetive to Fe chlorosis. Plant Soil 144, 167-176.
SAS Institute 1985 SAS for linear models, a guide to ANOVA and GLM procedures. SAS Inst., Cary, NC.
Schwab S M, Menge J A and Leonard R T 1983 Quantitative and qualitative effects of phosphorus on extracts and exudates of sudangrass roots in relation to vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza formation. Plant Physiol. 73, 761-765.
Senden MHMN, van der Meer AJGM, Limborgh J and Wolterbeek H Th 1992 Analysis of major tomato xylem organic acids and PITC-derivates of amino acids by RP-HPLC and UV detection. Plant Soil 142, 81-89.
Touraine B, Grignon N and Grignon C 1990 Interaction between nitrate assimilation in shoots and nitrate uptake by roots of soybean (Glycine max) plants, role of carboxylate. Plant Soil 124, 169-174.
Troelstra S R, Wagenaar R and Smat W 1990 Growth responses of Plantago to ammonium nutrition with and without pH control, Comparison of plants precultivated on nitrate or ammonium. InPlant Nutrition-Physiology and Applications. Ed. M L van Beusichem. pp 39-43. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Yan F, Schubert S and Mengel K 1992 Effect of low root medium pH on net proton release, root respiration and root growth of corn (Zea maysL.) and broad bean (Vicia fabaL.). Plant Physiol. 99, 415-421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imas, P., Bar-Yosef, B., Kafkafi, U. et al. Release of carboxylic anions and protons by tomato roots in response to ammonium nitrate ratio and pH in nutrient solution. Plant and Soil 191, 27–34 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004214814504
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004214814504