Abstract
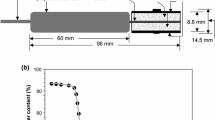
The performance of a micro soil solution sampling device was tested in a laboratory examination and in a field experiment. The instrument allows detection of temporal and spatial changes in soil solution chemistry at a spatially high resolution. The flexible tube of the suction cell is made of a porous polymer with a diameter of 2.3 mm. To achieve more stability and to minimize disturbance of the instrument during field installation, the original device was modified by embedding the suction cell in a stainless steel and pressure absorbing corpus. During a laboratory test the new sampling system was compared to ceramic P-80 suction cells. Solution samples taken with the new device adapted more quickly to the given concentrations compared to the ceramic suction cells. In a field test, micro samplers were implanted in an existing soil solution monitoring plot, equipped with standard ceramic samplers. Bi-weekly sampling using the micro cells indicated high temporal and spatial variation, and in June 1995 it was possible, to identify a distinct nitrification. However, in a statistical comparison of the entire sampling period and respective sub-sampling areas the two sampler types indicated identical concentration ranges for nitrate. It is concluded that the new micro samplers can help to identify processes in soils which may cause short-term changes in the soil solution chemistry, whereas the standard sampling technique with ceramic cells seems to be still a suitable tool if long-term mean soil solution concentrations are to be measured.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckmann T, Kücke M, Hasenpusch K and Altemüller H-J 1992 Einbaubedingte Gefügeänderungen in der Bodenzone um keramische Saugkerzen. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 155, 247—250.
Beier C and Hansen K 1992 Evaluation of porous cup soil-water samplers under controlled field conditions: comparison of ceramic and PTFE cups. Soil Sci. 43, 261–271.
Beier C, Hansen K, Gundersen P and Andersen B R 1992 Long-term field comparison of ceramic and poly(tetrafluoroethene) porous cup soil water samplers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26, 2005–2011.
Blanck K, Lamersdorf N und Bredemeier M 1993 Bodenchemie und Stoffhaushalt auf den Dachflächen im Solling. Forstarchiv 64, 164–172.
Bottcher A B, Miller L W and Campbell K L 1984 Phosphorus adsorption in various soil-water extraction cup materials: effect of acid wash. Soil Sci. 137(4), 239–244.
Bredemeier M, Lamersdorf N and Wiedey G 1990 A new mobile and easy to handle suction lysimeter for soil water sampling. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 336, 1–4.
Bredemeier M, Blanck K and Wiedey G 1993 Experimentelle Manipulation des Wasser-und Stoffhaushalts in einem Fichtenwald das Dachprojekt im Solling. Forstarchiv 64, 154–158.
Briggs L J and McCall A G 1904 An artificial root for inducing capillary movement of soil moisture. Science 20, 566–569.
Creasey C L and Dreiss S J 1988 Porous cup samplers: cleaning procedures and potential sample bias from trace element contamination. Soil Sci. 145, 93–101.
Göttlein A 1995 Mikroskalige Variabilität von Bodenlösungskonzentrationen und Saugspannungen in einem sauren Waldboden. Mitteilungen Deutsche Bodenkundliche Gesellschaft. 76, I. GÖttlein A, Hell U and Blasek R 1996 A system for microscale tensiometry and lysimetry. Geoderma 69, 147–156.
Grossmann J, Freitag G and Merkel B 1985 Eignung von Nylon-und Polyvinylidenfluorid-membranfiltern als Materialien zum Bau von Saugkerzen. Z. Wasser-Abwasser-Forsch. 18, 187–190.
Grossmann J 1988 Physikalische und chemische Prozesse bei der Probenahme von Sickerwasser mittels Saugsonden. Dissertation der Techn. Uni. München.
Grossmann J, Quentin K and Udluft P 1987 Sickerwassergewinnung mittels Saugkerzen – eine Literaturstudie. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 150, 258–261.
Grossman J and Udluft P 1991 The extraction of soil water by the suction-cup method: a review. J. Soil Sci. 42, 83–93.
Hansen E and Harris A R 1975 Validity of soil water samples collected with porous ceramic cups. Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 39, 528–536.
Heinrichs H and König N and Schultz R 1985 Atom-Absorptions-und Emissionsspektroskopische Bestimmungsmethoden für Haupt-und Spurenelemente in Probelösungen aus Waldökosystem-Untersuchungen. Berichte Forschungszentrum Waldökosysteme/Waldsterben. 8, 92.
Hendershot W H and Courchesne F 1991 Comparison of soil solution chemistry in zero tension and ceramic-cup tension lysimeters. Journal of Soil Sci. 42, 577–583.
Hetsch W, Beese F and Ulrich B 1979 Die Beeinflussung der Bodenlösung durch Saugkerzen aus Ni-Sintermetall und Keramik. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 42, 29–38.
Huges S and Reynolds B 1990 Evaluation of porous ceramic cups for monitoring soil-water aluminium in acid soils: comment on a paper by Raulund-Rasmussen (1989). Soil Sci. 41, 325–328.
Lamersdorf N P, Beier C, Blanck K, Bredemeier M, Cummins T, Farrell E P, Kreutzer K, Rasmussen L, Ryan M, Weis W and Xu Y-J 1997 Effect of Drought Experiments using Roof Installations on Acidification/Nitrification of Soils in Forest Ecology and Management. (In press).
Litaor M 1988 Review of Soil Solution Samplers. Water Resources Research. 24(5), 727–733.
Maitre V, Bourrie G and P Curmi 1991 Contamination of collected soil water samples by the dissolution of the mineral constituents of porous P.T.F.E. cups. Soil Sci. 152, 289–293.
Marquardt D W 1963 An Algorithm for Least Squares Estimation of Nonlinear Parameters. J. Soc. Indus. Appl. Math. 11, 431–441.
Menzies N W, Bell L C and Edwards D G 1991 Characteristics of membrane filters in relation to aluminium studies in soil solutions and natural waters. Soil Sci. 42, 585–597.
Quin B F and Forsythe L J 1976 All-plastic suction lysimeters for the rapid sampling of percolating soil water. New Zealand J. Sci. 19, 145–148.
Raulund-Rasmussen K 1991 Aluminium contamination of acid soil solution isolated by means of porcelain suction cups: a reply to a paper by Huges & Reynolds (1990) and an interpretation of aluminium release. Soil Sci. 42, 271–276.
Raulund-Rasmussen K 1989 Aluminium contamination and other changes of acid soil solution isolated by means of porcelain suction-cups. Soil Sci. 40, 95–101.
Rost-Siebert K 1983 Aluminium-Toxozität und-Toleranz an Keimpflanzen von Fichte (Picea abies Karst.) und Buche (Fagus sylvatica L.). Allge. Forst. 26/27, 686–689.
Schimmack W, Bunzl K and Kreutzer K 1984 Sorption von Schwermetallionen aus Bodenlösungen durch Saugkerzen: Einfluß der Huminsäuren. In Wald und Wasser, Prozesse im Wasser-und Stoffkreislauf von Waldgebieten. pp 285–290.
Spangenberg A and Lamersdorf N P 1997 Soil solution sampling with a new type of suction lysimeter. In Tagungsband der TERNTagung, UFZ-Bericht Nr. 5. Eds. H Mühle and S Eichler. pp 23. Umweltforschungszentrum Leipzig-Halle GmbH.
Ulrich B 1983 A concept of forest ecosystem stability and of acid deposition as driving force for destabilisation. In Effects of accumulation ofAir Pollutants in Forest Ecosystems Eds. B Ulrich and J Pankrath. pp 1–29. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dodrecht, Holland.
van der Ploeg R R and Beese F 1977 Model calculations for the extraction of soil water by ceramic cups and plates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 41, 466–470.
Wang Y 1996 —Auswirkungen klimatischer Umweltfaktoren auf die chemischen Eigenschaften eines versauerten Fichtenbodens in Berichte Forschungszentrum WaldÖ;kosysteme, Reihe A, Vol. 139, pp 171.
Wu L, Baker J M and Allmaras R R 1995 Numerical and field evaluation of soilwater sampled by suction lysimeters. J. Environ. Qual. 24, 147–152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spangenberg, A., Cecchini, G. & Lamersdorf, N. Analysing the performance of a micro soil solution sampling device in a laboratory examination and a field experiment. Plant and Soil 196, 59–70 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004213006295
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004213006295