Abstract
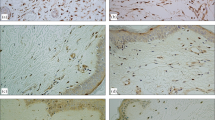
An immunohistochemical study on the temporal expression of c-Fos and c-Jun, both of which designate proto-oncogene products, was performed on 60 human skin wounds with different post-infliction intervals. In unwounded skin, c-Fos or c-Jun was immunolocalized at the nuclei of the epidermal cells in the basal layer, hair follicle cells and sweat gland cells. During the early inflammatory phase of wound healing, the nuclei of polymorphonuclear cells (probably neutrophils), mainly infiltrating at the wound site, were labeled with anti-c-Fos or -c-Jun antibody. As the wound age increased, the neutrophils had disappeared at the wound site, and both mononuclear cells (probably macrophages) and spindle-shaped fibroblastic cells, which expressed a c-Fos or c-Jun positive reaction in the nuclei, were mainly observed. Morphometrically, the distribution of the c-Fos-positive ratio was very similar to that of the c-Jun-positive ratio; the positive ratio was considerably increased in wound specimens with a post-infliction interval of ≥ 1 day, thus indicating the late inflammatory or proliferative phase. This study showed that c-Fos and c-Jun were closely involved in the inflammatory phase as well as the proliferative phase of the wound healing process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Angel P, Karin M (1991) The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1072: 129-157.
Antoniades HN, Galanopoulos T, Naville-Golden J, Kiritsy CP, Lynch SE (1994) p53 expression during normal tissue regeneration in response to acute cutaneous injury in swine. J Clin Invest 93: 2206-2214.
Betz P, Nerlich A, Wilske J, Tübel J, Wiest I, Penning R, Eisenmenger W (1992) Immunohistochemical localization of fibronectin as a tool for the age determination of human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 105: 21-26.
Betz P, Nerlich A, Wilske J, Tübel J, Penning R, Eisenmenger W (1993a) Analysis of the immunohistochemical localization of collagen type III and V for the time-estimation of human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 105: 329-332.
Betz P, Nerlich A, Wilske J, Tübel J, Penning R, Eisenmenger W (1993b) Immunohistochemical localization collagen types I and VI in human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 106: 31-34.
Betz P (1994) Histological and enzyme histochemical parameters for the age estimation of human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 107: 60-68.
Betz P, Nerlich A, Tübel J, Wiest I, Hausmann R (1997) Detection of cell death in human skin wounds of various ages by an in situ end labeling of nuclear DNA fragments. Int J Legal Med 110: 240-243.
Clark RAF (1996) Wound repair: overview and general considerations. In: Clark RAF, ed. The Molecular and Cellular Biology of Wound Repair 2nd edn. Plenum Press, New York, London, pp. 3-50.
Distel RJ, Spiegelman BM (1990) Protooncogene c-fos as a transcription factor. Adv Cancer Res 55: 37-55.
Dreβler J, Bachmann L, Kasper M, Hauck JG, Müller E (1997) Time dependence of the expression ICAM (CD-54) in human skin wound. Int J Legal Med 110: 299-304.
Dreβler J, Bachmann L, Koch R, Müller E (1998) Enhanced expression of selectins in human skin wounds. Int J Legal Med 112: 39-44.
Dreβler J, Bachmann L, Koch R, Müller E (1999) Estimation of wound age and VCAM-1 in human skin. Int J Legal Med 112: 159-162.
Eisenmenger W, Nerlich A, Glück G (1988) Die Bedeutung des Kollagens bei Wundaltersbestimmung. Z Rechtsmed 100: 79-100.
Farrar WL, Ferris DK, Harel-Bellan A (1989) The molecular basis of immune cytokine action. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 5: 229-261.
Garcia J, Lemercier B, Roman-Roman S, Rawadi G (1998) A Mycoplasma fermentans-derived synthetic lipopeptide induces AP-1 and NF-kappaB activity and cytokine secretion in macrophages via the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Biol Chem 273: 34391-34398.
Greenberg ME, Ziff EB (1984) Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature 331: 433-438.
Guan D, Ohshima T, Kondo T (2000) Immunohistochemical study on Fas and Fas ligand in skin wound healing. Histochem J 32: 85-91.
Haase M, Koslowski R, Lengnick A, Hahn R, Wenzel KW, Schuh D, Kasper M, Müller M (1997) Cellular distribution of c-Jun and c-Fos in rat lung before and after bleomycin induced injury. Virchow Arch 431: 441-448.
Halazonestis TD, Georgopoulos K, Greenberg ME, Leder P (1988) C-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell 5: 917-924
Hausmann R, Nerlich A, Betz P (1998) The time-related expression of p53 protein in human skin wounds-a quantitative immunohistochemical analysis. Int J Legal Med 111: 169-172.
Labus MB, Stirk CM, Thompson WD, Melvin WT (1998) Expression of Wnt genes in early wound healing. Wound Rep Rege 6: 58-64.
Kondo T, Ohshima T (1996) The dynamics of inflammatory cytokines in the healing process mouse skinwound: a preliminary study for possible wound age determination. Int J Legal Med 108: 231-236.
Kondo T, Ohshima T, Eisenmenger W (1999) Immunohistochemical and morphometrical study on the temporal expression of interleukin-1? (IL-1?) in human skin wounds for forensic wound age determination. Int J Legal Med 112: 249-252.
Martin P (1997) Wound healing-aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 276: 75-81.
Minden A, Karin M (1997) Regulation and function of the JNK subgroup of MAP kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1333: F85-F104.
Nogami M, Takatsu A, Endo N, Ishiyama I (1999) Immunohistochemical localization of c-fos in the nuclei of the medulla oblongata in relation to asphyxia. Int J Legal Med 112: 351-354.
Oehmichen M (1990) Die Wundheilung. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp. 5-67.
Ohshima T, Sato Y (1998) Time-dependent expression of interleukin-10 (IL-10) mRNA during the early phase of skin wound healing as possible indicator of wound vitality. Int J Legal Med 111: 251-255.
Ohta S, Yamamuro T, Lee K, Okumura H, Kasai R, Hiraki Y, Ikeda T, Iwasaki R, Kikuchi H, Konishi J, Shigeno C (1991) Fracture healing induces expression of the proto-oncogene c-fos in vivo. Possible involvement of the Fos protein in osteoblastic differentiation. FEBS Lett 284: 42-45.
Okada Y, Saika S, Shirai K, Hashizume N, Yamanaka O, Ohnishi Y, Senba E (1998) Immunolocalization of proto-oncogene products in keratocytes after epithelial ablation, alkali burn and penetrating injury of the cornea in rats. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Opthalmol 236: 853-858
Reitamo S, Anttila HSI, Didierjean L, Saurat JH (1990) Immunohistochemical identification of interleukin 1? and ? in human eccrine sweat-gland apparatus. Br J Dermatol 122: 315-323.
Sato Y, Ohshima T, Kondo T (1999) Regulatory role of endogenous interleukin-10 in cutaneous inflammatory response of murine wound healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265: 194-199.
Sato Y, Ohshima T (2000) The expression of mRNA by proinflammatory cytokines during skin wound healing in mice: a preliminary study for forensic wound age estimation (II). Int J Legal Med 113: 140-145.
Schonthal A, Herrlich P, Rahmsdorf HJ, Ponta H (1988) Requirement for fos gene expression in the transcriptional activation of collagenase by other oncogenes and phorbol esters. Cell 54: 325-334.
Setoyama C, Fruzio R, Liau G, Mudryj M, Crombruggle B (1986) Transcriptional activation encoded by the v-fos gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 3213-3217.
Singer AJ, Clark RAF (1999) Cutaneous wound healing. New Engl J Med 341: 738-746.
Wang JY, Johson LR (1994) Expression of protooncogenes c-fos and c-myc in healing of gastric mucosal stress ulcers. Am J Physiol 266: G878-G886.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondo, T., Ohshima, T., Sato, Y. et al. Immunohistochemical Study on the Expression of c-Fos and c-Jun in Human Skin Wounds. Histochem J 32, 509–514 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004164905041
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004164905041