Abstract
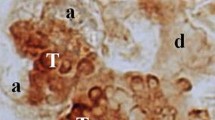
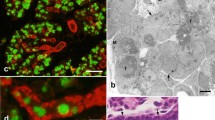
Epidermal growth factor in human submandibular gland was localized at the subcellular level by means of an immunogold staining method. Labelling was observed in serous acini and ducts. In the acini, gold particles were found within secretory granules, indicating that the growth factor is released into the saliva through granule exocytosis. In the ductal system, the most intense reactivity was revealed in the principal cells of striated ducts. In these cells, an abundant population of small cytoplasmic vesicles was specifically stained. Immunoreactive vesicles were found both apically and basally, suggesting that ductal cells can release their products not only into the saliva but also into the interstitium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Aida S, Tamai S, Sekiguchi S, Shimizu N (1994) Distribution of epidermal growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor in human lung: immunohistochemical and immunoelectron-microscopic studies. Respiration 61: 161–166.
Cossu M, Lantini MS, Puxeddu R (1994) Immunocytochemical localization of Lewis blood group antigens in human salivary glands. J Histochem Cytochem 42: 1135–1142.
Fisher DA, Lakshmanan J (1990) Metabolism and effects of epidermal growth factor and related growth factors in mammals. Endocr Rev 11: 418–442.
Garrett JR, Proctor GB, Zhang X-S, Anderson LC, Shori DK (1998) Constitutive secretion of kallikreins in vivo from rat submandibular glands. Eur J Morphol 36(Suppl.): 86–91.
Gesualdo L, Di S, Calabrò A, Milani S, Maiorano E, Ranieri E, Pannarale G, Schena FP (1996) Expression of epidermal growth factor and its receptor in normal and diseased human kidney: an immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization study. Kidney Int 49: 656–665.
Gray A, Dal TJ, Ullrich A (1983) A nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature 303: 722–725.
Gresik EW (1994) The granular convoluted tubule (GCT) cell of rodent submandibular glands. Microsc Res Tech 27: 1–24.
Gresik EW, Barka T (1977) Immunocytochemical localization of epidermal growth factor in mouse submandibular gland. J Histochem Cytochem 25: 1027–1035.
Jones DE Jr, Tran-Patterson R, Cui D, Davin D, Estell KP, Miller DM (1995) Epidermal growth factor secreted from the salivary gland is necessary for liver regeneration. Gastrointest Liver Physiol 31: G872-G878.
Kajikawa K, Yasui W, Sumiyoshi H, Yoshida K, Nakayama H, Ayhan A, Yokazaki H, Ito H, Tahara, E (1991) Expression of epidermal growth factor in human tissues. Immunohistochemical and biochemical analysis. Virchows Archiv A Pathol Anat 418: 7–32.
Kasselberg AG, Orth DN, Gray ME, Stahlman MT (1985) Immunocytochemical localization of human epidermal growth factor/urogastrone in several human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 33: 315–322.
Kurokawa R, Kyakumoto S, Ota M (1989) Autocrine growth factor in defined serum-free medium of human salivary gland adenocarcinoma cell line HSG. Cancer Res 49: 5136–5142.
Mori M, Naito R, Tsukitani K, Okada Y, Tsujimura T (1989)Widespread distribution of human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) in human tissues and organs under normal and tumorous conditions. Immunohistochemical studies with the use of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. Acta Histochem Cytochem 22: 15–34.
Mouihate A, Lestage J (1995) Epidermal growth factor: a potential paracrine and autocrine system within the pituitary. Neuroreport 6: 273–1276.
Murphy RA, Watson AY, Metz J, Forssmann WG (1980) The mouse submandibular gland: an exocrine organ for growth factors. J Histochem Cytochem 28: 890–902.
Palade G (1975) Intracellular aspects of the process of protein secretion. Science 189: 347–358.
Penschow JD, Coghlan JP (1993) Secretion of glandular kallikrein and renin from the basolateral pole of mouse submandibular gland duct cells: an immunocytochemical study. J Histochem Cytochem 41: 95–103.
Poulsen SS, Nexò E, Skov Olsen P, Hess J, Kirkegaard P (1986) Immunohistochemical localization of epidermal growth factor in rat and man. Histochemistry 85: 389–394.
Riva A (1974) A simple and rapid staining method for enhancing the contrast of tissues previously treated with uranyl acetate. J Microsc 19: 105–107.
Riva A, Lantini MS, Testa Riva F (1990) Normal human salivary glands. In: Riva A, Motta PM, eds. Ultrastructure of the Extraparietal Glands of the Digestive Tract. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 52–74.
Slomiany BL, Fekete Z, Liu J, Murty VLN, Slomiany A(1992) Activation of dihydropyridine-sensitive parotid salivary gland calcium channels by epidermal growth factor. Archs Oral Biol 11: 863–868.
Sporn MB, Roberts AB (1985) Autocrine growth factors and cancer. Nature 313: 45–47.
Tandler B (1993) Structure of the duct system in mammalian major salivary glands. Microsc Res Tech 26: 57–74.
Thesleff I, Viinikka L, Saxén L, Lehtonen E, Perheentupa J (1988) The parotid gland is the main source of human salivary epidermal growth factor. Life Sci 43: 13–18.
Wu-Wang CY, Patel M, Feng J, Milles M, Wang SL (1995) Decreased levels of salivary prostaglandin E2 and epidermal growth factor in recurrent aphtous stomatitis. Archs Oral Biol 40: 1093–1098.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cossu, M., Perra, M.T., Piludu, M. et al. Subcellular Localization of Epidermal Growth Factor in Human Submandibular Gland. Histochem J 32, 291–294 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004036929006
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004036929006