Abstract
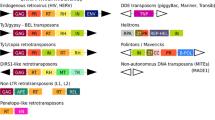
The evolution of transposable element structures can be analyzed in populations and species and by comparing the functional domains in the main classes of elements. We begin with a synthesis of what we know about the evolution of the mariner elements in the Drosophilidae family in terms of populations and species. We suggest that internal deletion does not occur at random, but appears to frequently occur between short internal repeats. We compared the functional domains of the DNA and/or amino acid sequences to detect similarities between the main classes of elements. This included the gag, reverse transcriptase, and envelope genes of retrotransposons and retroviruses, and the integrases of retrotransposons and retroviruses, and transposases of class II elements. We find that each domain can have its own evolutionary history. Thus, the evolution of transposable elements can be seen to be modular.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S.F., T.L. Madden, A.A. Schäffer, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, W. Miller & D.J. Lipman, 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25: 3389–3402.
Auge-Gouillou, C., Y. Bigot, N. Pollet, M.H. Hamelin, M. Meunier-Rotival & G. Periquet, 1995. Human and other mammalian genomes contain transposons of the mariner family. FEBS Lett. 368: 541–546.
Bailey, T.L. & C. Elkan, 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers, pp. 28–36 in Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology. AAAI Press, Menlo Park, California.
Bigot, Y., C. Augé-Gouillou & G. Periquet, 1996. Computer analyses reveal a hobo-like element in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, which presents a conserved transposase domain common with the Tc1-mariner transposon family. Gene 174: 265–271.
Black, D.M., M.S. Jackson, M.G. Kidwell & G.A. Dover, 1987. KP elements repress hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 6: 4125.
Brunet, F., F. Godin, C. Bazin & P. Capy, 1999. Phylogenetic analysis of Mos1-like transposable elements in the Drosophilidae. J. Mol. Evol. 49: 760–768.
Brunet, F., F. Godin, C. Bazin, J.R. David & P. Capy, 1996. The mariner transposable element in natural populations of Drosophila teissieri. J. Mol. Evol. 42: 669–675.
Calvi, B.R., T.J. Hong, S.D. Findley & W.M. Gelbart, 1991. Evidence for a common evolutionary origin of inverted repeat transposons in Drosophila and plants: hobo, Activator, and Tam3. Cell 66: 465–471.
Capy, P., C. Bazin, D. Higuet & T. Langin, 1997a. Dynamic and Evolution of Transposable Elements. R.G. Landes Company, Austin, Texas, USA.
Capy, P., C. Bazin, D. Higuet & T. Langin, 1997b. Evolution and Impact of Transposable Elements. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Capy, P., T. Langin, Y. Bigot, F. Brunet, M.J. Daboussi, G. Periquet, J.R. David & D.L. Hartl, 1994. Horizontal transmission versus ancient origin: mariner in the witness box. Genetica 93: 161–170.
Capy, P., T. Langin, D. Higuet, P. Maurer & C. Bazin, 1997c. Does the integrase of LTR-retrotransposons and most of the transposases of class II elements share a common ancestor? Genetica 100: 63–72.
Capy, P., R. Vitalis, T. Langin, D. Higuet & C. Bazin, 1996. Relationships between transposable elements based upon the integrase-transposase domains: is there a common ancestor? J. Mol. Evol. 42: 359–369.
Chaboissier, M.C., A. Bucheton & D.J. Finnegan, 1998. Copy number control of a transposable element, the I factor, a LINE-like element in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 11781–11785.
Covey, S.N., 1986. Amino acid sequence homology in gag region of reverse transcribing elements and the coat protein gene of cauliflower mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 14: 623–633.
Craven, R.C., A.E.L.-d. Pree, R.A.W. JR & J.W. Wills, 1995. Genetic analysis of the Major Homology Region for the Rous Sarcoma Virus gag protein. J. Virol. 69: 4213–4227.
Dayhoff, M.O., R.M. Schwartz & B.C. Orcutt, 1978. A model of evolutionary change in proteins, pp. 345–352 in Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure, edited by M. O. Dayhoff. Natl. Biomed. Res. Found., Washington, DC.
Doak, T.G., F.P. Doerder, C.L. Jahn & G. Herrick, 1994. A proposed superfamily of transposase-related genes: new members in transposon-like elements of cilliated protozoa and a common ‘D35E’ motif. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 942–946.
Doolittle, W.F. & C. Sapienza, 1980. Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature 284: 601–603.
Fayet, O., P. Ramond, P. Polard, M.F. Frère & M. Chandler, 1990. Functional similarities between retroviruses and the IS3 family of bacterial insertion sequences? Mol. Microbiol. 4: 1771–1777.
Felsenstein, J., 1993. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package). Version 3.5.c University of Washington, Seattle.
Feng, Q., J.V. Moran, H.J. Kazazian & J.D. Boeke, 1996. Human L1 retrotransposon encodes a conserved endonuclease required for retrotransposition. Cell 87: 905–916.
Finnegan, D.J., 1989. Eukaryotic transposable elements and genome evolution. Trends Genet. 5: 103–107.
Gaboriaud, C., V. Bissery, T. Benchetrit & J.P. Mornon, 1987. Hydrophobic cluster analysis: an efficient new way to compare and analyse amino acid sequences. Febs Lett 224: 149–155.
Garcia-Fernàndez, J., G. Marfany, J. Bagunà & E. Salò, 1993. Infiltration of mariner elements. Nature 364: 109–110.
George, D.G., L.T. Hunt & W.C. Barker, 1988. Current methods in sequence comparison and analysis, pp. 127–149 in Macromolecular Sequencing and Synthesis, edited by D. H. Schlesinger. A.R. Liss, New York.
Gilbert, D.G., 1998. SeqPup: a biosequence editor. Version 0.8c. Distributed by the author at seqpup@bio.indiana.edu.
Grenier, E., M. Abadon, F. Brunet, P. Capy & P. Abad, 1999. A mariner-like transposable element in the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabdis bacteriophora, horizontal trasmission versus ancient origin. J. Mol. Evol. 48: 328–336.
Jacobson, J.W., M.M. Medhora & D.L. Hartl, 1986. Molecular structure of a somatically unstable element in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83: 8684–8688.
Jarvik, T. & K.G. Lark, 1998. Characterization of Soymar1, a mariner element in soybean. Genetics 149: 1569–1574.
Jensen, S., M.P. Gassama & T. Heidmann, 1999. Taming of transposable elements by homology-dependent gene silencing. Nat. Genet. 21: 209–212.
Jordan, I.K. & J.F. McDonald, 1999a. Phylogenetic perspective reveals abundant Ty1/Ty2 hybrid elements in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome [letter]. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16: 419–422.
Jordan, I.K. & J.F. McDonald, 1999b. Comparative genomics and evolutionary dynamics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ty elements. Genetica 107: 3–13.
Labrador, M. & A. Fontdevila, 1994. High transposition rates of Osvaldo, a new Drosophila buzzatii retrotransposon. Mol. Gen. Genet. 245: 661–674.
Laten, H.M., A. Majumdar & E.A. Gaucher, 1998. SIRE-1, a copia/Ty1 retroelement from soybean, encodes a retroviral envelope-like protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 6897–6902.
Lemesle-Varloot, L., B. Henrissat, C. Gaboriaud, V. Bissery, A. Morgat & J.P. Mornon, 1990. Hydrophobic cluster analysis: procedures to derive structural and functional information from 2-D-representation of protein sequences. Biochimie 72: 555–574.
Lerat, E. & P. Capy, 1999. Retrotransposons and retroviruses: analysis of the envelope gene. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16: 1198–1207.
Luan, D.D., M.H. Korman, J.L. Jakubczak & T.H. Eickbush, 1993. Reverse transcription of R2Bm RNA is primed by a nick at the chromosomal traget site: a mechanism for non-LTR retrotransposition. Cell 72: 595–605.
Mammano, F., A. Öhagen, S. Höglund & H. Göttlinger, 1994. Role of the Major Homology Region of Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 in virion morphogenesis. J. Virol. 68: 4927–4936.
Maruyama, K. & D.L. Hartl, 1991. Evolution of the transposable element mariner in Drosophila species. Genetics 128: 319–329.
McClure, M., 1993. Evolutionary history of reverse transcriptase, pp. 425–444 in Reverse transcriptase, edited by M. Skalka, and S. P. Goff. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
McClure, M.A., 1991. Evolution of retroposons by acquisition or deletion of retrovirus-like genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 8: 835–856.
Morgan, G.T., 1995. Identification in the human genome of mobile elements spread by DNA-mediated transposition. J. Mol. Biol. 17: 1–5.
Okazaki, S., H. Ishikawa & H. Fujiwara, 1995. Structural analysis of TRAS1, a novel family of telomeric repeat-associated retro-transposons in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 4545–4552.
Oosumi, T., W.R. Belknap & B. Garlick, 1995. Mariner transposons in humans. Nature 378: 672–672.
Orgel, L.E. & F.H.C. Crick, 1980. Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature 284: 604–607.
Pardue, M.-L., O.N. Danilevskaya, K.L. Traverse & K. Lowenhaupt, 1997. Evolutionary links between telomeres and transposable elements. Genetica 100: 73–84.
Petrov, D.A., E.R. Lozovskaya & D.L. Hartl, 1996. High intrinsic rate of DNA loss in Drosophila. Nature 384: 346–349.
Reiter, L.T., T. Murakami, T. Koeuth, L. Pentao, D.M. Muzny, R.A. Gibbs & J.R. Lupski, 1996. A recombination hotspot responsible for two inherited peripheral neuropathies is located near a mariner transposon-like element. Nature Genet. 12: 288–297.
Robertson, H.M., 1997. Multiple mariner transposons in flatworms and hydras are related to those of insects. J. Heredity 88: 195–201.
Robertson, H.M. & E.G. MacLeod, 1993. Five major subfamilies of mariner transposable elements in insects, including the Mediterranean fruit fly, and related arthropods. Insect Mol. Biol. 2: 125–139.
Robertson, H.M. & R. Martos, 1997. Molecular evolution of the second ancient human mariner transposon, Hsmar2, illustrates patterns of neutral evolution in the human genome lineage. Gene 205: 219–228.
Robertson, H.M. & K.L. Zumpano, 1997. Molecular evolution of an ancient mariner transposon, Hsmar1, in the human genome. Gene 205: 203–217.
Robertson, H.M., Z.L. Zumpano, A.R. Lohe & D.L. Hartl, 1996. Reconstruction of the ancient mariners of humans. Nature Genet. 12: 360–361.
Rubin, E. & A.A. Levy, 1997. Abortive gap repair: underlying mechanism for Ds element formation. Mol. Cell Biol. 17: 6294–6302.
Sedensky, M.M., S.J. Hudson, B. Everson & P.G. Morgan, 1994. Identification of a mariner-like repetitive sequence in C. elegans. Nucleic Acids Res. 22: 1719–1723.
Streck, R.D., J.E. MacGaffey & S.K. Beckendorf, 1986. The structure of hobo transposable elements and their insertion. EMBO J. 5: 3615–3623.
Strimmer, K. & A. vonHaeseler, 1996. Quartet puzzling: a quartet maximum likelihood method for reconstructing tree topologies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 13: 964–969.
Swofford, D.L., 1993. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony. Version 3.1.1. Smithsonian Institution Washington DC.
Swofford, D.L., G.J. Olsen, P.J. Waddel & D.M. Hillis, 1996. Phylogenetic inference, pp. 407–514 in Molecular Systematics, edited by D. M. Hillis, Moritz and Mable. Sinauer.
Wiley, L.J., L.G. Riley, N.C. Sangster & A.S. Weiss, 1997. mle-1, a mariner-like transposable element in the nematode Trichostrongylus colubriformis. Gene 188: 235–237.
Xiong, Y. & T.H. Eickbush, 1990. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 9: 3353–3362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lerat, E., Brunet, F., Bazin, C. et al. Is the evolution of transposable elements modular?. Genetica 107, 15–25 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004026821539
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004026821539