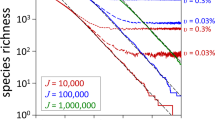
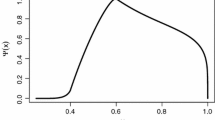
Abstract
An overview of the eleventh IAP Workshop is presented. Although significant progress has been made in the recognition of the factors governing species selection at differing trophic levels, it is recognised that the ultimate influences of species composition are precedent and stochasticity. No individual species is selected uniquely by a given combination of environmental conditions, although there are functional and morphological traits which pre-adapt some species above others to function preferentially in either oligotrophic or eutrophic conditions. With this in mind, a new set of rules of community assembly is offered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyruth, Z., 2000. Periodic disturbances, trophic gradient and phytoplankton characteristics related to cyanobacterial growth in Guarapiranga Reservoir, São Paulo state, Brazil. Hydrobiologia 424 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 150): 51–65.
Borics, G., I. Grigorszky, S. Szabó & J. Padisák, 2000. Phytoplankton associations in a small hypertrophic fishpond in East Hungary during a change from bottom-up to top-down control. Hydrobiologia 424 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 150): 79–90.
Braun-Blanquet, J., 1964. Pflanzensociologie. Springer, Wien.
Dokulil, M.T., 1999. Die Bedeutung hydroklimatischer Ereignisse für die Dynanikes Phytoplanktons in einem alpinum Klarwassersee (Mondsee, Österreich). Beitr. angewa. Gewässerökolo. Norddeutschlands, in press.
Dokulil, M.T & J. Mayer, 1996. Population dynamics and photosynthetic rates of a Cylindrospermopsis-Limnothrix association in a highly eutrophic urban lake, Alte Donau, Vienna, Austria. Algolo. Studies 83: 179–195.
Head, R.M., R.I. Jones & A.E. Bailey-Watts, 1999. An assessment of the influence of recruitment from the sediment on the development of planktonic populations of cyanobacteria in a temperate mesotrophic lake. Freshwat. Biol. 41: 759–769.
Huszar, V.L.M., L.H.S. Silva, M. Marinho, P. Domingos & C.L. Sant'Anna, 2000. Cyanoprokaryote assemblages in eight productive tropical Brazilian waters. Hydrobiologia 424 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 150): 67–77.
Leitão, M. & L. Léglize, 2000. Long-term variations of epilimnetic phytoplankton in an artificial reservoir during a 10-year survey. Hydrobiologia 424 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 150): 39–49.
Padisák, J., 1992. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton in a large, shallow lake (Balaton, Hungary)-a dynamic approach to biological memory, its possible role and mechanisms. J. Ecol. 80, 217–230.
Reynolds, C.S., 1987. The response of phytoplankton communities to changing lake environments. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 49: 220–236.
Reynolds, C.S., 1997. Vegetation processes in he pelagic: a model for ecosystem theory. Ecology Institute, Oldendorf.
Rojo, C., E. Ortega-Mayagoitia & M. Alvarez-Cobelas, 2000. Lack of pattern among phytoplankton assemblages. Or, what does the exception to the rule mean? Hydrobiologia 424 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 150): 133–140.
Southwood, T.R.E., 1997. Habitat, the templet for ecological strategies? J. anim. Ecol. 46: 337–365.
Temponeras, M., J. Kristiansen & M. Moustaka-Gouni, 2000. Seasonal variation in phytoplankton composition and physical-chemical features of the shallow Lake Doïrani, Macedonia, Greece. Hydrobiologia 424 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 150): 109–122.
Ter Braak, C.J.F., 1987. CANOCO-a FORTRAN program for canonical community ordination by partial, detrended canonical correspondence analysis, principal components analysis and redundancy analysis. ITI-INO, Wageningen.
Teubner, K., R. Feyerabend, M. Henning, A. Niklisch, P. Woitke & J.-G. Kohl, 1999. Alternative blooming of Aphanizomenon flosaquae or Planktothrix agardhii by the timing of ctical nitrogen; phosphorus ratio in hypertrophic riverine lakes. Adv. Limnol. 54: 325–344.
Tilman, D., 1996. Biodiversity: population versus ecosystem stability. Ecology 77: 350–363.
Tüxen, R., 1955. Das Systeme der nordwestdeutschen Pflanzengesellschaft. Mitt. Florist-soziolog. Arbeitsgem. 5: 1–119.
Ulanowicz, R.E., 1986. Growth and Development. Springer, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reynolds, C., Dokulil, M. & Padisák, J. Understanding the assembly of phytoplankton in relation to the trophic spectrum: where are we now?. Hydrobiologia 424, 147–152 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003973532706
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003973532706