Abstract
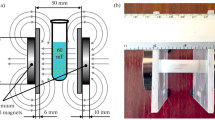
Cladophora glomerata (L.) Kz. was grown in Jaworski's algal culture medium and exposed to a fluctuating electromagnetic field which induced development of dark colouration, increased density and brittleness. After 4 weeks exposure, algae were unable to grow when transferred to unexposed culture medium. In addition, algal growth in culture medium exposed to a fluctuating magnetic field before the algae were introduced, was inhibited significantly compared with an appropriate control after 4 days, indicating a transfer of effect from the brief exposure to a magnetic field of less than 1 second to the 4-day period when growth was active.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett, R. A & S. A. Parsons, 1998. The influence of magnetic fields on calcium carbonate precipitiation. Wat. Res. 32: 609–612.
Bitton, G., J. L. Fox & H. G. Strickland, 1975. Removal of algae from lakes by magnetic filtration. Microbiology 30: 905–908.
Jones, D. & B. McLeod, 1995. Electromagnetic cell stimulation. In Lynch, P. T. & M. R. Davey (eds), Electrical Manipulation of Cells. Chapman & Hall, New York: 223–247.
Kovacs, P. E., R. L. Valentine & P. J Alvarez, 1997. The effect of static magnetic fields on biological systems: Implications for enhanced biodegradation. Critical Rev. Envir. Sci. Techn. 27: 319–382.
Maathuis, F. J. M., D. Sanders & D. Gradmann, 1997. Kinetics of high affinity KC uptake in plants, derived from KC-induced changes in current-voltage relationships. A modelling approach to the analysis of carrier-mediated transport. Planta 203: 229–236.
Mackereth, F. J. H., J. Heron & J. F. Talling, 1989. Water analysis. Some revised methods for limnologists. Freshwat. Biol. Assoc. Scient. Publ. 36.
Parsons, S. A., S. J. Judd, T. Stephenson, S. Udol & B.-L. Wang, 1997a. Magnetically augmented water treatment. Transac. Inst. Chem. Engin. 75: 98–104.
Parsons, S. A., B.-L. Wang, S. J. Judd & T. Stephenson, 1997b. Magnetic treatment of calcium carbonate scale - effect of pH control. Wat. Res. 31: 339–342.
Rigby, R. A., 1977. Algae growth control. Official Gazette of the United States Patent Office 965: 1487.
Smythe, A. G., C. L. Lange, T. M. Short, E. A., Dardeau & M. Brown-Hester, 1997. Evaluation of an in-line magnetic system as a control for zebra mussels. In Ditri, F. M. (ed.), Zebra Mussels and Aquatic Nuisance Species, Ann Arbor Press Inc.: 439–465.
Thompkins, J., M. M. De Ville, J. G. Day & M. F. Turner, 1995. Culture Collection of Algae and Protozoa. Catalogue of Strains. Natural Environment Research Council.
Wang, Y., A. J. Babchin, L. T. Chernyi, R. S. Chow & R. P. Sawatzky, 1997. Rapid onset of calcium carbonate crystallization under the influence of a magnetic field. Wat. Res. 31: 346–350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newman, J.R., Watson, R.C. Preliminary observations on the control of algal growth by magnetic treatment of water . Hydrobiologia 415, 319–322 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003841721176
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003841721176