Abstract
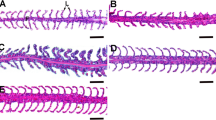
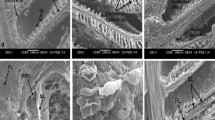
Metallothionein, a biomarker of exposure and toxicity of heavy metals, has been detected in the gills of brown trout (Salmo trutta fario L.) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Richardson) by means of immunohistochemistry. A very prominent labelling of chloride cells was found after exposure to diluted sewage plant effluents. No significant increase was observed in either the number of labelled cells or their labelling intensity after exposure to water of a polluted river compared to fish kept in tap water. These results do not correlate with findings of a histopathological study, suggesting that the metal levels at the sewage treatment plant were too low to produce gross histopathology. A comparison between the species indicated that the rainbow trout showed a generally higher metallothionein expression than the brown trout.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Abw V (1975) Verordnung über Abwassereinleitungen. AS 1993 3022 SR 814.225.21.
Aquaplus (1994) Beurteilung der Gewässergüte in der Langeten im Vergleich mit früheren Untersuchungen. Bern, Gewässerschutzamt des Kantons Bern.
Baer KN, Thomas P (1990) Influence of capture stress, salinity and reproductive status in zinc associated with metallothionein-like proteins in the livers of three marine teleost species. Marin Environm Research 29: 277-287.
Benson WH, Birge WJ (1985) Heavy metal tolerance and metallothionein induction in fathead minnows: Results from field and laboratory investigations. Environ Toxicol Chem 4: 209-217.
Conte FP, Lin DHY (1967) Kinetics of cellular morphogenesis in gill epithelium during sea water adaptation of Oncorhynchus (Walbaum). Comp Biochem Physiol 23: 945-957.
Dallinger R, Egg M, Köck G, Hofer R (1997) The role of metallothionein in cadmium accumulation of Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) from high alpine lakes. Aquat Toxicol 38: 47-66.
Dang ZC, Lock RAC, Flik G, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Hogstrand C (1998) Immunolocalization of metallothionein in the gill epithelial cells of copper exposed tilapia, VIII Int. Symposium on Fish Physiology, Uppsala, Sweden, 15-18 August 1998.
Farag AM, Stansbury MA, Hogstrand C, MacConnell E, Bergmann HL (1995) The physiological impairment of freeranging brown trout exposed to metals in the Clark Fork River, Montana. J Fish Aquat Sci 52: 2038-2050.
Frick E, Nowak D, Reust C, Burkhardt-Holm P (1998) Der Fischrückgang in den schweizerischen Fliessgewässern. GWA 4: 261-264.
Hodson PV (1988) The effect of metal metabolism on uptake, disposition and toxicity in fish. Aquat Toxicol 11: 3-18.
Hogstrand C, Haux C (1990a) Metallothionein as an indicator of heavy-metal exposure in two subtropical fish species. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 138: 69-84.
Hogstrand C, Haux C (1990b) A radioimmunoassay for perch (Perca fluviatilis) metallothionein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 103: 56-65.
Hogstrand C, Lithner G, Haux C (1991) The importance of metallothione in for the accumulation of copper, zinc and cadmium in environmental exposed perch, Perca fluviatilis. Pharmacol Toxicol 68: 492-501.
Hogstrand C, Verbost PM, Wendelaar Bonga, SE, Wood CM (1996) Mechanisms of zinc uptake in gills of freshwater rainbow trout: interplay with calcium transport. Am J Physiol 270: R1141-R1147.
Hogstrand C, Webb N, Wood CM (1998) Covariation in regulation of affinity for branchial zinc and calcium uptake in freshwater rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 201: 1809-1815.
Hogstrand C, Wood CM (1998) Toward a better understanding of the bioavailability, physiology, and toxicity of silver in fish: Implications for water quality criteria. Environ Toxicol Chem 17: 547-561.
Hylland K, Haux C, Hogstrand C, Sletten K, Andersen RA (1994) Properties of cod metallothionein, its presence in different tissues and effects of Cd and Zn treatment. Fish Physiol Biochem 13: 81-91.
Karlsson-Norrgren L, Runn P, Haux C, Förlin L (1985) Cadmiuminduced changes in gill morphology of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio (Hamilton-Buchanan), and rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J Fish Biol 27: 81-95.
Kito H, Ose Y, Sato T (1986) Cadmium-binding protein (metallothionein) in carp. Environ Health Persp 65: 117-124.
Klaasen CD, Lehman-McKeeman LD (1989) Induction of metallothionein. J Am Coll Toxicol 8: 1315-1321.
Kling P, Erkell LJ, Kille P, Olsson P-E (1996) Metallothionein induction in rainbow trout gonadal (RTG-2) cells during free radical exposure. Marin Environm Res 42: 33-36.
Maret W, Vallee BL (1998) Thiolate ligands in metallothionein confer redox activity on zinc clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3478-3482.
Mueller ME, Sanchez DA, Bergman HL, McDonald DG, Rhem RG, Wood CM (1991) Nature and time course of acclimation to aluminium in juvenile brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). II. Histology. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48: 2016-2027.
Norey CG, Lees WB, Darke BM, Stark JM, Baker TS, Cryer A, Kay J (1990) Immunological distinction between piscine and mammalian metallothioneins. Comp Biochem Physiol B 95: 597-601.
Ochsenbein U (1997) Schleichendes Fischsterben in bernischen Mittellandgew ässern. Informationsbulletin, Bau-Verkehrs-und Energiedirektion des Kantons Bern 1997: 2-6.
Olsson P-E, Kling P, Hogstrand C (1998) Mechanisms of heavy metal accumulation and toxicity in fish. In: Langston, Bebianne, eds. Metal Metabolism in Aquatic Environments London: Chapman & Hall Ltd., pp. 321-350.
Olsson PE, Kille P (1997) Functional comparison of the metalregulated transcriptional control regions of metallothionein genes from cadmium-sensitive and tolerant fish species. Biochem Biophys Acta 1350: 325-334.
Overnell J, McIntosh R, Fletcher TC (1987) The enhanced induction of metallothionein by zinc, its half-life in the marine fish Pleuronectes platessa, and the influence of stress factors on metallothionein levels. Experientia 43: 178-181.
Payan P, Mayer-Gostan N, Pang PKT (1981) Site of calcium uptake in the freshwater trout gill. J Exp Zool 216: 345-347.
Perry SF (1997) The chloride cell: Structure and function in the gills of freshwater fishes. Annu Rev Physiol 59: 325-347.
Perry SF, Laurent P (1993) Environmental effects on fish gill structure and function. In: Rankin C, Jensen FF eds. Fish Ecophysiology London: Chapman & Hall, pp. 231-285.
Perry SF, Wood CM (1985) Kinetics of branchial calcium uptake in the rainbowtrout: Effects of acclimation to various external calcium levels. J Exp Biol 116: 411-433.
Peter A (1995) Lebensraumänderungen in Fliessgewässern — eine fischbiologische Perspektive. Forschungszentrum für Limnologie 3: 159-173.
Pisam M, Le Moal C, Auperin B, Prunet P, Rambourg A (1995) Apical structures of ‘mitochondria-rich’ alpha and beta cells in euryhaline fish gill: their behaviour in various living conditions. Anat Rec 241: 13-24.
Pisam M, Rambourg A (1991) Mitochondria-rich cells in the gill epithelium of teleost fishes: an ultrastructural approach. Int Rev Cytol 130: 191-232.
Roberts KS, Cryer A, Kay J, Solbe JFDLG, Wharfe JR, Simpson WR (1979) The effects of exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of cadmium on enzyme activities and accumulation of the metal in tissues and organs of rainbow and brown trout (Salmo gairdneri, Richardson and Salmo trutta fario L.). Comp Biochem Physiol 62: 135-140.
Sabourin TD, Gant DB, Weber LJ (1986) The influence of metal and nonmetal stressors on hepatic metal-binding protein production in buffalo sculpin, Enophrys bison. In: Vernberg FJ, Thurberg FP, Calabrese A, Vernberg WB eds. Marine Pollution and Physiology: Recent advances Columbia: University of S. Carolina Press, pp. 247-266.
Schmidt H, Bernet D, Wahli T, Meier W, Burkhardt-Holm P (1999) Passive and active biomonitoring with trout in a polluted river and sewage plant effluents. J Fish Biol 54: 585-590.
Stagg RM, Goksoyr A, Rodger G (1992) Changes in the branchial Na+, K+-ATPase, metallothionein and P450 1A1 in dab Limanda limanda in the German Bight: indicators of sediment contamination? Marine Ecology Progress Series 91: 105-115.
StoV (1986) Verordnung über umweltgefährdende Stoffe. In: Council of Ministers of Switzerland, Berne.
Vallee BL (1995) The function of metallothionein. Neurochem Int 27: 23-33.
Verbost PM, Flik G, Lock RAC, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1987) Cadmium inhibition of Ca 2+ uptake in rainbow trout gills. Am J Physiol 253: R216-R221.
Verbost PM, Van Rooij J, Flik G, Lock RAC, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1989) The movement of cadmium through freshwater trout branchial epithelium and its interference with calcium transport. J Exp Biol 145: 185-197.
Van Veld PA, Vogelbein WK, Cochran MK, Goksoyr A, Stegeman JJ (1997) Route-specific cellular expression of cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A) in fish (Fundulus heteroclitus) following exposure to aqueous and dietary benzo(a)pyrene. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 142: 348-359.
Vokos (ed) (1997) Vollzugskonzept Siedlungsentwäserung. Bern, Switzerland, Bau-Verkehrs-und Energiedirektion.
VsBo (1986) Verordnung über Schadstoffe im Boden. In: Council of Ministers of Switzerland, Berne.
Wicklund Glynn A (1991) Cadmium and zinc kinetics in fish: studies on water-borne 109Cd and 65Zn turnover and intracellular distribution in the minnow, Phoxinus phoxinus. Pharmacol Toxicol 68: 485-491.
Wicklund Glynn A, Haux C, Hogstrand C (1992) Chronic toxicity and metabolism of Cd and Zn in juvenile minnows (Phoxinus phoxinus) exposed to a Cd and Zn mixture. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 49: 2070-2079.
Witters H, Berckmans P, Vangenechten C (1996) Immunolocalization of Na+, K+-ATPase in the gill epithelium of rainbowtrout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Cell Tissue Res 283: 461-468.
Wood CM (1992) Flux measurements as indices of HC and metal effects on freshwater fish. Aquat Toxicol 22: 239-264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burkhardt-Holm, P., Bernet, D. & Hogstrand, C. Increase of Metallothionein-immunopositive Chloride Cells in the Gills of Brown Trout and Rainbow Trout After Exposure to Sewage Treatment Plant Effluents. Histochem J 31, 339–346 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003726123083
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003726123083