Abstract
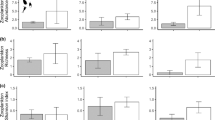
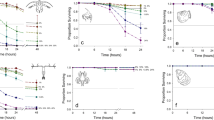
The effect of intermittent (2–4 h/day) treatments with chlorine or bromine at levels of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/L (total residual oxidant) upon settling and growth of veliger larvae of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, was examined in two successive flow-through studies. The work was conducted in a field laboratory which received a constant supply of water from western Lake Erie. Veliger densities in the water at the field site peaked at 530/L, while mussel densities on settling monitors reached 147,100/m2 over the course of the two studies (early July to late September 1991). In Study 1, a 2-h daily treatment with 1.0 mg/L chlorine reduced mussel settling by 91% as compared with controls, although mussel densities of up to 6,000/m2 still occurred. Treatment with 0.5 mg/L chlorine for 4 h/day produced a similar reduction in mussel settling during the second study. Bromine was less effective than chlorine at reducing settling of veligers. Mussels which remained settled in the treatment tanks had growth rates similar to controls, reaching 2–4 mm in length over a 30-day period. The intermittent halogen treatments similarly had no effect on whole body glycogen levels or growth of adult D. polymorpha. The intermittent chlorination regime used may therefore delay, but would not prevent a mussel fouling problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton, L. K., 1993. Control program for zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) at the Perry Nuclear Power Plant, Lake Erie. In T. F. Nalepa & D. W. Schloesser (eds), Zebra Mussels: Biology Impacts and Control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 555–562.
Bidwell, J. R., J. L. Farris & D. S. Cherry, 1995. Comparative response of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, and Asian clam, Corbicula fluminea, to a nonoxidizing molluscicide. Aquat. Tox. 33: 183–200.
Bij de Vaate, A., 1991. Distribution and aspects of population dynamics of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, (Pallas, 1771), in the Lake Ijsselmeer area (The Netherlands). Oecologia 86: 40–50.
Clarke, K. B., 1952. The infestation of waterworks by Dreissena polymorpha, a freshwater mussel. J. Inst. Water Works Eng. 6: 370–378.
Dexter, S. C., 1985. Fouling and corrosion. In W. Chow & Y. Mussalli (eds), EPRI Condenser Biofouling Control Symposium: The State of the Art. Electric Power Research Institute, Palo Alto, CA.
Fellers, B. D., E. L. Flock & J. C. Conley, 1988. Bromine replaces chlorine in cooling-water treatment. Power 132: 15–20.
Fraleigh, P. C., P. L. Klerks, G. Gubanich, G. Matisoff & R. C. Stevenson, 1993a. Abundance and settling of zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) veligers in western and central Lake Erie. In T. F. Nalepa & D. W. Schloesser (eds), Zebra Mussels: Biology, Impacts and Control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 129–142.
Fraleigh, P. C., W. R. Van Cott, M. E. Wenning & J. A. DeKam, 1993b. Effects of hypochlorite, permanganate, chlorine dioxide, and chloramines on zebra mussel settling. Preprint, EPRI Proceedings of the Third International Zebra Mussel Conference (Toronto, Ontario). Electric Power Research Institute, Palo Alto, CA.
Garton, D. W. & W. R. Haag, 1993. Seasonal reproductive cycles and settlement patterns of Dreissena polymorpha in western Lake Erie. In T. F. Nalepa & D. W. Schloesser (eds), Zebra Mussels: Biology, Impacts and Control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 111–128.
Griffiths, R. W., D. W. Schloesser, J. H. Leach & W. P. Kovalak, 1991. Distribution and dispersal of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in the Great Lakes Region. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 48: 1381–1388.
Holmes, N. J., 1970. The effects of chlorination on mussels. Central Electricity Research Laboratories, Leatherhead, Surrey, Report No. RD/L/R 1672, 20 pp.
James, W. G., 1967. Mussel fouling and use of exomotive chlorination. Chem. and Ind., 17 June 1967: 994–996.
Jenner, H. A., 1985. Chlorine minimization and macrofouling control in the Netherlands. In R. L. Jolley, R. J. Bull, W. P. Davis, S. Katz, M. H. Roberts Jr. & V.A. Jacobs (eds), Water Chlorination: Chemistry, Environmental Impacts, and Health Effects, Vol. 5, Lewis Publ. Inc., Chelsea, MI. 1425–1433.
Jenner, H. A. & J. P. M. Janssen-Mommen, 1993. Monitoring and Control of Dreissena polymorpha and other macrofouling bivalves in the Netherlands. In T. F. Nalepa & D. W. Schloesser (eds), Zebra Mussels: Biology Impacts and Control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 537–554.
Khalanski, M. & F. Bordet, 1980. Effects of chlorination on marine mussels. In R. L. Jolley, W. A. Brungs & R.B. Cumming (eds), Water Chlorination: Environmental Impact and Health Effects, Vol. 3. Ann Arbor Science, Inc., Ann Arbor, MI: 557–567.
Kilgour, B.W. & G. L. Mackie, 1993. Colonization of different construction materials by the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). In T. F. Nalepa & D. W. Schloesser (eds), Zebra Mussels: Biology Impacts and Control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 167–174.
Klerks, P. L. & P. C. Fraleigh, 1991. Controling adult zebra mussels with oxidants. J. Am. Wat. Wks. Assoc. 83: 92–100.
Klerks, P. L., P. C. Fraleigh & R. C. Stevenson, 1993. Controlling zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) veligers with thee oxidizing chemicals: chlorine, permanganate, and peroxide + iron. In T. F. Nalepa & D. W. Schloesser (eds), Zebra Mussels: Biology Impacts and Control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 621–642.
Lammarre, L., 1991. Invasion of the striped mollusks. EPRI Journal 16: 12–19.
Lauer, T. E. & D. K. Barnes, 1997. Competive interaction between Dreissena polymorpha and Lophopodella carteri (Bryozoa) in a southern Lake Michigan harbor. Seventh International Zebra Mussel Research Conference (New Orleans, LA), Proceedings: p. 25.
Mackie, G. L., 1991. Protocol for monitoring and control of zebra mussels. Mackie and Associates Water Systems Analysts, INC, Guelph, Ontario.
Mackie, G. L., W. N. Gibbons, B. W. Muncaster & I. M. Gray, 1989. The zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha: a synthesis of european experiences and a preview for North America. Water Resources Branch, Ontario Ministry of the Environment.
Marsden, E. J., 1992. Standard protocols for monitoring and sampling zebra mussels. Illinois Natural History Survey Biological Notes 138, 40 pp.
Marsden, E. J., 1993. Substrate preferences of newly settled zebra mussels. Third International Zebra Mussel Conference (Toronto, Ontario), Conference Abstracts, Monitoring and Assessment.
Mayer, F. L., D. J. Versteeg, M. J. McKee, L. C. Folmar, R. L. Graney, D. C. McCume and B. A. Rattner. 1992. Physiological and nonspecific biomarkers. In R. J. Huggett, R. A. Kimerle, P. M. Mehrle, Jr. & H. L. Bergman (eds), Biomarkers, Biochemical, Physiological, and Histological Markers of Anthropogenic Stress, Lewis, Chelsea, MI: 5–85.
McMahon, R. F. & J. L. Tsou, 1990. Impact of european zebra mussel infestation to the electric power industry. Proc. Am. Power Conf. 52: 988–997.
Menis-Croxall, N. and G. DeBruyn, 1997. Zebra mussel mitigation: elements of a successful chlorination system. Seventh International Zebra Mussel Research Conference (New Orleans, LA) Proceedings: 21.
Mills, J. F., 1980. Bromine chloride-an alternative to chlorine treatment for once-though cooling waters. In J. F. Garey, R. M. Jorden, A. H. Aitken, D. T. Burton & R. H. Gray (eds), Condensor Biofouling Control, Ann Arbor Science, Ann Arbor, MI.
Moore, T., 1997. New water regulations on the horizons. EPRI Journal 21: 18–25.
Neuhauser, E. F., J. E. Van Benschoten & J. N. Jensen, 1991. Effect of selected oxidants on zebra mussel veligers - Part III. Abstract, Zebra Mussel Mitigation Options for Industries, Toronto, Ontario (February 1991).
O'Neill, C. R., 1997. Economic impact of zebra mussels-results of the 1995 National Zebra Mussel Clearinghouse survey. New York Sea Grant Institute, Brockport.
O'Neill, C. R. & D. B. MacNeill, 1989. The zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha): An unwelcome North American invader. N.Y. Coop. Extension, Cornell Univ., N.Y.
Rajagopal, S., 1997. The ecology of tropical marine mussels and their control in industrial cooling water systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 184 pp.
Rajagopal, S., G. van der Velde & H. A. Jenner, 1994. Biology and control of the brackish water mussel, Mytilopsis leucophaeta in the Velsen and Hemweg power stations, The Netherlands. Part II. Control Measures. KEMA Environmental Services, Arnhem, Report No. 163871-KES/WBR 94–3128, 45 pp.
Roerhig, K. L. & J. B. Allred, 1974. Direct enzymatic procedure for determination of liver 9. glycogen. Analyt. Biochem. 58: 114–121.
Roper, J. M., 1994. Sediment toxicity and bioaccumulation of toxicants in the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, at Times Beach, Buffalo, NY. Masters Thesis, Virgina Tech, Department of Biology, Blacksburg, VA.
SAS, 1988. SAS/STAT User's Guide, Release 6.03 Edition. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC.
Smit, H., A. Bij de Vaate, H. H. Reeders, E. H. van Nes & R. Noordhuis, 1993. Colonization, ecology, and positive aspects of zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) in the Netherlands. In T. F. Nalepa & D. W. Schloesser (eds), Zebra Mussels: Biology, Impacts and Control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 55–78.
Sawyko, P. M, 1994. Zebra mussel mitigation: elements of a successful chlorination system. Fourth International Zebra Mussel Research Conference (Madison, WI) Proceedings: 69.
USEPA, 1980. Effluent limitation guidelines, Pretreatment standards and source performance standards under Clean Water Act, steam electric generating point source category, 40 CFR. Parts 125 and 423, Fed. Reg. 45: 68328–68337.
Van Benschoten, J. E., J. N. Jensen, D. Lewis & T. J. Brady, 1993. Chemical oxidants for controlling zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha): a synthesis of recent laboratory and field studies. In T. F. Nalepa & D.W. Schloesser (eds), ZebraMussels: Biology Impacts and Control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 599–619.
Van Cott, W. R., P. C. Fraleigh, M. E. Wenning & J. A. DeKam, 1992. Zebra mussel settling and infestation patterns. Preprint, EPRI Proceedings of the Third International Zebra Mussel Conference (Toronto, Ontario). Electric Power Research Institute, Palo Alto, CA.
Van Diepen, J. & C. Davids, 1986. Zebra mussels and polystyrene. Hydobiol. Bull. 19: 179–181.
Walz, N., 1975. The settlement of larvae of Dreissena polymorpha on artificial substrates. Arch. Hydrobiol., Suppl. 47: 423–431
Whitehouse, J. W., M. Khalanski, M. G. Saroglia & H. A. Jenner, 1985. The control of biofouling in marine and estuarine power stations: a collaborative research working group report for use by station designers and station managers, CEGB, EdF, ENEL and KEMA, CEGB NW-Region–191–9–85.
Zar, J. H., 1984. Biostatistical Analysis, 2nd edition. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., 718 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bidwell, J.R., Cherry, D.S., Farris, J.L. et al. Effects of intermittent halogenation on settlement, survival and growth of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha. Hydrobiologia 394, 53–62 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003553202996
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003553202996