Abstract
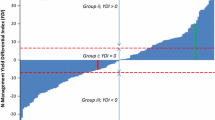
Cultivars of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) capable of yielding well at low levels of native or added phosphorus (P) are highly desirable in many tropical production systems. The objective of the present study was to identify geographical regions which might be sources of such genotypes. A total of 364 landraces, cultivars and wild genotypes, drawn from a broad geographic range, were divided on the basis of growth habit into four field trials, each comprising two levels of P, stressed and unstressed, on an infertile Andosol in Popayan, Colombia. The regression relationship between grain yield per plant in the presence and in the absence of stress was determined, and each genotype's deviation from this relationship was used as a measure of P-efficiency. There was highly significant variation in efficiency among genotypes in all growth habits, and in climbing beans there were consistent regional differences, superior genotypes being identified with greater frequency among those from Bolivia, West Mexico and South Mexico-West Guatemala. The latter region was promising for prostrate bush genotypes also. Wild beans in general performed relatively poorly; it appears that P-efficiency traits in P. vulgaris have been acquired during or after domestication. These results confirm that genetic differences in P-efficiency exist among common bean genotypes and suggest that these are related to geographic origin. Furthermore, the use of a representative sample of germplasm can help to identify segments of the gene bank that are especially promising as sources of desirable traits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, A.H.D., 1989. Core collections: a practical approach to genetic resources management. Genome 31: 818–824.
CIAT (Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical), 1982. Bean Program Annual Report. CIAT, Cali, Colombia.
CIAT (Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical), 1987. Standard system for the evaluation of bean germplasm. A. van Schoonhoven & M.A. Pastor-Corrales (compilers). Cali, Colombia.
CIAT (Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical), 1992. Constraints to and opportunities for improving bean production. A planning document 1993–98. An achievement document 1987–92. CIAT, Cali, Colombia.
CIAT (Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical), 1993. Trends in CIAT Commodities. Working Document No. 128.
Foy, C.D., A.L. Fleming & G.C. Gerloff, 1972. Differential aluminum tolerance in two snapbean varieties. Agron J 64: 815–818.
Galwey, N.W. & A.M. Evans, 1982. Alternative methods of interpreting measurements of resistance to the leafhopper Empoasca kraemeri Ross and Moore in the common bean, Phaseolus vulgaris L. Euphytica 31: 226–236.
Genstat 5 Committee, 1993. Genstat 5 Release 3 Reference Manual. Oxford University Press.
Gepts, P. & D. Debouck, 1991. Origin, domestication, and evolution of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). In: A. van Schoonhoven & O. Voysest (Eds), Common beans: Research for crop improvement, pp. 7–53. C.A.B. International, Wallingford, UK and CIAT, Cali, Colombia.
Gepts, P. & F.A. Bliss, 1986. Phaseolin variability among wild and cultivated common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) from Colombia. Econ Bot 40(4): 469–478.
Gonzalez, A., J. Lynch, J.M. Tohme, S.E. Beebe & R.E. Macchiavelli, 1995. Characters related to leaf photosynthesis in wild populations and landraces of common bean. Crop Sci 35: 1468–1476.
Lynch, J.P. & S.E. Beebe, 1995. Adaptation of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) to low phosphorus availability. HortSci 30(6): 1165–1171.
Lynch, J., A. Gonzalez, J. Tohme & J. Garcia, 1992. Variation for characters related to leaf photosynthesis in wild bean populations. Crop Sci 32: 633–640.
Nodari, R.O., S.M. Tsai, R.L. Gilbertson & P. Gepts, 1993. Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean. 2. Development of an RFLP-based linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 85: 513–520.
Sánchez, P.A. & G. Uehara, 1980. Management considerations for acid soils with high phosphorus fixation capacity. In: F.E. Khasawneh, E.C. Sample & E.J. Kamrath (Eds), The role of phosphorus in Agriculture, pp. 471–514. Am Soc Agron Sci Madison, Wisconsin.
Singh, S.P., P. Gepts & D.G. Debouck, 1991a. Races of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris, fabaceae). Econ Bot 45(3): 379–396.
Singh, S.P., R. Nodari & P. Gepts, 1991b. Genetic diversity in cultivated common bean: I. Allozymes. Crop Sci 31(1): 19–23.
Singh, S.P., C.A. Urrea, J.A. Gutierrez & J. Garcia, 1989. Selection for yield at two fertilizer levels in small-seeded common bean. Can J Plant Sci 69: 1011–1017.
Tapia, B.H., 1987. Variedades mejoradas de frijol Phaseolus vulgaris L. con grano rojo para Nicaragua. Instituto Superior de Ciencias Agropecuarias. Direccion de Investigacion y Postgrado, Managua, Nicaragua.
Thung, M., 1990. Phosphorus: A limiting nutrient in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) production in Latin America and field screening for efficiency and response. In: N. El Bassam, M. Dambroth & B.C. Lughman (Eds), Genetic aspects of plant mineral nutrition, pp. 501–502. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands.
Tohme, J., P. Jones, S. Beebe & M. Iwanaga, 1995. The combined use of agroecological and characterization data to establish the CIAT Phaseolus vulgaris core collection. In: T. Hodgkin, A.H.D. Brown, Th.J.L. van Hintum & E.A.V. Morales (Eds), Core collections of plant genetic resources, pp. 95–107. J. Wiley and Sons, Chichester, U.K.
Toro, O., J. Tohme & D.G. Debouck, 1990. Wild bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): Description and distribution. International Board for Plant Genetic Resources (IBPGR) and Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT). Cali, Colombia.
Whiteaker, G., G.C. Gerloff, W.H. Gabelman & D. Lindgren, 1976. Intraspecific differences in growth of beans at stress levels of phosphorus. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 101: 472–475.
Yan, Xiaolong, J.P. Lynch & S.E. Beebe, 1995a. Genetic variation for phosphorus efficiency of common bean in contrasting soil types: I. Vegetative response. Crop Sci 35: 1086–1093.
Yan, Xiaolong, S.E. Beebe & J.P. Lynch, 1995b. Genetic variation for phosphorus efficiency of common bean in contrasting soil types: II. Yield response. Crop Sci 35: 1094–1099.
Youngdahl, L.J. 1990. Differences in phosphorus efficiency in bean genotypes. J Plant Nutr 13(11): 1381–1392.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beebe, S., Lynch, J., Galwey, N. et al. A geographical approach to identify phosphorus-efficient genotypes among landraces and wild ancestors of common bean. Euphytica 95, 325–338 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003008617829
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003008617829