Abstract
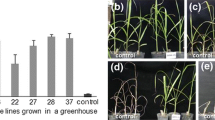
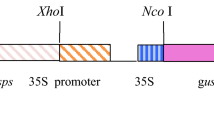
Sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) lines transformed with the 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase gene (CP4 EPSPS) from Agrobacterium sp. CP4 and a glyphosate oxidase reductase gene (GOX) also isolated from bacteria resulted in the development of lines highly tolerant to glyphosate. Glyphosate (N-phosphonomethyl-glycine) is the active ingredient in Roundup®, herbicide. The EPSPS enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids. Glyphosate binds irreversible to the EPSPS and inhibits the pathway. GOX degrades glyphosate into non-toxic compounds. 260 independent transformants have been evaluated in greenhouse and field trials for tolerance to Roundup® in 1993 and 1994. Variation of tolerance was recorded between different transformants, ranging from complete susceptibility to full tolerance. The Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation resulted in a negative correlation between copy number of the T-DNA insert and the level of tolerance to the herbicide. Transformants which contain a single copy insert showed tolerance to higher doses of glyphosate than transformants with multiple copies. Two transgenic lines were identified that showed agronomically useful tolerance to glyphosate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry, G., G. Kishore, M. Padgette, K. Kolacz, M. Weldon, D. Re, D. Eichholtz, K. Fincher & L. Hallas, 1992. Inhibitors of Amino Acid Biosynthesis: Strategies for Imparting Glyphosate Tolerance to Crop Plants. In Biosynthesis and Molecular Regulation of Amino Acids in Plants.B.K. Singh H, Flores E and Shannon JC, editors. American Society of Plant Physiologists, 139–145.
Benfey, P.N., N-H. Chau, 1989. Regulated genes in transgenic plants. Science 244: 174–188.
Delannay, X., T.T. Bauman, D.H. Beighley, M.J. Buettner, H.D. Coble, M.S. DeFelice, C.W. Derting, T.J. Diedrick, J.L. Griffin, E.S. Hagood, F.G. Hancock, S.E. Hart, B.J. La Vallee, M.M. Loux, W.E. Lueschen, K.W. Matson, C.K. Moots, E. Murdock, A.D. Nickel, M.D.K. Owen, E..H. Paschal II, L.M. Prochaska, P.J. Raymond, D.B. Reynolds, W.K. Rhodes, F.W. Roeth, P.L. Sprankle, L.J. Tarochione, C.N. Tinius, R.J. Walker, L.M. Wax, H.D. Weigelt & S.R. Padgette, 1995. Yield evaluation of a glyphosate-tolerant soybean line after treatment with glyphosate. Crop Sci. 35: 1461–1467.
della-Cioppa, G., S.C. Bauer, B.K. Klein, D.M. Shah, R.T. Fraley & G. Kishore, 1986. Translocation of the precursor of 5-enol-pyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase into chloroplasts of higher plants in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83: 6873–6877.
Delores, S.C. & R.C. Gardner, 1988. Expression and inheritance of kanamycin resistance in a large number of transgenic petunias generated by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Plant Mol. Biol. 11: 355–364.
Doyle, J.J. & J.L. Doyle, 1990. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12: 13–15 (published by Life Technologies Inc.).
Fry, J.E., A.R. Barnason & M. Hinchee, 1991. Genotype-independent transformation of sugarbeet using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Third international congress of plant mol. biol., Tuscon, Arizona, USA.
Gasser, C.S., J.A. Winter, C.M. Hironaka & D.M. Shah, 1988. Structure, expression, and evolution of the 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase genes of petunia and tomato. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 4280–4289.
Gowda, S., F.C. Wu & R.J. Shepard, 1989. Identification of promoter sequences for the major RNA transcripts of figwort mosaic and peanut chlorotic streak viruses (Caulimovirus group). J. Cell. Biochem. 13D(supplement): 301.
Hobbs, S.L.A., T.D. Warkentin & C.M.O. DeLong, 1993. Transgenic copy number can be positively or negatively associated with transgene expression. Plant Mol. Biol. 21: 17–26.
Holt, J.S., S.B. Powles & J.A.M. Holtum, 1993. Mechanisms and agronomic aspects of herbicide resistance. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.
Jacq, B., O. Lesobre, S.R. Sanngwan & B.S. Sangwan-Norreel, 1993. Factors influencing T-DNA transfer in Agrobacterium tumefaciens transformation of sugarbeet. Plant Cell Rep. 12: 621–624.
Jefferson, R.A., T.A. Kavanagh & M. Bevan, 1987. GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 6: 3901–3909.
Jefferson, R.A, 1987. Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 5: 387–405.
Jones, J.D.G., D.E. Gilbert, K.L. Grady & R.A. Jorgensen, 1987. T-DNA structure and gene expression in petunia plants transformed with Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 derivatives. Mol. Gen. Genet. 207: 478–485.
Jorgensen, J, 1992. Silencing of plant genes by by homologous transgenes. Agbiotech. News Info. 4: 265N–273N
Konwar B.K., 1994. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of sugar beet (Beta Vulgaris L.). J. Plant Biochem & Biotech 3: 37–41.
Laemmli, U.K., 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Linn, F., I. Heidmann, H. Saedler & P. Meyer, 1990. Epigenetic changes in the expression of the maize A1 gene in petunia hybrida: role of numbers of integrated gene copies and state of methylation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 222: 329–336.
Liu, C.-M., P.A. Mclean, C.C. Sookdeo & F.C. Cannon, 1991. Degradation of herbicide glyphosate by members of the family Rhizobiaceae. Appl. and Environ. Microbiol. 57: 1799–1804.
Madsen, K.H. & J.E. Jensen, 1995. Weed control in glyphosate-tolerant sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Weed Res. 35: 105–111.
Maniatis, T., E.F. Fritsch & J. Sambrook, 1982. Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbour, NY: Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory
Matzke, M.A. & A.J.M. Matzke, 1993. Genomic imprinting in plants: parental effects and trans-inactivation phenomena. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 44: 53–76.
Meyer, P.I., I. Heidmann, G. Forkmann & H. Saedler, 1987. A new petunia flower colour generated by transformation of a mutant with a maize gene. Nature 330: 677–678.
Meyer, P, 1995. Variation of transgene expression in plants. Euphytica 85: 359–366.
Miller, S.D & K.J. Fornstrom, 1989. Weed control and labor requirements in sugarbeets. J. Sugar Beets Res. 26: 3–4.
Mittelstein, S.O., J. Paszkowski & I. Potrykus, 1991. Reversible inactivation of a transgene inArabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Gen. Genet. 228: 104–112
Odell, J.T., F. Nagy & N-H Chua, 1985. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S promoter. Nature 313: 810–812.
Padgette, S.R., K.H. Kolacz, X. Delannay, D.B. Re, B.J. La Vallee, C.N. Tinius, W.K. Rhodes, Y.I. Otero, G.F. Barry, D.A. Eichholtz, V.M. Peschke, D.L. Nida, N.B. Taylor & G.M. Kishore, 1995. Development, identification, and characterization of a glyphosate-tolerant soybean line. Crop Sci. 35: 1451–14611.
Rao, R.N. & S.G. Rogers, 1979. Plasmid pKC7: A vector containing ten restriction endonucleases sites suitable for cloning DNA segments. Gene 7: 79–82.
Revenkova, E.V., A.S. Kraev & K.G. Skryabin, 1990. Transformation of cotton (Gossypium-Hirsutun L) by supervirulent Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain A281. Mol. Biol. 24: 1017–1021.
SAS Institute Inc. 1985. SAS user's guide, 5th ed. North Carolina Cary, SAS Institute Inc.
Schweizer, E.E., P. Westra, 1991. Potential for weeds to develop resistance to sugar beet herbicides in North America. J. of Sugar Beet Research 28: 1–23.
Shah, D.M., R.B. Horsch, H.J. Kle, G.M. Kishore, J.A Winter, N.E. Tumer, C.M. Hironaka, P.R. Sanders, C.S. Gasser, S. Ayken, N.R. Siegel, S.G. Rogers & R.T. Fraley, 1986. Engineering herbicide tolerance in transgenic plants. Science 233: 478–481.
Steinrucken, H.C. & N. Amrhein, 1980. The herbicide glyphosate is a potent inhibitor of 5-enolpyruvyl shikimate acid-2-phosphate synthase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 94: 1207–1212.
Tai, T.H. & S.D. Tanksley, 1990. A rapid and inexpensive method for isolation of total DNA from dehydrated plant tissue. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep 8: 297–303.
Torstensson, N.T.L. & A. Hamisepp, 1977. Detoxification of glyphosate in soil. Weed Res. 17: 209–212.
Towbin, H., T. Staehelin & J. Gordon, 1979. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76: 4350–4354.
Williamson, J.D., M.E. Hirsch-Wyncott, B.A. Larkins & S.B. Gelvin, 1989. Differential accumulation of a transcript driven by the CaMV 35S promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol. 90: 1570–1576.
von Wordragen, M.F. & H.J.M. Dons, 1992. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-transformation of recalcitrant crops. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 10(1): 12–36.
Zhou, H., J.W. Arrowsmith, M.E. Fromm, C.M. Hironaka, M.L. Taylot, D. Rodriguez, M.E. Pajeau, S.M. Brown, C.G. Santino & J.E. Fry, 1995. Glyphosate-tolerant CP4 and GOX genes as a selectable marker in wheat transformation. Plant Cell Rep. 15: 159–163.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mannerlöf, M., Tuvesson, S., Steen, P. et al. Transgenic sugar beet tolerant to glyphosate. Euphytica 94, 83–91 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002967607727
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002967607727