Abstract
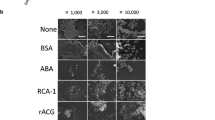
Streptococcus mutans is a major etiological agent in dental caries. Salivary agglutinin is one of the main salivary components binding to S.mutans. To learn more about the interaction of salivary agglutinin with S.mutans, parotid, submandibular, sublingual and palatal saliva samples were incubated with S. mutans suspension. Both depleted saliva samples and bacterial extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Salivary agglutinin was present in all types of glandular saliva and in all cases bound to S.mutans, also to PC337C, a P1− mutant of S.mutans. Agglutinin was separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing and non-reducing conditions and then transferred to nitrocellulose. Non-reduced agglutinin bound S.mutans, but reduced agglutinin did not. Adhesion of S.mutans to agglutinin-coated microplates was inhibited by amine-containing components, 1 M NaCl or KCl and EDTA. Adhesion decreased with decreasing pH with no adhesion below pH 5.0. These data suggest that calcium-dependent electrostatic interactions play a role in binding. By immunoblotting was demonstrated that blood group antigens and Lewis antigens were present on agglutinin. Synthetic blood group antigens and Lewis antigens covalently coupled to polyacrylamide were tested for binding to S.mutans. Only Lea(Galβ1,3(Fucα1,4)GlcNAc) bound to S.mutans, whereas the blood group antigens Leb, Lex, Ley, H1, H2, A, B and sialylated Lea did not. Lea without galactose (Fucα1,4GlcNAc) still bound to S. mutans, but Lea without fucose (Galβ1,3GlcNAc) did not. Binding of agglutinin to S. mutans was not inhibited by Lea. In conclusion, S. mutans can bind to Lea carbohydrate epitopes in which the fucose is an essential residue. Lea carbohydrate epitopes are present on salivary agglutinin but play no major role in binding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong EA, Ziola B, Habbick BF & Komiyama K (1993) Role of cations and IgA in saliva-mediated aggregation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 22: 207–213
Bleiweis AS (1993) Adhesion and cohesion of plaque microflora: a function of microbial fimbriae and fibrils. In: Bowen WH & Tabak LA (Eds), Cariology for the Nineties (pp 287–299). University of Rochester Press, Rochester.
Boackle RJ, Connor MH & Vesely J (1993) High molecular weight non-immunoglobulin salivary agglutinins (NIA) bind C1Q globular heads and have the potential to activate the first complement component. Mol. Immunol. 30: 309–319
Brady LJ, Piacentini DA, Crowley PJ & Bleiweis AS (1991) Identification of monoclonal antibody-binding domains within antigen P1 of Streptococcus mutans and cross-reactivity with related surface antigens of oral streptococci. Infect. Immun. 59: 4425–4435
Brady LJ, Crowley PJ, Piacentini DA & Bleiweis AS (1993) The interactions of the cell surface P1 adhesin molecule of Streptococcus mutans with human salivary agglutinin. J. Microbiol. Meth. 18: 181–196
Carlén A & Olsson J (1995) Monoclonal antibodies against highmolecular-weight agglutinin block adherence to experimental pellicles on hydroxyapatite and aggregation of Streptococcus mutans. J. Dent. Res. 74: 1040–1047
Carlén A, Olsson J & Börjesson A-C (1996) Saliva-mediated binding in vitro and prevalence in vivo of Streptococcus mutans. Archs Oral Biol. 41: 35–39
Carlén A, Bratt P, Stenudd C, Olsson J & Strömberg N (1998) Agglutinin and acidic proline-rich protein receptor patterns may modulate bacterial adherence and colonization on tooth surfaces. J. Dent. Res. 77: 81–90.
Ciopraga J, Motas C & Doyle RJ (1995) Inhibition of saliva-induced aggregation by blood group glycoproteins. FEMS Immunol. & Med. Microbiol.10: 145–149
Davis CA, Malamud D & Lally E (1986) Monoclonal antibodies raised to human salivary agglutinin. J. Dent. Res. 65: abst. 303, 759
Demuth DR, Lammey MS, Huck M, Tally ET & Malamud D (1990) Comparison of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis receptors for human salivary agglutinin. Microbial Pathog. 9: 199–211
Ericson T & Rundegren J (1983) Characterization of a salivary agglutinin reacting with a serotype c strain of Streptococcus mutans. Eur. J. Biochem. 133: 255–261
Estilo C & Malamud D (1996) Role of carbohydrate in aggregation of S. mutans by human salivary agglutinin. J. Dent. Res. 75: abstr. 2342, 310
Gibbons RJ & van Houte J (1980) Bacterial adherence and the formation of dental plaque. In: Beachey EH (Ed) Bacterial Adherence. Receptors and Recognition, series B, vol 6 (pp 60–104) Chapman & Hall, London
Gibbons RJ & Qureshi JV (1978) Selective binding of blood groupreactive salivary mucins by Streptococcus mutans and other oral organisms. Infect. Immun. 22: 665–671
Hajishengallis G, Koga T & Russell MW (1994) Affinity and specificity of the interactions between Streptococcus mutans antigen I/II and salivary components. J. Dent. Res. 73: 1493–1502
Hamada S & Slade HD (1980) Biology, immunology and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol. Rev. 34: 331–384
Jenkinson HF & Demuth DR (1997) Structure, function, and immunogenicity of streptococcal antigen I/II polypeptides. Mol. Microbiol. 23: 183–190
Kishimoto E, Hay DI & Gibbons RJ (1991) Inhibition of adhesionpromoting activity of a human salivary protein which promotes adhesion of Streptococcus mutans JBP to hydroxyapatite. FEMS Microbiol. Letts. 90: 19–22
Lamont RJ, Demuth DR, Davis CA, Malamud D & Rosan B (1991) Salivary-agglutinin-mediated adherence of Streptococcus mutans to early plaque bacteria. Infect. Immun. 59: 3446–3450
Lee SF, Progulske-Fox A, Erdos GW, Piacentini DA, Ayakawa GY, Crowley PJ & Bleiweis AS (1989) Construction and characterization of isogenic mutants of Streptococcus mutans deficient in major surface protein antigen P1 (I/II). Infect. Immun. 57: 3306–3313
Levine MJ, Reddy MS, Tabak LA, Loomis RE, Bergey EJ, Jones PC, Cohen RE, Stinson MW & Al-Hashimi I (1987) Structural aspects of salivary glycoproteins. J. Dent. Res. 66: 436–441
Ligtenberg AJM, Veerman ECI, de Graaff J & Nieuw Amerongen AV (1990a) Influence of the blood group reactive substances in saliva on the aggregation of Streptococcus rattus. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 57: 97–107
Ligtenberg AJM, Veerman ECI, de Graaff J & Nieuw Amerongen AV (1990b) Saliva-induced aggregation of oral streptococci and the influence of blood group reactive substances. Archs Oral Biol. 35: 141S-143S
Ligtenberg AJM, Walgreen-Weterings E, Veerman ECI, de Soet JJ, de Graaff J & Nieuw Amerongen AV (1992) Influence of saliva on the aggregation and adherence of Streptococcus gordonii HG 222. Infect. Immun. 60: 3878–3884
Ligtenberg AJM, Walgreen-Weterings E, Veerman ECI, de Soet JJ & Nieuw Amerongen AV (1995) Attachment of Streptococcus gordonii HG 222 to Streptococcus oralis NY 586 and the influence of saliva. Microb. Ecol. Hlth Dis. 8: 243–254
Loesche WJ (1986) Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol. Rev. 50: 353–380
Nieuw Amerongen AV, Bolscher JGM & Veerman ECI (1995) Salivary mucins; protective functions in relation to their diversity. Glycobiology 5: 733–740
Oho T, Yu H, Yamashita Y & Koga T (1998) Binding of salivary glycoprotein-immunoglobulin-A complex to the surface protein antigen of Streptococcus mutans. Infect. Immun. 66: 115–121
Prakobphol A, Leffler H & Fisher SJ (1993) The high molecular weight human mucin is the primary salivary carrier of ABH, Lea, and Leb blood group antigens. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 4: 325–333
Rathman WM, Van Zeyl MJ, van den Keijbus PAM, Döpp EA, Veerman ECI & Nieuw Amerongen AV (1990) Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to human salivary glycoproteins. Cellular localization of mucin, cystatin-like 14 kD protein and 20 kD glycoprotein in the human submandibular gland. J. Biol. Buccale 18: 19–27
Rundegren J (1986) Calcium-dependent salivary agglutinin with reactivity to various oral bacterial species. Infect. Immun. 53: 173–178
Rundegren J & Arnold RR (1987) Differentiation and interaction of secretory immunoglobulin A and calcium-dependent parotid agglutinin for several bacterial strains. Infect. Immun. 55: 288–292
Russell MW & Månsson-Rahemtulla B (1989) Interaction between surface antigens of Streptococcus mutans and human salivary components. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 4: 106–111
de Soet JJ, van Dalen PJ, Pavicic MJ & de Graaff J (1990) Enumeration of mutans streptococci in clinical samples by using monoclonal antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 28: 2467–2472
Takano K, Bogert M, Malamud D, Lally E & Hand AR (1991) Differential distribution of salivary agglutinin and amylase in the Golgi apparatus and secretory granules of human salivary gland acinar cells. Anat. Rec. 230: 307–318
Tart RC & van de Rijn I (1991) Analysis of adherence of Streptococcus defectivus and endocarditis-associated streptococci to extracellular matrix. Infect. Immun. 59: 857–862
Veerman ECI, Valentijn-Benz M, van den Keijbus PAM, Rathman WM, Sheehan JK & Nieuw Amerongen AV (1991) Immunochemical analysis of high molecular weight human salivary mucins (MG-1) using monoclonal antibodies. Archs Oral Biol. 36: 923–932
Veerman ECI, Ligtenberg AJM, Schenkels LCPM, Walgreen-Weterings E & Nieuw Amerongen AV (1995) Binding of human high-molecular weight salivary mucins (MG1) to Hemophilus parainfluenzae. J. Dent. Res. 74: 351–357
Veerman ECI, van den Keijbus PAM, Vissink A & Nieuw Amerongen AV (1996) Human glandular salivas: their separate collection and analysis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 104: 346–352
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ligtenberg, A., Veerman, E. & Nieuw Amerongen, A. A Role for Lewis a antigens on salivary agglutinin in binding to Streptococcus mutans. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 77, 21–30 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002054810170
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002054810170