Abstract
Penicillins and cephalosporins are synthesized by a series of enzymatic reactions that form the tripeptide δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine and convert this tripeptide into the final penicillin or cephalosporin molecules. One of the enzymes, isopenicillin N synthase has been crystallyzed and its active center identified. The three genes pcbAB, pcbC and penDE involved in penicillin biosynthesis are clustered in Penicillium chrysogenum, Aspergillus nidulans and Penicillium nalgiovense. Carbon catabolite regulation of penicillin biosynthesis is exerted by glucose and other easily utilizable carbon sources but not by lactose. The glucose effect is enhanced by high phosphate concentrations. Glucose represses the biosynthesis of penicillin by preventing the formation of the penicillin biosynthesis enzymes. Transcription of the pcbAB, pcbC and penDE genes of P. chrysogenum is strongly repressed by glucose and the repression is not reversed by alkaline pHs. Carbon catabolite repression of penicillin biosynthesis in A. nidulans is not mediated by CreA and the same appears to be true in P. chrysogenum. The first two genes of the penicillin pathway (pcbAB and pcbC) are expressed from a bidirectional promoter region. Analysis of different DNA fragments of this bidirectional promoter region revealed two important DNA sequences (boxes A and B) for expression and glucose catabolite regulation of the pcbAB gene. Using protein extracts from mycelia grown under carbon catabolite repressing or derepressing conditions DNA-binding proteins that interact with the bidirectional promoter region were purified to near homogeneity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonowitz Y, Bergmeyer J, Cantoral JM, Cohen G, Demain AL, Fink U, Kinghorn J, Kleinkauf H, MacCabe A, Palissa H, Pfeifer E, Schwecke T, Liempt H van, Döhren H von, Wolfe S & Zhang J (1993) δ-(L-α-Aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase, the multienzyme integrating the four primary rections in β-lactam biosynthesis, as a model peptide synthetase. Biotechnology 11: 807–810
Aharonowitz Y, Cohen G & Martín JF (1992) Penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthetic genes: structure, organization, regulation and evolution. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 46: 461–496
Alvarez E, Cantoral JM, Barredo JL, Díez B & Martín JF (1987) Purification to homogeneity and characterization of the acyl-CoA:6-APA acyltransferase of Penicillium chrysogenum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 31: 1675–1682
Alvarez E, Meeschaert B, Montenegro E, Gutiérrez S, Díez B, Barredo JL & Martín JF (1993) The isopenicillin N acyltransferase of Penicillium chrysogenum has isopenicillin N amidohydrolase, 6-aminopenicillanic acid acyltransferase and penicillin amidase activities, all of which are encoded by the single penDE gene. Eur. J. Biochem. 215: 323–332
Aplin RT, Baldwin JE, Cole SCJ, Sutherland JD & Tobin MB (1993a) On the production of α,β-heterodimeric acyl-coenzyme A:isopenicillin N acyltransferase of Pencillium chrysogenum: studies using a recombinant source. FEBS Lett. 319: 166–170
Aplin RT, Baldwin JE, Cole SCJ, Sutherland JD & Tobin MB (1993b) Investigations into the post-translational modification and mechanisms of isopenicillin N:acyl-CoA acyltransferase using electrospray mass spectrometry. Biochem. J. 294: 357–363
Arnstein HRV & Morris D (1960) The structure of a peptide containing α-aminoadipic acid, cysteine, and valine, present in the mycelium of Penicillium chrysogenum. Biochem. J. 76: 357–361
Arst HN Jr & MacDonals DW (1975) A gene cluster in Aspergillus nidulans with an internally located cis-acting regulatory region. Nature 254: 26–31
Bailey C & Arst Jr HN (1975) Carbon catabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Eur. J. Biochem. 51: 573–577
Baldwin JE & Abraham EP (1988) The biosynthesis of penicillins and cephalosporins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 5: 129–145
Baldwin JE, Adlington RM, Coates B, Crabee MJC, Crouch NP, Keeping JW, Knight GC, Schofield CJ, Ting H-H, Vallejo CA, Thorniley M & Abraham EP (1987) Purification and initial characterization of an enzyme with deacetoxycephalosporin C synthetase and hydroxylase activities. Biochem. J. 245: 831–841
Banko G, Demain AL & Wolfe S (1987) δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl-L-cysteinyl-D-valine: a multifunctional enzyme with broad substrate specificity for synthesis of penicillin and cephalosporin precursors. J. Am Chem. Soc. 109: 2858–2860
Barredo JL, Alvarez E, Cantoral JM, Díez B & Martín JF (1988) Glucokinase-deficient mutant of Penicillium chrysogenum is derepressed in glucose catabolite regulation of both β-galactosidase and penicillin biosynthesis. Antimicrob. Agent Chemother. 32: 1061–1067
Behmer CJ & Demain AL (1983) Further studies on carbon catabolite regulation of β-lactam antibiotic synthesis in Cephalosporium acremonium. Curr. Microbiol. 8: 107–114
Borovok I, Landman O, Kreisberg-Zakarin R, Aharonowtiz Y & Cohen G (1996) Ferrous active site of isopenicillin N synthase: genetic and sequence analysis of the endogenous ligands. Biochemistry 35: 1981–1987
Brakhage AA (1998a) Molecular regulation of penicillin biosynthesis in Aspergillus (Emericella) nidulans. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 148: 1–10
Brakhage AA (1998b) Molecular regulation of β-lactam biosynthesis in filamentous fungi. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62: 547–585
Brakhage AA & Turner G (1995) Biotechnical genetics of antibiotics biosynthesis. In: Kück U (Ed) The Mycota II. Genetics and Biotechnology (pp 263–285). Springer-Verlag KG, Berlin, Germany
Brakhage AA, Browne P & Turner G (1992) Regulation of Aspergillus nidulans penicillin biosynthesis and penicillin biosynthesis gene acvA and ipnA by glucose. J. Bacteriol. 174: 3789–3799
Caddick MX, Brownlee AG & Arst HN Jr (1986) Regulation of gene expression by pH of the growth medium in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Gen. Genet. 203: 346–353
Cortés J, Martín JF, Castro JM, Láiz L & Liras P. (1987) Purification and characterization of a 2-oxoglutarate linked ATP-independent deacetoxycephalosporin C synthase of S. lactamdurans. J. Gen. Microbiol. 133: 3165–3174
Chater K & Bibb M (1997) Regulation of bacterial antibiotic production. In: Rehm H-J, Reed G (Ed) Biotechnology (pp 57–105). VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Germany
Chu Y-W, Renno D & Saunders G (1995) Detection of a protein which binds specifically to the upstream region of the pcbAB gene in Penicillium chrysogenum. Curr. Genet. 27: 184–189
Chu Y-W, Renno D & Saunders G (1997) Extracellular pH affects regulation of the pcbAB gene in Penicillium chrysogenum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 47(3): 250–254
Davies J (1990) What are antibiotics? Archaic functions for modern activities. Mol. Microbiol. 4: 1227–1232
Demain AL (1980) Do antibiotics function in nature? Search 11: 148
Demain AL (1963) Synthesis of cephalosporin C by resting cells of Cephalosporium sp. Clin. Med. 70: 2045–2051
Demain AL (1983) Biosynthesis of β-lactam antibiotics. In Demain AL, Solomon NA (Ed) Antibiotics Containing the β-lactam structure. Springer Verlag, New York
Demain AL, Kennel YM & Aharonowitz Y (1979) Carbon catabolite regulation of secondary metabolism. In: Bull AT, Ellwood DC, Ratledge C (Ed) Microbial Technology: Current State, Future Prospects. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Dotzlaf JE & Yeh W-K (1987) Copurification and characterization of deacetoxycephalosporin C synthetase/hydroxylase from Cephalosporium acremonium. J. Bacteriol. 169: 1611–1618
Dowzer CEA & Kelly JM (1991) Analysis of the creA gene, a regulator of carbon catabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11: 5701–5709
Espeso EA & Peñalva MA (1992) Carbon catabolite repression can account for temporal pattern of expression of a penicillin biosynthetic gene in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 6: 1457–1465
Espeso EA, Fernández-Cañón JM & Peñalva MA (1995) Carbon regulation of penicillin biosynthesis in Aspergillus nidulans: A minor effect of mutations in creB and creC. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 126: 63–68
Espeso EA, Tilburn J, Arst HN Jr & Peñalva MA (1993) pH regulation is a major determinant in expression of a fungal penicillin biosynthetic gene. EMBO J. 12: 3947–3956
Feng B, Friedlin E & Marzluf GA (1994) A reporter gene analysis of penicillin biosynthesis gene expression in Penicillium chrysogenum and its regulation by nitrogen and glucose catabolite repression. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 60: 4432–4439
Feng B, Friedlin E & Marzluf GA (1995) Nuclear DNA-binding proteins which recognize the intergenic control region of penicillin biosynthetic genes. Curr. Genet. 27: 351–358
Fierro F, Barredo JL, Díez B, Gutiérrez S, Fernández FJ & Martín JF (1995) The penicillin gene cluster is amplified in tandem repeats linked by conserved hexanucleotide sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 6200–6204
Fierro F, Gutiérrez S, Díez B & Martín JF (1993) Resolution of four chromosomes in penicillin-producing filamentous fungi: the penicillin gene cluster is located on chromosome II (9.6 Mb) in Penicillium notatum and chromosome I (10.4 Mb) in Penicillium chrysogenum. Mol. Gen. Genet. 241: 573–578
Fujisawa Y, Shirafuji H, Kida M, Nara K, Yoneda M & Kanzaki T (1973) New findings on cephalosporin C biosynthesis. Nature New Biol. 246: 154–155
Fujisawa Y, Shirafuji H, Kida M, Nara K, Yoneda M & Kanzaki T (1975) Accumulation of deacetylcephalosporin C by cephalosporin C negative mutants of Cephalosporium acremonium. Agric. Biol. Chem. 39: 1295–1301
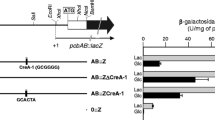
Gutiérrez S, Marcos AT, Casqueiro J, Kosalková K, Fernández FJ, Velasco J & Martín JF (1999) Transcription of the pcbAB, pcbC and penDE genes of Penicillium chrysogenum AS-P-78 is strongly repressed by glucose and the repression is not reversed by alkaline pHs. Microbiology 145: 317–324
Gutiérrez S, Velasco J, Fernández FJ & Martín JF (1992) The cefG gene of Cephalosporium acremonium is linked to the cefEF gene and encodes a deacetylcephalosporin C acetyltransferase closely related to homoserine O-acetyltransferase. J. Bacteriol. 174: 3056–3064
Haas H, Redl B, Friedlin E & Stöffler G (1992) Isolation and analysis of the Penicillium chrysogenum phoA gene encoding a secreted phosphate-repressible acid phosphatase. Gene 113: 129–133
Hollander IJ, Shen YQ, Heim J, Demain AL & Wolfe S (1984) Pure enzyme catalyzing penicillin biosynthesis. Science 224: 610–612
Hönlinger C & Kubicek CP (1989) Regulation of δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine and isopenicillin N biosynthesis in Penicillium chrysogenum by the α-aminoadipate pool size. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 65: 71–76
Hopwood DA (1988) Towards an understanding of gene switching in Streptomyces, the basis of sporulation and antibiotic production. Proc. Royal Society London B 235, 121–138
Jayatilake GS, Huddleston JA & Abraham EP (1981) Conversion of isopenicillin N into penicillin N in cell-free extracts of Cephalosporium acremonium. Biochem. J. 194: 645–648
Jensen SE (1986) Biosynthesis of cephalosporins. CRC Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 3: 277–310
Jensen SE, Westlake DWS & Wolfe S (1985) Deacetoxycephalosporin C synthetase and deacetoxycephalosporin C hydroxylase are two separate enzymes in Streptomyces clavuligerus. J. Antibiot. 38: 263–265
Jensen SE, Westlake DWS & Wolfe S (1982 ) Cyclization of δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine to penicillins by cell-free extracts of Streptomyces clavuligerus. J. Antibiot. 35: 483–490
Jensen SE, Westlake DWS & Wolfe S (1988) Production of the penicillin precursor δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine (ACV) by cell-free extracts from Streptomyces clavuligerus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 49: 213–218
Kennedy J & Turner G (1996) Delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase is a rate limiting enzyme for penicillin production in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Gen. Genet. 253: 189–197
Kleinkauf H & von Döhren H (1990) Non-ribosomal biosynthesis of peptide antibiotics. Eur. J. Biochem. 192: 1–15
Kolar M, Holzmann K, Weber G, Leitner E & Schwab H (1991) Molecular characterization and functional analysis in Aspergillus nidulans of the 5′-region of the Penicillium chrysogenum isopenicillin N synthetase gene. J. Biotechnol. 17: 67–80
Kozma J, Bartok G & Szentirmai A (1993) Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate level and β-lactam formation in Penicillium chrysogenum. Int. J. Basic Microbiol. 33: 27–34
Kulmburg P, Mathieu M, Dowzer C, Kelly J & Felenbok B (1993) Specific binding sites in the alcR and alcA promoters of the ethanol regulon for the CREA repressor mediating carbon catabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 7: 847–857
Kupka J, Shen YQ, Wolfe S & Demain AL (1983) Partial purification and properties of the α-ketoglutarate-linked ring-expansion enzyme of β-lactam biosynthesis of Cephalosporium acremonium. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 16: 1–6
Laich F, Fierro F, Cardoza RE & Martín JF (1999) Organization of the gene cluster for biosynthesis of penicillin in Penicillium nalgiovense and antibiotic production in cured dry sausages. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 65 (in press)
Landman O, Borovok I, Aharonowtiz Y & Cohen G (1997) The glutamine ligand in the ferrous iron active site of isopenicillin N synthase of Streptomyces jumonjinensis is not essential for catalysis. FEBS Lett. 405: 172–174
Litzka O, Then Bergh K & Brakhage AA (1995) The Aspergillus nidulans penicillin biosynthesis gene aat (penDE) is controlled by a CCAAT containing DNA element. Eur. J. Biochem. 238: 675–682
Luengo JM (1995) Enzymatic synthesis of hydrophobic penicillins. J. Antibiot. 48: 1195–1212
Marahiel MA, Stachelhaus T & Mootz HD (1997) Modular peptide synthetases involved in nonribosomal peptide synthesis. Chem. Rev. 97: 2651–2673
Martín JF (1998) New aspects of genes and enzymes for β-lactam antibiotic biosynthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 50: 1–15
Martín JF & Aharonowitz Y (1983) Regulation of biosynthesis of β-lactam antibiotics. In: Demain AL, Solomon NA (Ed) Antibiotics Containing the β-Lactam Structure (pp 189–228). Springer, New York
Martín JF & Demain AL (1980) Control of antibiotic synthesis. Microbiol. Rev. 44: 230–251
Martín JF & Gutiérrez S (1995) Genes for β-lactam antibiotic biosynthesis. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 67: 181–200
Martín JF & Liras P (1989) Enzymes involved in penicillin, cephalosporin and cephamycin biosynthesis. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 39: 153–187
Martín JF, Coque JJR, Gutiérrez S, Barredo JL, Díez B, Montenegro E, Calzada JG & Liras P (1991) Clusters of genes involved in penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthesis. In: Kleinkauf H, von Döhren H (Ed) Fifty Years of Penicillin Application — History and Trends. Akademia Czechoslovakia, Praga
Martín JF, Díez B, Alvarez E, Barredo JL & Cantoral JM (1987) Development of a transformation system in Penicillium chrysogenum: cloning of genes involved in penicillin biosynthesis. In: Alacevic M, Hranueli D, Toman Z (Ed) Genetics of Industrial Microorganisms (pp 297–308). Pliva, Zagreb
Martín JF, Gutiérrez S & Demain AL (1997) β-Lactams. In: Anke T (Ed) Fungal Biotechnology (pp 91–127). Chapman & Hall, Weinheim
Martín JF, Kosalková K, Marcos AT, Fierro F, Fernández FJ & Gutiérrez S (1998) Molecular genetics of carbon catabolite regulation of penicillin biosynthesis. 8th International Symposium on the Genetics of Industrial Microorganisms (p 22). Jerusalem, Israel
Matsumara M, Imanaka T, Yoshida T & Taguchi H (1978) Effect of glucose and methionine consumption rates on cephalosporin C production by Cephalosporium acremonium. J. Fement. Technol. 56: 345–353
Menne S, Walz M & Kück U (1994) Expression studies with the bidirectional pcbAB-pcbC promoter region from Acremonium chrysogenum using reporter gene fusions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 42: 57–66
Pang CP, Chakravarti B, Adlington RM, Ting HH, White RL, Jayatilake GS, Baldwin JE & Abraham EP (1984) Purification of isopenicillin N synthetase. Biochem. J. 222: 789–795
Pérez-Esteban B, Orejas M, Gómez-Pardo E & Peñalva MA (1993) Molecular characterization of a fungal secondary metabolism promoter: transcription of the Aspergillus nidulans isopenicillin N synthetase gene is modulated by upstream negative elements. Mol. Microbiol. 9: 881–895
Ramos FR, López-Nieto MJ & Martín JF (1985) Isopenicillin N synthetase of Penicillium chrysogenum, an enzyme that converts δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine to isopenicillin N. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 27: 380–387
Revilla G (1983) Regulación de la biosíntesis de penicilina en Penicillium chrysogenum. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Salamanca, Spain
Revilla G, López-Nieto MJ & Martín JF (1984) Carbon catabolite repression of penicillin biosynthesis by Penicillium chrysogenum. J. Antibiot. 37: 781–789
Revilla G, Ramos FR, López-Nieto MJ, Alvarez E & Martín JF (1986) Glucose represses formation of δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine and isopenicillin N synthase but not penicillin acyltransferase in Penicillium chrysogenum. J. Bacteriol. 168: 947–952
Roach PL, Clifton JC, Fülöp V, Harlos K, Barton GJ, Hajdu J, Andersson I, Schofield CJ & Baldwin JE (1995) Crystal structure of isopenicillin N synthase is the first from a new structural family of enzymes. Nature 375: 700–704
Scheidegger A, Kuenzi MT & Nüesch J (1984) Partial purification and catalytic properties of a bifunctional enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway of beta-lactams in Cephalosporium acremonium. J. Antibiot. 37: 522–531
Schwecke T, Aharonowitz Y, Palissa H, Döhren H von, Kleinkauf H, Liempt H van (1992) Enzymatic characterization of the multifunctional enzyme δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Eur. J. Biochem. 205: 687–694
Shah AJ, Tilburn J, Adlard MW & Arst Jr HN (1991) pH regulation of penicillin production in Aspergillus nidulans. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 77: 209–212
Soltero FV & Johnson MJ (1952) The effect of the carbohydrate nutrition on penicillin production by Penicillium chrysogenum Q-176. Appl. Microbiol. 1: 52–57
Suárez T & Peñalva MA (1996) Characterisation of a Penicillium chrysogenum gene encoding a PacC transcription factor and its binding sites in the divergent pcbAB-pcbC promoter of the penicillin biosynthetic cluster. Mol. Microbiol. 20: 529–540
Tilburn J, Sarkar S, Widdick DA, Espeso EA, Orejas M, Mungroo J, Peñalva MA & Arst Jr HN (1995) The Aspergillus PacC zinc finger transcription factor mediates regulation of both acidic-and alkaline-expressed genes by ambient pH. EMBO J. 14: 779–790
Van Liempt H, Döhren H von & Kleinkauf H (1989) δ-(L-α-Aminoadipyl)L-cysteinyl-v aline synthetase from Aspergillus nidulans. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 3680–3684
Velasco J, Gutiérrez S, Campoy S & Martín JF (1998) Molecular characterization of the Acremonium chrysogenum cefG gene product: The native deacetylcephalosporin C acetyltransferase is not processed into subunits. Biochem. J. 337: 379–385
Velasco J, Gutiérrez S, Fernández FJ, Marcos AT, Arenós C & Martín JF (1994) Exogenous methionine increases levels of mRNAs transcribed from pcbAB, pcbC, and cefEF genes, encoding enzymes of the cephalosporin biosynthetic pathway, in Acremonium chrysogenum. J. Bacteriol. 176: 985–991
Whiteman PA, Abraham EP, Baldwin FL, Fleming MD, Schofield CJ, Sutherland JD & Willis AC (1990) Acyl-coenzyme A:6-aminoapenicillanic acid acyltransferase from Penicillium chrysogenum and Aspergillus nidulans. FEBS Lett. 262: 342–344
Xiao X, Wolf S & Demain AL (1991) Purification and characterization of cephalosporin 7α-hydroxylase from S. clavuligerus. Biochem. J. 280: 471–474
Zanca DM & Martín JF (1983) Carbon catabolite regulation of the conversion of penicillin N into cephalosporin C. J. Antibiot. 36: 700–708
Zhang J-Y & Demain AL (1989) Phosphate regulation of ACV synthetase and cephalosporin biosynthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 57: 145–150
Zhang J, Wolfe S & Demain AL (1989) Carbon source regulation of the ACV synthetase in Cephalosporium acremonium C-10. Curr. Microbiol. 18: 361–367
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martín, J.F., Casqueiro, J., Kosalková, K. et al. Penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthesis: Mechanism of carbon catabolite regulation of penicillin production. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 75, 21–31 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001820109140
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001820109140