Abstract
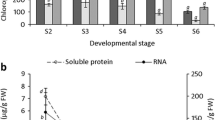
Accumulation of the pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins localised in intercellular spaces of barley primary leaves, chlorophyll content, structure of chloroplasts, and photosynthesis were examined during natural and in vitro induced leaf senescence (cultivation of whole plants in the dark or detached leaves under nutrient deficiency). Some of PR proteins accumulated during natural senescence, but their accumulation pattern was different from those of pathogen-induced as well as during in vitro-induced senescence, which indicate different molecular bases of these processes. Photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll content indicate that natural senescence of barley primary leaves began from 15th day after sowing. In 35-d-old first leaves, the chloroplasts showed typical characteristics of senescence as significant decrease of size, greater grana, and prominent plastoglobuli. The chloroplasts contained more grana under in vitro induced senescence and they had reduced length in the dark. Correspondingly, accumulation of PR proteins was detectable on about the 15th day but the content of some PR proteins increased in later stages of senescence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker, W., Apel, K.: Differences in gene expression between natural and artificially induced leaf senescence.-Planta 189: 74-79, 1993.
Biswal, U.C., Bergfeld, R., Kasemir, H.: Phytochrome mediated delay of plastid senescence in mustard cotyledons: changes in pigment content and ultrastructure.-Planta 157: 85-90, 1983.
Bradford, M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding.-Anal. Biochem. 72: 248-254, 1976.
Buchanan-Wollaston, V.: Isolation of cDNA clones for genes that are expressed during leaf senescence in Brassica napus.-Plant Physiol. 105: 839-846, 1994.
Gan, S., Amasino, R.M.: Making sense of senescence. Molecular genetic regulation and manipulation of leaf senescence.-Plant Physiol. 113: 313-319, 1997.
Gut, H., Matile, P.: Apparent induction of key enzymes of the glyoxylic acid cycle in senescent barley leaves.-Planta 176: 548-550, 1988.
Hanfrey, C., Fife, M., Buchanan-Wollaston, V.: Leaf senescence in Brassica napus: expression of genes encoding pathogenesis-related proteins.-Plant mol. Biol. 30: 597-609, 1996.
Hashimoto, H., Kura-Hoita, M., Katoh, S.: Changes in protein content and in structure and number of chloroplasts during leaf senescence in rice seedlings.-Plant Cell Physiol. 30: 707-715, 1989.
Hensel, L.L., Grbic, V., Baumgarten, D.A., Bleecker, A.B.: Developmental and age-related processes that influence the longevity and senescence of photosynthetic tissues in Arabidopsis.-Plant Cell 5: 553-564, 1993.
Heukesloven, J., Dernick, R.: Simplified method for silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels and the mechanism of silver staining.-Electrophoresis 6: 103-112, 1985.
Hill, C.M., Pearson, S.A., Smith, A.J., Rogers, L.J.: Inhibition of chlorophyll synthesis in Hordeum vulgare by 3-amino 2,3-dihydrobenzoic acid (gabaculin).-BioSci. Rep. 5: 775-781, 1985.
John, I., Hackett, R., Cooper, W., Drake, R., Farrel, A., Grierson, D.: Cloning and characterisation of tomato leaf senescence-related cDNAs.-Plant mol. Biol. 33: 641-651, 1997.
Kamach, K., Yamata, T., Mae, T., Ojima, K.: A role for glutamine synthase in the remobilization of leaf nitrogen during natural senescence in rice leaves.-Plant Physiol. 96: 411-417, 1991.
Kutík, J.: Chloroplast development.-In: Šesták, Z. (ed.): Photosynthesis during Leaf Development. Pp. 51-75. Academia, Praha; Dr. W. Junk Publishers, The Hague 1985.
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4.-Nature 277: 680-685, 1970.
Lohman, K.N., Gan, S., John, M.C., Amasimo, M.: Molecular analysis of natural leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana.-Physiol Plant. 92: 322-328, 1994.
Lotan, T., Ori, N., Fluhr, R.: Pathogenesis-related proteins are developmentally regulated in tobacco flowers.-Plant Cell 1: 881-887, 1989.
Mauch, F., Staehelin, L.A.: Functional implication of the subcellular localisation of ethylene-induced chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase in bean leaves.-Plant Cell 1: 447-457, 1989.
Matile, P., Hörtensteiner, S., Thomas, H., Kräutler, B.: Chlorophyll breakdown in senescent leaves.-Plant Physiol. 112: 1403-1409, 1996.
Rodrígez, M.T., González, M.P., Linares, J.M.: Degradation of chlorophyll and chlorophyllase activity in senescing barley leaves.-J. Plant Physiol. 129: 369-374, 1987.
Rohringer, R., Ebrahim-Nesbat, F., Wolf, G.: Proteins in intercellular washing fluid from leaves of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).-J. exp. Bot. 34: 1589-1605, 1983.
Smart, C.M.: Gene expression during leaf senescence.-New Phytol. 126: 419-448, 1994.
Tamás, L., Huttová, J.: Accumulation of pathogenesis-related proteins in barley induced by phosphate and salicylic acid.-Biológia (Bratislava) 51: 479-484, 1996.
Tamás, L., Huttová, J., Žigová, Z.: Pathogenesis-related proteins in near-isogenic barley lines induced by powdery mildew infection.-Biológia (Bratislava) 52: 99-104, 1997.
Tamás, L., Huttová, J., Žigová, Z.: Accumulation of stress-proteins in intercellular spaces of barley leaves induced by biotic or abiotic factors.-Biol. Plant. 39: 387-394, 1997.
Taylor, C.B., Bariola, P.A., Delcardayre, S.B., Raines, R.T., Green, J.: RNS2 -- a senescence-associated RNAse of Arabidopsis that diverged from the sRNAses before speciation.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 5118-5122, 1993.
Van Loon, L.C.: Pathogenesis-related proteins.-Plant mol. Biol. 4: 111-116, 1985.
Van Loon, L.C., Pierpoint, W.S., Boller, T., Conjero, V.: Recommendations for naming plant pathogenesis-related proteins.-Plant mol. Biol. Rep. 12: 245-264, 1994.
Wrischer, M.: Structural and functional changes in chloroplast of senescent leaves of Sophora japonica L.-Acta bot. croat. 53: 15-19, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamás, L., Čiamporová, M. & Luxová, M. Accumulation of pathogenesis-related proteins in barley leaf intercellular spaces during leaf senescence. Biologia Plantarum 41, 451–460 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001814930794
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001814930794