Abstract
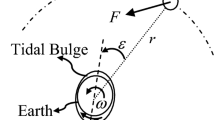
The long period variation of the earth rotation is generally explained by the tidal friction. The tidal friction, however, is not the only source to influence the earth rotation in long term. In this paper, by means of the interaction between the solar wind and the magnetosphere of the earth, the additional magnetic pressure will exist in the magnetic tail due to the crowding and sparseness of the magnetic lines in the consideration of the earth rotation, which could be considered as a source of effecting the long term variation of the earth rotation. It is shown in this paper that this mechanism can produce angular deceleration of the Earth rotation in the magnitude of ω = −1.7 × 10-22 s-2. This result might be a prompt to search for other sources in the secular variation of the rate of the Earth rotation variation further in order to regulate the observed result with the theoretical one.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akasofu, S.-I. and Chapman, S.: 1972, Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Oxford, Clarendon Press.
Behannon, K.W.: 1970, J.Geophys.Res. 75, 743.
Chen, D. and Liu, L.-C.: 1983, Modern Planet Physics, Shanghai Scientific Technique Press 277.
Christodoulidis, D.C., Smith, D.E., Williams, R.G. and Klosko, S.M.: 1988, J.Geophys.Res. 93, 6216.
Coleman, P.J.: 1971, J.Geophys. 76, 3800.
Dicke, R.H.: 1969, J.Geophys.Res. 79, 5895.
Gu, Z. and Paquet, P.: 1993, Earth, Moon, and Planet 62, 34.
Hill, T.W.: 1979, J.Geophys.Res. 84, 6554.
Hines, C.O.: 1959, Proc.Inst.Rad.Engrs. 47, 176.
Hines, C.O.: 1960, J.Geophys.Res. 65, 141.
Hirshberg, J.: 1972, J.Geophys.Res. 77, 4855.
Munk, W.H. and McDonald, G.J.F.: 1960, The Rotation of the Earth, Univ. Press Cambridge.
Newton, R.R.: 1985, Geophys.J.R.Astron.Soc. 80, 313.
Spreiter, J.R. and Alksne, A.Y.: 1969, Planet.Space Sci. 233.
Stephenson, R.F. and Said, S.S.: 1989, Astron.Astrophys. 215, 181.
Volland, H.: 1990, Earth's Rotation from Eons to Days, Berlin, Springer-Verlag, 127.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Z. An Interpretation of the Non-Tidal Secular Variation in the Earth Rotation: the Interaction Between the Solar Wind and the Earth's Magnetosphere. Astrophysics and Space Science 259, 427–432 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001721302305
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001721302305