Abstract
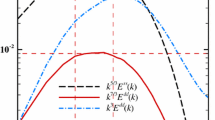
A new method for deriving the Lagrangian decorrelation time scales for inhomogeneous turbulence is described. The expression for the time scales here derived for the convective boundary layer is compared to those estimated by Hanna during the Phoenix experiment. Then the values of C0, the Lagrangian velocity structure function constant, and of Bi, the Lagrangian velocity spectrum constant, were evaluated from the Eulerian velocity spectra and from the Lagrangian time scales derived, under unstable conditions, from Taylor's statistical diffusion theory. The numerical coefficient of the lateral and vertical Lagrangian spectra in the inertial subrange was found equal to 0.21, in good agreement with previous experimental estimates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand, M. S. and Pope, S. B.: 1985, in L. J. S. Bradbury, F. Durst, B. E. Lauder, F. W. Schmidt, and J. H. Whitelaw (eds.), ‘Diffusion Behind a Line Source in a Grid Turbulence’, Turbulent Shear Flows, Vol. 4, SpringerVerlag, Berlin, pp. 46-61.
Angell, J. K.: 1964, ‘Measurements of Lagrangian and Eulerian Properties of Turbulence at a Height of 2500 ft’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 90, 57-71.
Baerentsen, J. H. and Berkowicz, R.: 1984, ‘Monte-Carlo Simulation of Plume Diffusion in the Convective Boundary Layer’, Atmos. Environ. 18, 701-712.
Batchelor G. K.: 1949, ‘Diffusion in a Field of Homogeneous Turbulence, I: Eulerian Analysis’, Aust. J. Sci. Res. 2, 437-450.
Caughey S. J.: 1982, ‘Observed Characteristics of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, in F. T. M. Nieuwstadt and H. van Dop (eds.), Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modelling, Reidel, Dordrecht, pp. 107-158.
Champagne F. H., Friehe J. C., La Rue J. C., and Wyngaard, J. C.: 1977, ‘Flux Measurements, Flux Estimation Techniques, and Fine-Scale Turbulence Measurements in the Unstable Surface Layer over Land’, J. Atmos. Sci. 34, 515-530.
De Baas, H. F., Van Dop, H., and Nieuwstadt F. T. M.: 1986, ‘An Application of the Langevin Equation for Inhomogeneous Conditions to Dispersion in a Convective Boundary Layer’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 112, 165-180.
Degrazia, G. A. and Moraes, O. L. L.: 1992, ‘A Model for Eddy Diffusivity in a Stable Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 58, 205-214.
Degrazia, G. A., Moraes, O. L. L., and Oliveira, A. P.: 1996, ‘An Analytical Method to Evaluate Mixing Length Scales for the Planetary Boundary Layer’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 35, 974-977.
Ferrero, E. and Anfossi, D.: 1997, ‘Sensitivity Analysis of Lagrangian Stochastic Models for CBL with Different PDF's and Turbulence Parameterizations’, in S. E. Gryning and N. Chaumerliac (eds.), Air Pollution Modelling and its Applications XI, Plenum Press, New York, Vol. 22, in press.
Gifford, F. A.: 1984, ‘The Random Force Theory: Application toMeso-and Large-Scale Atmospheric Diffusion’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 30, 159-175.
Hanna, S. R.: 1981, ‘Lagrangian and Eulerian Time-Scale in the Daytime Boundary Layer’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 20, 242-249.
Hinze, J. O.: 1975, Turbulence, Mc Graw Hill, 790 pp.
Hurley, P. and Physick, W. L.: 1991, ‘A Skewed Homogeneous Lagrangian Particle Model for Convective Conditions’, Atmos. Environ. 25A, 1313-1325.
Hurley, P. J. and Physick, W. L.: 1993, ‘A Lagrangian Particle Model of Fumigation by Breakdown of the Nocturnal Inversion’, Atmos. Environ. 27A, 619-642.
Kaimal, J. C., Wyngaard, J.C., Haugen, D. A., Cote', O. R., Izumi, Y., Caughey, S. J., and Readings, C. J.: 1976, ‘Turbulence Structure in the Convective Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 33, 2152-2169.
Luhar, A. K. and Britter, R. E.: 1989, ‘A Random Walk Model for Dispersion in Inhomogeneous Turbulence in a Convective Boundary Layer’, Atmos. Environ. 23, 1191-1924.
Monin, A. S. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1975, Statistical Fluid Mechanics: Mechanics of Turbulence, Vol. 2, MIT Press, 874 pp.
Pasquill F.: 1974, Atmospheric Diffusion, Wiley & Sons, 429 pp.
Pasquill, F. and Smith, F. B.: 1983, Atmospheric Diffusion, Wiley & Sons, 437 pp.
Physick, W. L., Noonan, J. A., McGregor, J. L., Hurley, P. J., Abbs, D. J., and Manins, P. C.: 1994, ‘LADM: A Lagrangian Atmospheric Dispersion Model’, CSIRO Division of Atmospheric Research, Australia, Technical Report No. 24, 137 pp.
Rodean, H. C.: 1991, ‘The Universal Constant for the Lagrangian Structure Function’, Phys. Fluids A3, 1479-1480.
Rodean, H. C.: 1994, ‘Notes on the Langevin Model for Turbulent Diffusion of “Marked” Particles’, UCRL-ID-115869 Report of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 122 pp.
Rotach, M. W., Gryning, S. E., and Tassone, C.: 1996, ‘A TwoDimensional Lagrangian Stochastic Dispersion Model for Daytime Conditions’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 122, 367-389.
Sawford, B. L.: 1991, ‘Reynolds Number Effects in Lagrangian Stochastic Models of Turbulent Dispersion’, Phys. Fluids A3, 1577-1566.
Sawford, B. L.: 1993, ‘Recent Developments in the Lagrangian Stochastic Theory of Turbulent Dispersion’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 62, 197-215.
Sawford, B. L. and Guest, F. M.: 1988, ‘Uniqueness and Universality of Lagrangian Stochastic Models of Turbulent Dispersion’, in 8th Symposium on Turbulence and Diffusion, San Diego, CA, A.M.S., pp. 96-99.
Sawford, B. L. and Tivendale, C.M.: 1992, ‘Measurements of Concentrations Statistics Downstream of a Line Source in Grid Turbulence’, in Proc. 11th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, University of Tasmania, pp. 945-948.
Sawford, B. L. and Borgas, M. S.: 1994, ‘On the Continuity of Stochastic Models for the Lagrangian Velocity in Turbulence’, Physica D 76, 297-311.
Sorbjan, Z.: 1989, Structure of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Prentice Hall, NJ, 317 pp.
Tassone, C., Gryning, S. E., and Rotach, M.: 1994, ‘A Random Walk Model for Atmospheric Dispersion in The Daytime Boundary Layer’, in S. E. Gryning and Millan M. Millan (eds.), Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application X, Plenum Press, pp. 243-251.
Tennekes, H.: 1982, ‘Similarity Relations, Scaling Laws and Spectral Dynamics’, in F. T. M. Nieuwstadt and H. van Dop (eds.), Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modelling, Reidel, Dordrecht, pp. 37-68.
Thomson, D. J.: 1987, ‘Criteria for the Selection of Stochastic Models of Particle Trajectories in Turbulent Flows’, J. Fluid Mech. 180, 529-556.
Wandel, C. F. and Kofoed-Hansen, O.: 1962, ‘On the Eulerian-Lagrangian Transform in the Statistical Theory of Turbulence’, J. Geophys. Res. 76, 3089-3093.
Weil, J. C.: 1989, ‘Stochastic Modeling of Dispersion in the Convective Boundary Layer’, in H. van Dop (ed.), Air Pollution Modelling and its Applications VII, Plenum Press, 620 pp.
Weil, J. C.: 1990, ‘A Diagnosis of the Asymmetry in Top-Down and Bottom-Up Diffusion Using a Lagrangian Stochastic Model’, J. Atmos. Sci. 47, 501-515.
Willis, G. E. and Deardorff, J.: 1976, ‘A Laboratory Model of Diffusion into the Convective Planetary Boundary Layer’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 102, 427-445.
Willis, G. E. and Deardorff, J.: 1978, ‘A Laboratory Study of Dispersion from an Elevated Source Within a Modeled Convective Planetary Boundary Layer’, Atmos. Environ. 12, 1305-1311.
Willis, G. E. and Deardorff, J.: 1981, ‘A Laboratory Study of Dispersion from a Source in the Middle of the Convective Mixed Boundary Layer’, Atmos. Environ. 15, 109-117.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Degrazia, G., Anfossi, D., De Campos Velho, H.F. et al. A Lagrangian Decorrelation Time Scale in the Convective Boundary Layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 86, 525–534 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000734626931
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000734626931