Abstract
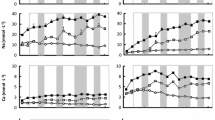
Concentrations of major ions, total phosphorus, dissolved organic carbon, biological oxygen demand and chlorophyll-a of epilithic algae were determined weekly at nine sites in a Japanese stream receiving effluent from a groundwater treatment plant. The concentrations of four major cations (Na, K, Ca and Mg) and chloride ion increased significantly immediately at downstream sites of the effluent outfall. The ionic concentrations decreased with increasing dilution from merging tributaries but never reached the original concentrations and relative composition of stream water within a 10.7 km stream distance from the outfall. The changes in total ionic concentration and relative ionic proportion also changed the chlorophyll-a content of epilithic algae. The results also showed significantly higher chlorophyll-a content in epilithic algae under moderate salinity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, B. G., 1948. The apparent threshold of toxicity of Daphnia magna for chlorides of various metals when added to Lake Erie Water. Trans. am. Fish Soc. 78: 96–113.
Allison, G. B., P. G. Cook, S. R. Barnet, G. R. Walker, I. D. Jolly & M. W. Hughes, 1990. Land clearance and river salinization in the western Murray Basin. Aust. J. Hydrol. 1191/4:120.
APHA, 1989. Standard Methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 17th edn. American Public Health Association.
Arunin, S., P. Rungsangchan, C. Dissataporn & A. Yuvaniyama, 1988. Impact of reservoirs on salinization in northeast Thailand (in Thai). J. Ari. Sci. (Thailand) 21: 331–345.
Azimi Zoonooz, A. & C. J. Duffy, 1993. Modeling transport of subsurface salinity from a Mancos Shale hill slope. Ground Water. 31: 972–981.
Barmuta, L. A., R. Marchant & P. S. Lake, 1992. Degradation of Australian Streams and progress towards conservation and management in Victoria. In Boon, P. J., P. Calow & G. E. Petts (eds), River Conservation and Management. Wiley: 65-79
Bernstein, L., 1961. Osmotic adjustment of plants to saline media II. Dynamic Phase. Ibid. 50: 360-370.
Berry, J. A. & W. J. S. Dowton, 1982. Environmental Regulations of Photosynthesis. In Govinjee (ed.), Photosynthesis Vol. II, Development, Carbon Metabolism and Plant Productivity: 263-343.
Biswas, A. K., 1992. Sustainable water development: A. global perspective. Wat. Int. 17(2): 68–80.
Blinn, D. W., M. Hurley & L. Brokaw, 1981. The effects of saline seeps and the restricted light upon the seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton communities within a southwestern (U.S.A.) desert Canyon Stream. Arch. Hydrobiol. 92: 287–305.
Bierhuizen, J. F. H. & E. E. Prepas, 1985. Relationship between nutrients, dominant ions and phytoplankton standing crop in prairie saline lakes. Can. J. aquat. Sci. 42: 1588–1596.
Brock, M. A., 1985. Are Australian salt lake ecosystems different? Evidence from the submerged aquatic plant communities. Proc. ecol. Soc. Aust. 14: 43–50.
Calow, P., P. Armitage, P. Boon, P. Chave, E. Cox, A. Hildrew, M. Learer, L. Maltby, G. Morris, J. Seager & B. Whitton, 1990. River water quality. Ecological Issues No. 1. British Ecological Society, London.
Clark, R. M., 1974. A summary of toxicity information for major ef-fluent components from inorganic chemical industries. Fisheries and Marine Service, Technical Report No. CEN / T-74-9.
Clarke, R., 1991. Water: The International Crisis. London: Earths-can Publications Ltd: 193 pp.
Collet, K. O., 1978. The present salinity position in the river Murray Basin. Proc. r. Soc. Vict. 90: 826–835.
Crowther, R. A. & H. B. N. Hynes, 1977. The Effects of road deicing salt on the drift of stream benthos. Envir. Pollut. 14: 133–126.
Dickman, M. D. & M. B. Gochnauer, 1978. Impact of NaCl on the microbiota of a small stream. Envir. Pollut. 17: 109–126.
Du Plessis H. M. & M. Van Veelen, 1991. Water Quality: salinization and eutrophication time series tends in South Africa. South. Afri. J. Sci. 87: 1–16.
El-Ashry, M. T., J. Van Schilfgarde & S. Schiffman, 1985. Salinity Pollution from irrigated Agriculture. J. Soil Wat. Conserv. 40: 48–52.
El-Ashry, M. T. & D.C. Gibbsons, 1990. Adverse impacts and alternatives to large dams and interbasin transfers in the Colorado River Baisn, U.S.A. In The impacts of large water projects on the Environment, Paris: UNESCO 137–144.
Forbes, A. T. & B. R. Allanson, 1970. Ecology of Sunday River. Part 1. Water Chemistry. Hydrobiologia 36: 479–488.
Frank, E., 1962. Vergleichende Untersuchungen zum Calcium-, Kalium-, und Phos-phathaushalt von Grunalgen. Flora 152: 157–167.
Ghassemi, F., A. J. Jakeman & H. A. Nix, 1995. Salinisation of Land and Water Resources: Human Causes, Extent, Management & Case Studies. CAB International: 526 pp.
Greeff, G. J., 1994. Ground water contribution to stream salinity in a shale catchment, R.S.A. Ground Water 32: 63–70.
Gregory, L., 1974. The effects of effluent components from Chlor-Alkali Plants on aquatic organisms: A Literature Review. Fisheries Research Board of Canada. Technical Report No. 25.
Hans, R. E., L., Zelanzy & R. E. Balser, 1970. Effects of deicing salts on water quality and biota. Highways Research National Academy of Science-National Engineering Washington D.C. Rep. 91.
Hart, B. T., P. Bailey, R. Edwards, K. Hortle, K. James, A. Mc-Mohan, C. Meredith & K. Swadling, 1990. Effects of salinity on river, stream and wetland ecosystems in Victoria, Australia. Wat. Res. 42: 1103–1117.
Hart, B. T., P. Bailey, R. Edwards, K. Hortle, K. James, A. Mc-Mohan, C. Meredith & K. Swadling, 1991. A review of the salt sensitivity of the Australian freshwater biota. Hydrobiologia 210: 105–144.
Hedlund, J. D., 1988. Wellton-Mohawk farmers deliver water conservation. J. Soil Wat. Conserv. 43: 462–464.
Horward, K. W. F. & J. Haynes, 1993. Groundwater contamination due to road de-icing chemicals: salt balance implications. Geosci. Can. 20: 1–8.
Jolly, I. D., 1989. Investigation into the potential for increased stream salinisation in the Darling Basin, Glen Osmond, South Australia. Center for Research in Groundwater Processes, Report No. 10: 103 pp.
Jacobsen, T., 1982. Salinity and irrigation agriculture in antiquity, Diyala Basin archaeological projects: report on essential results 1957-58. Bibliothica Mesopotamica. Malibu, California: Undena Publications. v.14: 107 pp.
Judd, J. H., 1970. Lake stratification caused by runoff from street deicing. Wat. Res. 4: 521–532.
Longstreth, D. J. & P. S. Nobel, 1979. Salinity effects of leaf anatomy consequences for photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 63: 700–703.
Kirchner, J. & F. Walraven, 1993. Use of strontium isotopes to establish the influence of ground water on the salinization of the Breede River. In Africa Needs ground Water. An International GroundWater Convention. Johannesburg University of the Witwatersrand. Convention Papers v.2: 11 pp.
Krairapanond, N., A. Krairapanond, D. Sinthuwanich & T. Junper, 1992. Environmental impact of rock salt mining operations on land and water resources of northeast Thailand. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Strategies for Utilizing Salt Affected Lands. Bangkok, 17-25 February 1992. Bangkok. Department of Land Development, Minister of Agriculture and Cooperatives: 309–322.
Marcus, B. A., S. H. Forest & B. Shero, 1984. Establishment of freshwater biota in an inland stream following reduction of salt input. Can. Field Natur. 98: 198–208.
Marker, A. F. H., C. A. Crowther & R. J. M. Gunn, 1980. Methanol and acetone as solvents for estimating chlorophyll-a and phaeopigments by spectrophotometry. Arch. Hydrobiol. (Suppl.) 14: 52–69.
Maucha, R., 1932. Hydrochemische Methoden in der Limnologie. Binnengewasser. 12: 173 pp.
Meybeck, M., 1985. The GEMS/Water Program 1978-1983. Wat. Qual. Bull. 10: 167–173.
Meybeck, M., D. V. Chapman & R. Helmer (eds), 1989. Global Freshwater Quality: A First Assessment. Oxford: Blackwell Reference. (Published on behalf of the World Health Organization and the United Nations Environmental Programme): 360 pp.
Morton, R. & R. B. Cunningham, 1985. Longitudinal profiles of trends in salinity in the River Murray. Aust. J. Soil Res. 23: 1–13.
Peck, A. J., J. F. Thomas & D. R. Williamson, 1983. Effects of man on salinity in Australia. Water 2000, Consultants Report No. 8. Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra.
Pieterse, T., 1989. Salt pollution of mine dumps monitored. South Africa Water Bulletin 15: 4–7.
Potts, W. T. W., 1954. The energetic of osmotic regulation in brackish and fresh water animals. J. exp. Biol. 31: 618–630.
Pressey, B., 1990. Wetlands. In Mackay, N. & D. Eastburn (eds), The Murray, Canberra: Murray-Darling Basin Commission: 167–181.
Rao, K. V. G. K., P. S. Kumbhare, S. K. Kamra & R. J. Oosterbaan, 1990. Reclamation of waterlogged saline aluvial soils in India by subsurface drainage. In, proceedings of the symposium on land drainage for salinity control in arid and semi-arid regions. Cairo, 25 February-2 March, 1990, Cairo Drainage Research Institute v2: 17-25.
Sandhu, G. R. & R. H. Qureshi, 1986. Salt affected soils in Pakistan and their utilization. Reclamation and Revegetation Research 5: 105–113.
Selby, J., 1981. The salty problem for the River Murray. New Sci. 90: 442–408.
Shaw, J., 1963. Kinetic aspects of ion regulation in aquatic animals. In MaCarthy, J. D. & C. L. Duddinton (eds), View Points in Biology 2. Butterworths, London: 163–201.
Silva, E. I. L & R. W. Davies, 1997. The effects of irrigation effluent on a Western Canadian prairie river. Hydrobiologia 344: 103–109.
Silva, E. I. L & R. W. Davies, 1999. The effects of simulated irrigation induced changes in salinity on metabolism of lotic biota. Hydrobiologia 416: 193–202.
Smith, D. I. & B. Findlayson, 1988. Water in Australia: its role on environment degradation. In Heathcote, R. L & J. A. Mabbutt (eds), Land, Water and People. Geographical Essays in Australian Resource Management. Allen and Unwin, Sydney: 7–48.
Smith, S. E. & H. M. Al-Rawahy, 1990. The Blue Nile: Potential for conflict and alternatives for meeting future demands. Wat. Int. 15: 217–222.
Sutcliffe, D. W., 1967. Re-examination of observation on the distribution of Gammarus duebeni in relation to salt content in freshwater. J. anim. Ecol. 36: 579–597.
Thompson, B., 1974. The effects of effluents from the Canadian textile industry on aquatic organisms. A literature review. Fish. mar. Services Tech. Rep. 49.
Valles, V., M. Gholami & R. Lambert, 1990. Soil alkalinization and salinization in the Djajerud Basin, Iran. Iran Land Drainage and Reclamation 2: 43–55.
Wilcox, L. V., 1962. Salinity caused by irrigation. J. am.Wat.Works Assoc. 54: 217–222.
Wetzel, R. G. & D. L. McGregor, 1968. Axenic culture and nutritional studies of aquatic macrophytes. Am. Midl. Nat. 80: 52–64.
Williams, W. D., 1987. Salinity of rivers and streams. An important environmental hazard. Ambio 16: 180–185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, E.I.L., Shimizu, A. & Matsunami, H. Salt pollution in a Japanese stream and its effects on water chemistry and epilithic algal chlorophyll-a. Hydrobiologia 437, 139–148 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026598723329
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026598723329