Abstract
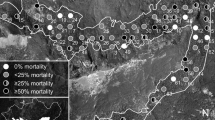
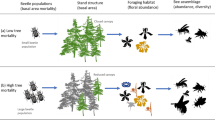
To maintain biodiversity in forests more wind-felled trees must be left. However, there is concern among forest owners that this may result in higher tree mortality caused by the spruce bark beetle (SBB). Data from six studies on number of trees killed by the SBB in storm-disturbed stands was analysed. The studies include 16 areas, 2–346 ha in size, where wind-felled spruce trees were left. In one of the studies also stands where all wind-felled trees were removed directly after the storm were included. Few trees were killed in the first summer following the storm disturbance. In most stands the tree mortality peaked already in the second or third summer following the storm. But in five of the stands tree mortality peaked later. The number of trees killed per ha by the SBB varies much between the studied stands. There was a trend that the larger areas experienced on average higher tree mortality per ha than the smaller areas. One of the studies, including six stands, demonstrated an almost perfect correlation between the number of colonised wind-felled trees and the number of killed trees in a 4-year period following the storm disturbance. In the same study the removal of wind-felled trees resulted in a 50% reduction in number of trees killed per ha in the 4-years following the storm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderbrant, O. (1990) Gallery construction and oviposition of the bark beetle Ips typographus (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) at different breeding densities. Ecologic. Entomol. 15, 1–8.
Anderbrant, O., Schlyter, F. and Birgersson, G. (1985) Intraspecific competition affecting parents and offspring in the bark beetle Ips typographus. Oikos 45, 89–98.
Becker, T. and Schröter, H. (2001) Die Ausbreitung des Borkenkäferbefalls im Bereich von Sturmwurf-Sukzessions-flächen. Berichte Freiburger Forstliche Forschung 26, 79 pp.
Bombosch, S. (1954) Zur Epidemiologie des Buchdruckers (Ips typographus L.). In: G. Wellenstein (ed.), Die Grosse Borkenkäferkalamität in Südwestdeutschland 1944–1951, pp. 239–83. Ringingen, Ebner, Ulm: Forstschutzstelle Südwest.
Botterweg, P.F. (1983) The effect of attack density on size, fat content and emergence of the spruce bark beetle Ips typographus L. Zeitschrift für angewandte Entomologie 96, 47–55.
Butovitsch, V. (1971) Undersökningar över skadeinsekternas uppträdande i de stormhärjade skogarna i mellersta Norrlands kustland åren 1967–69. Department of Forest Zoology, Research Notes, Vol. 8, 204 pp (in Swedish with German summary).
Christiansen, E. (1985) Ips/Ceratocystis-infection of Norway spruce: What is a deadly dosage? Zeitschrift für angewandte Entomologie 99, 6–11.
Christiansen, E. and Bakke, A. (1988) The spruce bark beetle of Eurasia. In. A. A. Berrymann (ed.), Dynamics of Forest Insect Populations, pp. 479–503. New York: Plenum.
Christiansen, E., Waring, R.H. and Berrymann, A.A. (1987) Resistance of conifers to bark Beetle attack: Searching for general relationships. Forest Ecol. Manag. 22, 89–106.
Forsse, E. and Solbreck, Ch. (1985) Migration in the bark beetle Ips typographus L.: Duration, timing and height of flight. Zeitschrift für angewandte Entomologie 100, 47–57.
Forster, B. (1998) Storm damages and bark beetle management: How to set priorities. Methodology of forest insect and disease survey in central Europe. In Proc. IUFRO WP 7.03.10 Workshop, pp. 161–5. Ustron'-Jaszowiec, Poland.
Furuta, K. (1989) A comparison of endemic and epidemic populations of the spruce beetle (Ips typographus japonicus Niijima) in Hokkaido. J. Appl. Entomol. 107, 289–95.
Göthlin, E., Schroeder, L.M. and Lindelöw, Å. (2000) Attacks by Ips typographus and Pityogenes chalcographus on windthrown spruces (Picea abies) during two years following a storm felling. Scand. J. For. Res. 15, 542–9.
Inouye, M. (1963) Details of bark beetle control in the stormswept areas in the natural forest of Hokkaido, Japan. Zeitschrift für angewandte Entomologie 51, 160–4.
Lekander, B. (1955) Skadeinsekternas uppträdande i de av januaristormen 1954 drabbade skogarna. Meddelande från Statens Skogsforskningsinstitut, Vol. 45, 35 pp. (in Swedish with German summary).
Lekander, B. (1972) A mass outbreak of Ips typographus in Gästrikland, Central Sweden, in 1945–1952. Department of Forest Zoology, Research notes, Vol. 10, 39 pp. Royal College of Forestry, Stockholm. (in Swedish with English summary).
Mulock, P. and Christiansen, E. (1986) The threshold of successful attack by Ips typographus on Picea abies: A field experiment. Forest Ecol. Manag. 14, 125–32.
Niemeyer, H., Ackermann, J. and Watzek, G. (1995) Eine ungestörte Massenvermehrung des Buchdruckers (Ips typographus) im Hochharz. Forst und Holz 50, 239–43.
Ogibin, B.N. (1974) Effect of population density on fertility in Ips typographus L. Soviet J. Ecol. 4, 420–5.
Ravn, H.P. (1985) Expansion of the populations of Ips typographus (L.) (Coleoptera, Scolytidae) and their local dispersal following gale disaster in Denmark. Zeitschrift für angewandte Entomologie 99, 26–33.
Schopf, R. and Köhler,U. (1999) Untersuchungen zur Populationdynamik der Fichtenborkenkäfer im Nationalpark Bayerischer Wald. National park Bayerischer Wald-25 Jahre auf dem Weg zum Naturwald, pp. 89–110. Nationalparkverwaltung Bayerischer Wald, D-Neuschönau.
Schroeder, L.M. and Lindelöw, å. (2002) Attacks on living spruce trees by the bark beetle Ips typographus (Col. Scolytidae) following a storm-felling: A comparison between stands with and without removal of wind-felled trees. Agricult. Forest Entomol. 4, 47–56.
Schwerdtfeger, F. (1955) Pathogenese der Borkenkäfer-Epidemie 1946–1950 in Nordtwestdeutschland. Schriftenreihe der Forstlichen Fakultät der Universitet Göttingen 13/14, 1–135.
Thalenhorst, W. (1958) Grundzüge der Populationdynamik des grossen Fichtenborkenkäfers Ips typographus L. Schriftenreihe der Forstlichen Fakultät der Universitet Göttingen 21, 1–126.
Weslien, J. and Schröter, H. (1996) Naturliche Dynamik des Borkenkäferbefalls nach Windwurf. Allgemeine Forst-Zeitschrift 51, 1052–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schroeder, L. Tree Mortality by the Bark Beetle Ips typographus (L.) in storm-disturbed stands. Integrated Pest Management Reviews 6, 169–175 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025771318285
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025771318285