Abstract
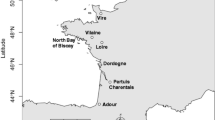
The structure of gastropod communities was examined from January to June 1999 in four sites of the streams of Mont Saint-Michel Bay along a gradient of salinity, and the occurrence of larval trematodes infecting snails was studied. Abundance and species richness of gastropods increased from polyhaline (95 snails, 1 species) to oligohaline waters (6672 snails, 6 species). Whatever the salinity, the most abundant species was Potamopyrgus antipodarum, an invasive non-indigenous species that represented 80% of the gastropods. Only one male was found in P. antipodarum populations suggesting a predominantly parthenogenetic mode of reproduction. Among 7218 gastropods collected, 1.2% were infected by larval trematodes: 5 species in Lymnaea peregra (4.4%), 4 species in Planorbis planorbis (12.0%), one echinostome in Physa acuta (0.2%), and a new species of Sanguinicola in P. antipodarum (0.5%). This is the first record of infected P. antipodarum in Europe. No parasites were found in polyhaline waters. The prevalence per host population varied from 0 to 100% depending on time of collection, salinity and host species. In the lowest-salinity site, abundance of gastropods and prevalence of trematodes were negatively correlated. The dominance of P. antipodarum in the gastropod communities is discussed in relation with euryhalinity, parthenogenesis and weak rate of parasitism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baudoin, M., 1975. Host castration as a parasitic strategy. Evolution 29: 335–352.
Colburn, E. A., 1988. Factors influencing species diversity in saline waters of Death Valley, U.S.A. Hydrobiologia 158: 215–226.
Costil, K., G. B. J. Dussart & J. Daguzan, 2001. Parameters structuring populations of aquatic gastropods in the region of Mont Saint–Michel (France). Biodiv. Cons. 10: 1–18.
Dybdahl, M. F. & C. M. Lively, 1998. Host–parasite coevolution: evidence for rare advantage and time–lagged selection in a natural population. Evolution 52: 1057–1066.
Gérard, C., 1997. Importance du parasitisme dans la communauté de Gastéropodes de l’étang de Combourg (Bretagne, France). Parasite 4: 49–54.
Gérard, C., 2001. Structure and temporal variation of trematode and gastropod communities in a freshwater ecosystem. Parasite 8: 275–287.
Haynes, A., B. J. R. Taylor & M. E. Varley, 1985. The influence of the mobility of Potamopyrgus jenkinsi (Smith, E. A.) (Prosobranchia:Hydrobiidae) on its spread. Arch. Hydrobiol. 103: 497–508.
Hughes, R. N., 1996. Evolutionary ecology of parthenogenetic strains of the prosobranch snail, Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Gray). Malacol. Rev. 6: 101–113.
Hurd, H., 1990. Physiological and behavioural interactions between parasites and invertebrate host. Adv. Parasitol. 29: 271–318.
Jacobsen, R. & V. E., Forbes, 1997. Clonal variation in life–history traits and feeding rates in the gastropod, Potamopyrgus antipodarum: performance across a salinity gradient. Funct. Ecol. 11: 260–267.
Jokela, J. & C. M. Lively, 1995. Spatial variation in infection by digenetic trematodes in a population of freshwater snails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). Oecologia 103: 509–517. 172
Lafferty, K. D., 1993. Effects of parasitic castration on growth, reproduction and population dynamics of the marine snail Cerithidea californica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 96: 229–237.
Lively, C. M., 1992. Parthenogenesis in a freshwater snail: reproductive assurance versus parasitic release. Evolution 46: 907–913.
Lively, C. M., 2001. Trematode infection and the distribution and dynamics of parthenogenetic snail populations. Parasitology 123: 19–26.
Lively, C. M. & J. Jokela, 2002. Temporal and spatial distributions of parasites and sex in a freshwater snail. Evol. Ecol. Res. 4: 219–226.
Lucas, A., 1965. Progrès récents en Europe d’une espèce envahissante: Hydrobia jenkinsi (Smith), Mollusque, Gastéropode. PhD thesis, Brest University, France: 42 pp.
Machin, J., 1975.Water relationships. In V. Fretter & J. Peake (eds), Pulmonates 1. Academic Press, London: 105–163.
Marazanof, F., 1969. Contribution à l’étude écologique des Mollusques des eaux douces et saumâtres de Camargue. Tome I: Milieux–espèces. Ann. Limnol. 5: 201–323.
Ponder, W. F., 1988. Potamopyrgus antipodarum a molluscan coloniser of Europe and Australia. J. moll. Stud. 54: 271–285.
Robson, G. C., 1923. Parthenogenesis in the mollusc Palusdestrina jenkinsi. J. exp. Biol. 1: 65–77.
Siegismund, H. & J. Hylleberg, 1987. Dispersal–mediated coexistence of mud snails (Hydrobiidae) in an estuary. Mar. Biol. 94: 395–402.
Thompson, S. N., 1985. Review: metabolic integration during the host associations of multicellular animal endoparasites. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 81: 21–42.
Todd, M. E., 1964. Osmotic balance in Hydrobia ulvae and Potamopyrgus jenkinsi (Gastropoda: Hydrobiidae). J. exp. Biol. 41: 665–667.
Wallace, C., 1979. Notes of the occurrence of males in populations of Potamopyrgus jenkinsi. J. moll. Stud. 45: 61–67.
Winterbourn, M. J., 1973. The New Zealand species of Potamopyrgus (Gastropoda: Hydrobiidae). Malacologia 10: 283–321.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gérard, C., Blanc, A. & Costil, K. Potamopyrgus antipodarum(Mollusca:Hydrobiidae) in continental aquatic gastropod communities: impact of salinity and trematode parasitism. Hydrobiologia 493, 167–172 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025443910836
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025443910836