Abstract
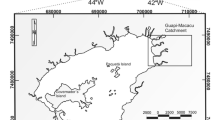
Increased discharges of organic matter from different sources in Morales Stream, one of the main tributaries of the Matanza-Riachuelo River, caused not only an increase in its primary production but also drastic changes in the composition of its sediments, thus favoring eutrophication processes. An in situ study was carried out in order to assess the effects of an organic point source contamination (from intensive cattle rearing) on the sediments of Morales Stream. Surface water and sediment samples were analysed to determine the chemical characteristics of the water–sediment system. The amounts and forms of sediment phosphorus were determined using the `EDTA method' (Golterman, 1996) at two sites of the stream having different nutrient loads. The increase in the organic load of Morales Stream waters influences the dynamics of sediment P, producing two main effects: (1) an increase in the organic matter amount of the sediment that leads to an increase in the amount of P associated to organic fractions, which may be released by bacterial activity under anoxic conditions; and (2) a decrease in the concentration of P in the fraction bound to iron. Morales Stream sediments may act as a potential source of P, which can release this nutrient to water under the reducing conditions originated by uncontrolled discharges of organic residues to this water body.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, L. E. & C. D. Moodie, 1965. Carbonate. In Black, C. A. (ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties. ASA, Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A.: 1379-1396.
APHA, AWWA, WPCF, 1992. Métodos Normalizados Para el Análisis de Aguas Potables y Residuales. Ed. Díaz de Santos, S.A. Madrid, España: 1816 pp.
Bargiela, M., A. Rendina & A. F. de Iorio, 1997. Determinación de fósforo total en suelos de la pampa deprimida. R. Internacional Información Tecnológica 8/6: 147-152.
Boström, B., I. Ahlgren & R. Bell, 1985. Internal nutrient loading in a eutrophic lake, reflected in seasonal variations of some sediment parameters. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 3335-3339.
CEMR (Comité Ejecutor del Plan de Gestión Ambiental y de Manejo de la Cuenca Hídrica Matanza-Riachuelo), 1997. Extracto de la propuesta del plan de gestión ambiental y manejo de la cuenca Matanza-Riachuelo, ENGEVIX-COWI-ICONAS, 5: 20-21.
De Groot, C. J. & H. L. Golterman, 1990. Sequential fractionation of sediment phosphate. Hydrobiologia 192: 143-148.
De Groot, C. J. & H. L. Golterman, 1993. On the presence of organic phosphate in some Camargue sediments: evidence for the importance of phytate. Hydrobiologia 252: 117-126.
Farmer, J. G., 1994. Phosphorus fractionation and mobility in Loch Leven sediments. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshwat. Ecosyst. 4: 45-56.
Gächter, R. & J. S. Meyer, 1993. The role of microorganisms in mobilization and fixation of phosphorus in sediments. Hydrobiologia 253: 103-121.
Gächter, R., J. S. Meyer & A. Mares, 1988. Contribution of bacteria to release and fixation of phosphorus in lake sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33: 1542-1558.
Golterman, H. L., 1984. Sediments, modifying and equilibrating factors in the chemistry of freshwater. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 23-59.
Golterman, H. L., 1995. The labyrinth of nutrient cycles and buffers in wetlands: results based on research in the Camargue (southern France). Hydrobiologia 315: 39-58.
Golterman, H. L., 1996. Fractionation of sediment phosphate with chelating compounds: a simplification, and comparison with other methods. Hydrobiologia 335: 87-95.
Golterman, H. L., 1998. Presence of and phosphate release from polyphosphates or phytate phosphate in lake sediments. Hydrobiologia 364: 99-104.
Golterman, H. L., 2001a. Phosphate release from anoxic sediments or 'What did Mortimer really write?'. Hydrobiologia 450: 99-106.
Golterman, H. L., 2001b. Fractionation and bioavailability of phosphates in lacustrine sediments: a review. Limnetica 20: 15-29.
Graf, G., 1982. Benthic response to sedimentation of a spring phytoplankton bloom process and budget. Mar. Biol. 67: 201-208.
Graf, G., 1989. Benthic-pelagic coupling in a deep-sea benthic community. Nature 341: 437-439.
Harper, D. M., 1992. Eutrophication of Freshwaters: Principles, Problems and Restoration. Chapman and Hall, London: 327 pp.
Herbes, S. E., H. E. Allen & K. H. Mancy, 1975. Enzymatic characterization of soluble organic phosphorus in lake water. Science (Washington, DC) 187: 432-434.
Iorio A. F. de, 1999. Distribución y dinámica de las formas químicas de cobre en relación con el hierro y el manganeso, en un natracuol de la pampa deprimida. Tesis Magister Scientiae. EpG-FAUBA "Dr. Alberto Soriano", Buenos Aires.
INTA (Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria), 1997. Carta de suelos de la RepÚblica Argentina. Hoja 3560-18 "General Las Heras". Buenos Aires, 75 pp.
Itsvanovics, V., 1994. Fractional composition, adsorption and release of sediment phosphorus in the Kis-Balanton reservoir. Wat. Res. 28: 717-726.
Jensen, M. H., E. Lomstein & J. Sorensen, 1990. Benthic NH4+ and NO3- flux following sedimentation of a spring phytoplankton bloom in Aarhus Bight, Denmark. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 61: 87- 96.
Kleeberg, A. & G. Schlungbaum, 1993. In situ phosphorus release experiments in the Warnow River (Mecklenburg, northern Germany). Hydrobiologia 253: 263-274.
Kleeberg, A. & P. Kozerski, 1997. Phosphorus release in Lake Größer Müggelsee and its implications for lake restoration. Hydrobiologia 342/ 343: 9-26.
Lee, G. F.,W. C. Sonzogni & R. D. Spear, 1977. Significance of oxic vs. anoxic conditions for LakeMendota sediment phosphorus release. In Golterman, H. L (ed.), Interactions between Sediments and Fresh Water. Dr. W. Junk Publishers, The Hague: 294-306.
Levesque, M. & M. Schnitzer, 1967. Characterization of model and soil organic matter-metal-phosphate complexes. Soil Science 103: 183-190.
Lijklema, L., 1993. Considerations in modeling the sediment-water exchange of phosphorus. Hydrobiologia 253: 219-231.
McKelvie, I. D., B. T. Hart & T. J. Cardwell, 1993. Speciation of dissolved phosphorus in environmental samples by gel filtration and flow-injection analysis. Talanta 40: 1981-1993.
Mortimer, C. H., 1941. The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. J. Ecol. 29: 280-329.
Mortimer, C. H., 1942. The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. J. Ecol. 30: 147-201.
Montigny, C. & Y. T. Prairie, 1993. The relative importance of biological and chemical processes in the release of phosphorus from a highly organic sediment. Hydrobiologia 253: 141-150.
Murphy, J. & J. R. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analyt. chim. Acta 27: 31-36.
Newman & Reddy, 1993. Alkaline activity in the sediment-water column of a hypereutrophic lake. J. Envir. Qual. 22: 832-838.
Psenner, R., R. Pucsko & M. Sager, 1984. Fractionation of organicand inorganic phosphorus compounds in lake sediments. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 70: 111-155.
Prairie, Y., C. de Montigny & P. Giorgio. 2000. Phosphorus release from anoxic sediment: Mortimers paradigma revisited. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 27: 3787-3793.
Petersen, W., K. Wallmann, P. Li, F. Schroeder & H. D. Knauth, 1996. The influence of diagenetic processes on the exchange of trace contaminants at the sediment-water interface. In Calmano, W. & U. Förstner (eds), Sediments and Toxic Substances. Springer V. B. H. Publ., New York: 37-50.
Sallade, Y. E. & J. T. Sims, 1997.Phosphorus transformations in the sediments of Delaware+s Agricultural Drainageways: Effect of reducing conditions on phosphorus release. J. Envir. Qual. 26: 1579-1588.
Slomp, C. P., W. Van Raaphorst, J. F. P. Malschaert, A. Kok & A. J. J. Sandee, 1993. The effect of deposition of organic matter on phosphorus dynamics in experimental marine sediment systems. Hydrobiologia 253: 83-98.
Suzumura, M. & A. Kamatani, 1993. Isolation and determination of inositol hexaphosphate in sediments from Tokyo Bay. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 57: 2197-2202.
Van PLiere, L., J. Peters, A. Mutijin & L. R. Mur, 1983. Release of sediment-phosphorus, and the influence of algae growth. Hydrobiol. Bull. 16: 191-200.
Walkley, A., 1947. A critical examination of a rapid method for determining organic carbon in soil. Soil Sci. 63: 251-263.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García, A.R., de Iorio, A.F. Phosphorus distribution in sediments of Morales Stream (tributary of the Matanza-Riachuelo River, Argentina). The influence of organic point source contamination. Hydrobiologia 492, 129–138 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024874030418
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024874030418