Abstract
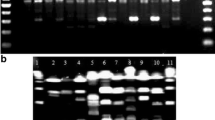
In this study, 97 epidemiologically unrelated Shigella flexneri strains isolated during 1994 (69 isolates) and 1997 (28 isolates) were characterised by ribotyping, enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus sequence-based PCR typing, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Number of strains belonging to each of the six serotypes is selected equal to their distribution in Romania. The isolates comprise 24 ribotypes based on combination of two restriction patterns obtained with HindIII and PstI, respectively, 7 enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus (ERIC)-PCR types, and 92 XbaI pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) patterns grouped in 31 pulsotypes at Dice coefficients of 85% similarity. We find no significant difference in the distribution of isolates collected during the two periods. Macrorestriction analysis by PFGE offers maximal discrimination. There seems to be little genetic variability among circulating S. flexneri strains of serotype 2a, suggesting that even a combination of several molecular techniques, including PFGE, could not easily differentiate an outbreak strain from temporally associated independent isolates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Navia MM, Capitano L, Ruiz J, et al. Typing and characterization of mechanisms of resistance of Shigella spp. isolated from feces of children under 5 years of age from Ifakara, Tanzania. J Clin Microbiol 1999; 37: 3113–3117.
Lima AAM, Sidrim JJC, Lima NL, et al. Molecular epidemiology of multiply antibiotic-resistant Shigella flexneri in Fortaleza, Brazil. J Clin Microbiol 1997; 35: 1061–1065.
Casalino M, Nicoletti M, Salvia A, et al. Characterization of endemic Shigella flexneri strains in Somalia: Antimicrobial resistance, plasmid profiles, and serotype correlation. J Clin Microbiol 1994; 32: 1179–1183.
Faruque SM, Haider K, Rahman MM, et al. Differentiation of Shigella flexneri strains by rRNA gene restriction patterns. J Clin Microbiol 1992; 30: 2996–2999.
Kariuki S, Muthotho N, Kimari J, Waiyaki P, Hart CA, Gilks CF. Molecular typing of multi-drug resistant Shigella dysenteriae type 1 by plasmid analysis and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Trans Roy Soc Trop Med Hyg 1996; 90: 712–714.
Yagupsky P, Loeffelholz M, Bell K, Menegus MA. Use of multiple markers for investigation of an epidemic of Shigella sonnei infections in Monroe County, New York. J Clin Microbiol 1991; 29: 2850–2855.
Litwin CM, Leonard RB, Carroll KC, Drummond WK, Pavia AT. Characterization of endemic strains of Shigella sonnei by use of plasmid DNA analysis and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to detect patterns of transmission. J Infect Dis 1997; 175: 864-870.
Gericke B, Liesegang A, Reissbrodt R. Analysis of a foodborne Shigella sonnei outbreak in northern Europe by conventional and molecular methods. Med Microbiol Lett 1995; 4: 165–172.
Preston MA, Borczyk AA. Genetic variability and molecular typing of Shigella sonnei strains isolated in Canada. J Clin Microbiol 1994; 32: 1427–1430.
Karaolis DKR, Lan R, Reeves PR. Sequence variation in Shigella sonnei (Sonnei), a pathogenic clone of Escherichia coli, over four continents and 41 years. J Clin Microbiol 1994; 32: 796–802.
Brian MJ, Van R, Townsend I, Murray BE, Cleary TG, Pickering LK. Evaluation of the molecular epidemiology of an outbreak of multiply resistant Shigella sonnei in a day-care center by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and plasmid DNA analysis. J Clin Microbiol 1993; 31: 2152–2156.
Litwin CM, Storm AL, Chipowsky S, Ryan KJ. Molecular epidemiology of Shigella infections: Plasmid profiles, serotype correlation, and restriction endonuclease analysis. J Clin Microbiol 1991; 29: 104–108.
Marranzano M, Giammanco G, d'Hauteville H, Sansonetti P. Epidemiological markers of Shigella sonnei infections: R-plasmid fingerprinting, phage-typing and biotyping. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol 1985; 136 A: 339–345.
Nastasi A, Pignato S, Mammina C, Giammanco G. rRNA gene restriction patterns and biotypes of Shigella sonnei. Epidemiol Infect 1993; 110: 23–30.
Hinojosa-Ahumada M, Swaminathan B, Hunter SB, et al. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in rRNA operons for subtyping Shigella sonnei. J Clin Microbiol 1991; 29: 2380–2384.
Liu PYF, Lau YJ, Hu BS, et al. Analysis of clonal relationships among isolates of Shigella sonnei by different molecular typing methods. J Clin Microbiol 1995; 33: 1779–1783.
Chiou CS, Hsu WB, Wei HL, Chen JH. Molecular epidemiology of a Shigella flexneri outbreak in a mountainous township in Taiwan, Republic of China. J Clin Microbiol 2001; 39: 1048–1056.
Houang ETS, Chu YW, Ng TK, Cheng AFB. Study of the relatedness of isolates of Shigella flexneri and Shigella sonnei obtained in 1986 and 1987 and in 1994 and 1995 from Hong Kong. J Clin Microbiol 1998; 36: 2404–2407.
Soldati L, Piffaretti JC. Molecular typing of Shigella strains using pulsed field gel electrophoresis and genome hybridization with insertion sequences. Res Microbiol 1991; 142: 489–498.
Surdeanu M, Pencu E, Tonciu M, Mihai I, Ciudin L. Differentiation of Shigella strains by plasmid profile analysis, serotyping and phage typing. Rom Arch Microbiol Immunol 2000; T 59, 1-2: 103–117.
Edwards PR, Ewing WH. Identification of Enterobacteriaceae. Burgess Publishing Company, 1972; 120–136.
Ausubel FM, Brent M, Kingston RE, et al. (eds), Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. John Wiley & sons, 1994.
Grimont F, Grimont PAD. Determination of rRNA gene restriction patterns. In: Howard J, Whitcombe DM (eds), Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 46: Diagnostic Bacteriology Protocols. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press Inc., 1995: 181–200.
Regnault B, Grimont F, Grimont PAD. Universal ribotyping method using a chemically labelled oligonucleotide probe mixture. Res Microbiol 1997; 148: 649–659.
Regnault B, Grimont F, Grimont PAD. Author' correction. Res Microbiol 1998; 149: 73.
Grimont PAD. User' manual of Taxotron® package 1998.
Versalovic J, Koeuth T, Lupski JR. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 1991; 19: 6823–6831.
Coimbra RS, Grimont F, Grimont PAD. Identification of Shigella serotypes by restriction of amplified O-antigen gene cluster. Res Microbiol 1999; 150: 543–553.
Giammanco G, Natoli D. Conversions antigéniques chez Shigella flexneri II. - Effets de la lysogénisation de cultures sérotype 1, sérotype 2, variante X et variante Y par un phage issu d'une culture sérotype 5. Ann Inst Pasteur 1969; 117: 16–25.
Mendoza MC, Martín MC, González-Hevia MA. Usefulness of ribotyping in a molecular epidemiology study of shigellosis. Epidemiol Infect 1996; 116: 127–135.
Allison GE, Verma NK. Serotype-converting bacteriophages and O-antigen modification in Shigella flexneri. Trends Microbiol 2000; 8: 17–23.
Coimbra RS, Nicastro G, Grimont PAD, Grimont F. Computer identification of Shigella species by rRNA gene restriction patterns. Res Microbiol 2001; 152: 47–55.
Millemann Y, Lesage-Descauses MC, Lafont JP, Chaslus-Dancla E. Comparison of random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis and enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus-PCR for epidemiological studies of Salmonella. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 1996; 14: 129–134.
Reboli AC, Houston ED, Monteforte JS, Wood CA, Hamill RJ. Discrimination of epidemic and sporadic isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii by repetitive element PCR-mediated DNA fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol 1994; 32: 2635–2640.
Moissenet D, Valcin M, Marchand V, Grimprel E, Bégué, Garbarg-Chenon A, Vu-Thien H. Comparative DNA analysis of Bordetella pertussis clinical isolates by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, randomly amplified polymorphism DNA, and ERIC polymerase chain reaction. FEMS Microbiol Lett 1996; 143: 127–132.
Matsumoto M, Suzuki Y, Saito M, Ishikawa N, Ohta M. Epidemiologic study of Shigella sonnei from sequential outbreaks and sporadic cases using different typing techniques. Microbiol Immunol 1998; 42: 259–264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surdeanu, M., Ciudin, L., Pencu, E. et al. Comparative study of three different DNA fingerprint techniques for molecular typing of Shigella flexneri strains isolated in Romania. Eur J Epidemiol 18, 703–710 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024831609901
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024831609901