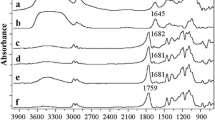
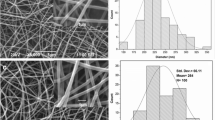
Abstract
Natural proteins such as casein and enzymes cannot be processed into fibrous forms. With the addition of another polymer such as poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) or poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), casein, a natural protein, was electrospun into ultra-thin fibrous membranes. Fibers in these membranes had diameters between 100 and 500 nm. These fibrous membranes were rendered insoluble by chemical crosslinking with 4,4′-methylenebis(phenyl diisocyanate) (MDI) in THF. The electrospinning method has also been utilized for enzyme immobilization on solid support. The lipase encapsulated in the ultra-fine fibrous membranes exhibits higher catalytic activity towards hydrolyzing olive oil than that in the cast films from the same solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Formhals, US Patent no. 1975504 (1934).
J. Doshi and D. H. Reneker, J. Electrostatics 35 (1995) 151.
D. H. Reneker and I. Chun, Nanotechnology 7 (1996) 216.
J. M. Deitzel, J. Kleinmeyer, D. Harris and N. C. B. Tan, Polymer 42 (2001) 261.
C. J. Buchko, L. C. Chen, Y. Shen and D. C. Martin, ibid. 40 (1999) 7397.
H. Fong, I. Chun and D. H. Reneker, ibid. 40 (1999) 4585.
J.-S. Kim and D. S. Lee, ibid. 32 (2000) 616.
P. Gibson, H. Schreuder-Gibson and D. Rivin, Coll. Surf. 187/188 (2001) 469.
I. D. NORRIS, M. M. Shaker, F. K. Ko and A. G. Macdiarmid, Synt. Meta. 114 (2000) 109.
M. Bognitzki, W. Czado, T. Frese, A. Schaper, M. Hellwig, M. Steinhart, A. Greiner and J. H. Wendorff, Adv. Mater. 13 (2001) 70.
M. M. Bergshoef and G. J. Vancso, ibid. 11 (1999) 1362.
J.-S. Kim and D. H. Reneker, Polym. Comp. 20 (1999) 124.
R. A. Caruso, J. H. Schattka and A. Greiner, Adv. Mater. 13 (2001) 1577.
X. Fang and D. H. Reneker, J. Macromol. Sci.-Phys. B 36 (1997) 169.
J. Y. Lu, K. A. Runnels and C. Norman, Inorg. Chem. 40 (2001) 4516.
L. Huang, R. A. Mcmillan, R. P. Apkarian, B. Pourdeyhimi, V. P. Conticello and E. L. Chaikof, Macromolecules 33 (2000) 2989.
F. H. Schmidt, H. Stork and K. Von dahl, in “Methods of Enzymatic Analysis,” 2nd ed, Vol. 2, edited by H. U. Bergmeyer (Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, 1974) p. 819.
W. Eigel, J. Butler, C. Ernstrom, H. Farrell, V. Harwalkar, R. Jenness and R. Whitney, J. Dairy Sci. 67 (1984) 1599.
S. Morimoto, Symp. Ind. Eng. Chem. 62 (1970) 23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, J., Hsieh, YL. Ultra-high surface fibrous membranes from electrospinning of natural proteins: casein and lipase enzyme. Journal of Materials Science 38, 2125–2133 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023763727747
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023763727747