Abstract
In the present project, twenty materials (e.g., polyhydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate, polycaprolactone, cellulose acetate, polyacticacid, polyethylene), representing varied biodegradability levels were studied. An aerobic respirometric test, based on the CEN Draft, was setup. The biodegradability of each plastic film was evaluated by measuring the percentage of carbon converted into CO2 during 35 days. The values of the CO2 production were plotted versus days as a cumulative function. In order to reduce its number of points, the cumulative curve was modeled using a sigmoïd function (Hill sigmoïd). This model was compared to one found in the literature. A χ 2i test showed that the biodegradation curve was more accurately fitted with the model than the previous one. Three kinetic parameters were determined by this “Hill model”: one represents the maximal percentage of carbon converted into CO2, the second the “half-life time” in days of the degrading part of the material and the third one the curve radius.
In addition, the following analyses were carried out on each sample: elemental analysis, thickness, hydrophobicity and surface free energy measurements. In order to compress the information and to keep only relevant pieces, these parameters were submitted to a Principal Component Analysis. PCA found linear combinations of variables that describe major trends in the data. The two principal components which separate groups of materials were closely related to a chemical and a physical axis respectively. Materials showing a high biodegradability were related to high oxygen (and nitrogen) contents and low hydrophobicity: Material thickness did not influence the likeliness to biodegradability described by the maximum biodegradation rate. Finally, this study established the correlation between the biodegradation and the structure of biopolymers.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
G. L. Fuller, T. A. McKeon and D. D. Bills (1996) Agricultural Materials on Renewable Resources, ACS Symposium Series 647, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
E. Chiellini and R. Solaro (1996) Adv. Mater. 8(4), 305–313.
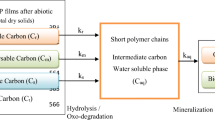
C. Clicquot de Mentque (1998) Environment magazine. 1566, 54–55.
R. Barili (1990) in Report “Association pour la Promotion Industrie-Agriculture” (Eds). European symposium: Biodegradable packagings and agricultural films. pp. 55–86.
Y. Doi, Y. Kumagai, N. Tanahashi and K. Mukai (1992) in M. Vert, J. Feijen, A. Albertsson, G. Scott and E. Chiellini (Eds.). Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 139–148.
Y. Poirier, D. Dennis, K. Klomparens, C. Nawrath and C. Somerville (1992) FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 103, 237–246.
Y. Yokota, R. Ishioka, Y. Moketi and N. Watanabe (1994 in Y. Doi and K. Fukuda (Eds.) Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics, Elsevier, Amsterdam-London-New York-Tokyo, pp. 577–583.
C. Bastioli, A. Cerutti, I. Guanella, G. C. Romano and M. Tosin (1994). Third Annual Meeting Bio/Environmentally degradable polymer society, June 6–8, 1994 Boston Massachusetts.
P. Ehret (1996) T. U. T. 19, 25–26.
A. Calmon-Décriaud, V. Bellon-Maurel and F. Silvestre (1997) Adv. Polym. Sci. 135, 207–226.
R. J. Müller, J. Augusta, T. Walter and H. Widdecke (1997) in Y. Doi and K. Fukuda (Eds.). Biodegrable Plastics and Polymers, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 237–49.
M. Itävaara and M. Vikman (1995) Chemosphere 31, 4359–4373.
OECD (1992) Ligne directive de l'OCDE pour les essais de produits chimiques, Paris. OECD 301B.
ASTM (1993). Standard on Environmentally Degradable Plastics, Philadelphia. ASTM D 5209–91.
Draft Method (1995) Evaluation of the ultimate aerobic biodegrad-ability and desintegration of packaging materials under aqueous medium. Doc. 15/02/95. CEN/TC 261/SC4/N42.
G. T. G. Keursten and P. H. Groenevelt (1996) Biodegradation. 7, 329–333.
G. Swift (1992) FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 103, 339–346.
R. J. Larson, R. T. Williams and G. Swift (1992) Polym. Mat. Sci. Eng. 67, 348–350.
A. L. Andrady and Y. Song (1997) Polym. Mat. Sci. Eng. 76, 470–471.
S. J. Huang, M. S. Roby, C. A. Macri and J. A. Cameron (1992) in M. Vert, J. Feijen, A. Albertsson, G. Scott and E. Chiellini (Eds.). Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 149–157.
M. Parick, R. A. Gross and S. P. Mc Carthy (1993) in C. Ching, D. Kaplan and E. Thomas, Biodegradable Polymers and Packaging, Technomic, Lancaster, pp. 159–170.
C. M. Buchanan, R. M. Gardnerand and R. J. Komarek (1993) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 47, 1709–1719.
M. Okada, Y. Okada, A. Tao and K. Aoi (1996) J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 62, 2257–2265.
M. Van Der Zee, Dissertation, University of Twente Enschede, NL.
S. Thiebaud (1995) Thesis, University of INP Toulouse, France, no 1087.
K. C. Marshall (1990) in R. C. W. Berkeley, J. M. Lynch, J. Melling, P. R. Rutter and B. Vincent (Eds.) Microbial Adhesion to surface, Ellis Howwood Ltd., Chichester, pp. 187–196.
J. D. Andrade, L. M. Smith and D. E. Gregonis (1985) in: J. D. Andrade (ed.) Surface and interfacial aspects of biomedical polymers. 1-Surface chemistry and physics. Plenum Press, New York and London pp. 249–292.
R. N. Sturm (1973) J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 50, 159–167.
B. Spitzer, C. Mende, M. Menner and T. Luck (1996). J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 4, 157–171.
S. Urstadt, J. Augusta, R. J. Müller and W. D. Deckwer (1995) J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 3, 121–131.
G. Swift, M. Creamer, X. Wei and K. M. Yocom (1998) Macromol. Symp. 130, 379–391.
N. Mozes, F. Marchal, M. P. Hermesse, J. L. Van Haecht, L. Reuliaux, A. J. Leonard and P. G. Rouxhet (1987) Biotechnol. Bioeng. 30, 439–450.
J. E. Guillet, H. X. Huber and J. Scott (1992) in M. Vert, J. Feijen, A. Albertsson, G. Scott and E. Chiellini (Eds.). Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 55–70.
N. Pujos (1996) DESS Dissertation, University of Toulouse (INSA-GBA), France.
S. H. Imam (1990) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 1317–1322.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calmon, A., Silvestre, F., Bellon-Maurel, V. et al. Modelling Easily Biodegradability of Materials in Liquid Medium-Relationship Between Structure and Biodegradability. Journal of Polymers and the Environment 7, 135–144 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022845605474
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022845605474