Abstract
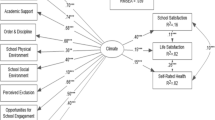
This study examined factors contributing to the quality of school life of secondary school students. A path model, expressing interrelationships between students' background characteristics, their expectations of schools, the perceived quality of both the formal and the informal school curriculum, the classroom environment and students' quality of school life, was developed and tested. The sample comprised 8265 Grade 12 students from 70 schools in New South Wales, Australia. Analysis indicated that, after controlling for other variables in the model, students' experience of the classroom environment was the single most important factor explaining their quality of school life.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ainley, J. (1991). High school factors that influence students to remain in school. Journal of Educational Research, 85(2), 69-80.
Ainley, J. (1999, July). Schools and the social development of young Australians: Frameworks, outcomes and influences. Paper presented at the 1999 National Social Outcomes of Schooling Forum organized by the Performance Measurement and Review Branch, Education Queensland, Surfers Paradise, Australia.
Ainley, J., Batten, M., & Miller, H. (1984). Staying at high school in Victoria (ACER Research Monograph No. 23). Melbourne, Australia: Australian Council for Educational Research.
Ainley, J., & Bourke, S. F. (1988, November-December). Quality of life in primary schools. Paper presented at the annual conference of the Australian Association for Research in Education, University of New England, Armidale, Australia.
Ainley, J., & Bourke, S. (1992). Student views of primary schooling. Research Papers in Education Policy and Practice, 7(2), 107-128.
Ainley, J., Foreman, J., & Sheret, M. (1991). High school factors that influence students to remain in school. The Journal of Educational Research, 85(2), 69-80.
Ainley, J., Reed, R., & Miller, H. (1986). School organisation and the quality of schooling. Melbourne, Australia: Australian Council for Educational Research.
Ainley, J., & Sheret, M. (1992). Progress through high school: A study of senior secondary schooling in New South Wales (ACER Research Monograph No. 43). Melbourne, Australia: Australian Council for Educational Research.
Anderson, L. W., & Bourke, S. F. (2000). Assessing affective characteristics in the schools (2nd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 238-246.
Bourke, S. (1993). Quality of life of primary and secondary students: Studies of classrooms and schools. In John S. Shellard (Ed.), New South Wales Institute for Educational Research Bulletin of Proceedings 1992 (pp. 71-77). Kingswood, Australia: New South Wales Institute for Educational Research.
Bourke, S., & Smith, M. (1989, November-December). Quality of school life and intentions for further education: The case of a rural high school. Paper presented at the annual conference of the Australian Association for Research in Education, Adelaide, Australia.
Bryk, A., Lee, V. E., & Holland, P. B. (1993). Catholic schools and the common good. Cambridge. MA: Harvard University Press.
Bulcock, J. W., Whitt, M. E., & Beebe, M. J. (1991). Gender differences, student wellbeing and high school achievement. The Alberta Journal of Educational Research, 37, 209-224.
Delors, J. (1996). Learning: The treasure within (Report to UNESCO of the International Commission on Education for the Twenty-First Century). Paris: UNESCO Publishing.
Dorman, J. P., Fraser, B. J., & McRobbie, C. J. (1997). Relationship between school-level and classroom-level environments in secondary schools. Journal of Educational Administration, 35, 74-91.
Education Commission. (2000). Review of education system reform proposals consultation document: Education blueprint for the 21st Century. Hong Kong: Author.
Epstein, J. L., & McPartland, J. M. (1976). The concept and measurement of the quality of school life. American Educational Research Journal, 13, 15-30.
Flynn, M. (1993). The culture of Catholic schools. Homebush, Australia: St Paul's Publications
Goldstein, H. (1995). Multilevel statistical models. London: Edward Arnold.
James, L. R., Mulaik, S. A., & Brett, J. M. (1982). Causal analysis: Assumptions, models, and data. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage Publications.
Joreskog, K. G., & Sorbom, D. (1986). LISREL VI: Analysis of linear structural relationships by maximum likelihood and least square methods. Mooresville, IN: Scientific Software.
Linnakyla, P. (1996). Quality of school life in the Finnish comprehensive school: A comparative view. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 40(1), 69-85.
MacCallum, R. C., & Hong, S. (1997). Power analysis in covariance structure modeling using GFI and AGFI. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 32, 193-210.
McDonald, R. P., & Marsh, H. (1990). Choosing a multivariate model: Noncentrality and goodness of fit. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 247-255.
Ministerial Council on Education, Employment, Training and Youth Affairs (1999). The Adelaide declaration on national goals for schooling in the twenty-first century. Melbourne, Australia: Author. [On-line]. Available: http://www.curriculum.edu.au/mceetya/ nationalgoals/natgoals.htm
Mok, M. (1992). Construct validity of the Quality of School Life scale. Psychological Test Bulletin, 5, 47-51.
Mok, M., & Flynn, M. (1998). Effect of Catholic school culture on students' achievement in the Higher School Certificate Examination: A multilevel path analysis. Educational Psychology, 18, 409-432.
Pang, N. S. (1999, July). Students' quality of school life in Hong Kong. Paper presented at the National Forum on the Social Outcomes of Schooling organized by the Performance Measurement and Review Branch, Education Queensland, Surfers Paradise, Brisbane, Australia.
Schliecher, A. (2002, April). First results from PISA. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA.
Slee, R. (1992). Reforms and ravines: Diminishing risk in schools through systematic change. In R. Slee (Ed.), Discipline in Australian public education, changing policy and practice (pp. 177-198). Melbourne, Australia: Australian Council for Educational Research.
Steiger, J. H., & Lind, J. M. (1980, May). Statistically based tests for the number of common factors. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Psychometric Society, Iowa City, IA.
Tanaka, J. S., & Huba, G. J. (1985). A fit index for covariance structure models under arbitrary GLS estimation. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 38, 197-201.
Thompson, B. (1998). In praise of brilliance: Where that praise really belongs. American Psychologist, 53, 799-800.
Wilkinson, L., & APA Task Force on Statistical Inference. (1999). Statistical methods in psychology journals: Guidelines and explanations. American Psychologist, 54, 594-604.
Williams, T., & Batten, M. (1981). The quality of school life. Melbourne, Australia: Australian Council for Educational Research.
Wilson, M. (1988). Internal construct validity and reliability of a quality of school life instrument across nationality and school level. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 48, 995-1009.
Wolf, F. M., Chandler, T. A., & Spies, C. J. (1980, March). Quality of school life: Cause or effect of beliefs of academic responsibility? A Cross-lagged panel correlation analysis. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Eastern Educational Research Association, Norfolk, VA. (ERIC Document Services ED 194 537)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mo Ching Mok, M. Determinants of Students' Quality of School Life: A Path Model. Learning Environments Research 5, 275–300 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021924322950
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021924322950