Abstract
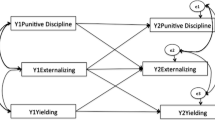
The association between children's externalizing behavior problems and mothers' overreactive discipline was examined in a longitudinally assessed sample of toddlers and their mothers. Path analyses indicated that mothers' overreactive discipline and children's externalizing behaviors were significantly and similarly stable over a 2 1/2-year period. No evidence of a cross-time influence of either variable on the other was observed. Mothers' overreactive discipline at Time 2 had a significant effect on Time 2 externalizing behavior. No significant effects of children's behavior on mothers' discipline were found. Mothers' depressive symptomatology and marital discord predicted initial overreactivity and were related to externalizing problems through their relations to overreactivity. The results support the appropriateness of implementing parenting interventions for externalizing problems before age 2 years.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4–18 and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont.
Achenbach, T. M. (1992). Manual for the ChildBehavior Checklist/land 1992 Profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont.
Achenbach, T. M., Edelbrock, C., & Howell, C. T. (1987). Empirically based assessment of the behavior/emotional problems of 2-and 3-year-old children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 15, 629–650.
Anderson, K. E., Lytton, H., & Romney, D. M. (1986). Mothers' interactions with normal and conduct-disordered boys: Who affects whom? Developmental Psychology, 22, 604–609.
Arnold, D. S., O'Leary, S. G., Wolff, L. S., & Acker, M. M. (1993). The Parenting Scale: A measure of dysfunctional parenting in discipline situations. Psychological Assessment, 5, 137–144.
Arnold, E. H., O'Leary, S. G., & Edwards, G. H. (1997). Father involvement and self-reported parenting of children with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 337–342.
Bandura, A., & Huston, A. C. (1961). Identification as a process of incidental learning. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 63, 575–582.
Barkley, R., & Cunningham, E. (1979). The effects of methylphenidate on mother-child interaction of hyperactive children. Archives of General Psychiatry, 36, 201–208.
Barling, J., MacEwen, K. E., & Nolte, M. (1993). Homemaker role experiences affect toddler behaviors via maternal well-being and parenting behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 21, 213–229.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173–1182.
Baumrind, D., & Black, A. (1967). Socialization practices associated with dimensions of competence in preschool boys and girls. Child Development, 38, 291–327.
Beck, A. T, Steer, R. A., & Garbin, M. G. (1988). Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory: Twenty-five years of evaluation. Clinical Psychology Review, 8, 77–100.
Bentler, P. M. (1995). EQS: Structural equations program manual. Encino, CA: Multivariate Software, Inc.
Campbell, S. B. (1994). Hard-to-manage preschool boys: Externalizing behavior, social competence, and family context at twoyear followup. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22, 147–166.
Campbell, S. B., Pierce, E. W., Moore, G., Marakovitz, S., & Newby, K. (1996). Boys' externalizing problems at elementary school age: Pathways from early behavior problems, maternal control, and family stress. Development and Psychopathology, 8, 701–719.
Crane, D. R., Allgood, S. M., Larson, J. H., & Griffin, W. (1990). Assessing marital quality with distressed and nondistressed couples: A comparison and equivalency table for three frequently used measures. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 52, 87–93.
Dadds, M. R., Sheffield, J. K., & Holbeck, J. G. (1990). An examination of the differential relationship of marital discord to parents' discipline strategies for boys and girls. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 18, 121–129.
Downey, C., & Coyne, J. C. (1990). Children of depressed parents: An integrative review. Psychological Bulletin, 108, 50–76.
Fagot, B. I. (1984). The consequents of problem behavior in toddler children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 12, 385–396.
Farrington, D. P. (1989). Early predictors of adolescent aggression and adult violence. Violence and Victims, 4, 79–100.
Glueck, S., & Glueck, E. (1950). Unraveling juvenile delinquency. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
James, L. R., & Singh, B. K. (1978). An introduction to the logic, assumptions, and basic analytic procedures of two-stage least squares. Psychological Bulletin, 85, 1104–1122.
Keenan, K., & Shaw, D. S. (1994). The development of aggression in toddlers: A study of low-income families. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22, 53–77.
Kimmel, D. C., & Van der Veen, F. (1974). Factors of the marital adjustment test. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 36, 57–63.
Locke, H. J., & Wallace, K. M. (1959). Short marital adjustment and prediction tests: Their reliability and validity. Marriage and Family Living, 21, 231–235.
Lytton, H. (1990). Child and parent effects in boys' conduct disorder: A reinterpretation. Developmental Psychology, 26, 683–697.
McCord, W., McCord, J., & Howard, A. (1961). Familial correlates of aggression in non-delinquent male children. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 62, 79–93.
Minton, C., Kagan, J., & Levine, J. A. (1971). Maternal control and obedience in the two-year-old. Child Development, 42,1873–1894.
Olweus, D. (1979). Stability of aggressive reaction patterns in males: A review. Psychological Bulletin, 86, 852–875.
Parke, R. D. (1995). Father and families. In M. H. Bomstein (Ed.), Handbook of parenting: Volume 3. Status and social conditions of parenting (pp. 27–63). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Patterson, G. R., Chamberlain, P., & Reid, J. B. (1982). A comparative evaluation of parent training procedures. Behavior Therapy, 3, 638–650.
Patterson, G. R., DeBaryshe, B. D., & Ramsey, E. (1989). A developmental perspective on antisocial behavior. American Psychologist, 44, 329–335.
Patterson, G. R., Reid, J. B., & Dishion, T. J. (1992). Antisocial boys. Eugene, OR: Castalia.
Pettit, G., & Bates, J. (1989). Family interaction patterns and children's behavior problems from infancy to 4 years. Developmental Psychology, 25, 413–420.
Power, T. J., & Chapieski, M. L. (1986). Childrearing and impulse control in toddlers: A naturalistic investigation. Developmental Psychology, 22, 271–275.
Reid, W. J., & Crisafulli, A. (1990). Marital discord and child behavior problems: A meta-analysis. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 18, 105–117.
Roberts, W., & Strayer, J. (1987). Parents' response to the emotional distress of their children: Relations with children's competence. Developmental Psychology, 23, 415–422.
Shaw, D. S., Winslow, E. B., Owens, E. B., Vondra, J. I., Conn, J. F., & Bell, R. Q. (1998). The development of early externalizing problems among children from low-income families: A transformational perspective. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 26, 95–107.
Spanier, G. B. (1976). Measuring dyadic adjustment: New scales for assessing the quality of marriage and similar dyads. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 38, 15–28.
Taylor, T. K., & Biglan, A. (1998). Behavioral family interventions for improving child-rearing: A review of the literature for clinicians and policy makers. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 1, 41–60.
Vuchinich, S., Bank, L., & Patterson, G. R. (1992). Parenting, peers, and the stability of antisocial behavior in preadolescent boys. Developmental Psychology, 28, 510–521.
Webster-Stratton, C. (1998). Preventing conduct problems in Head Start children: Strengthening parenting competencies. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65,715–730.
Webster-Stratton, C., & Hammond, M. (1997). Treating children with early-onset conduct problems: A comparison of child and parent training interventions. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 93–109.
Webster-Stratton, C., Kolpacoff, M., & Hollinsworth, T. (1988). Selfadministered videotape therapy for families with conduct problem children: Comparison with two cost-effective treatments and a control group. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 56, 558–566.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Leary, S.G., Slep, A.M.S. & Reid, M.J. A Longitudinal Study of Mothers' Overreactive Discipline and Toddlers' Externalizing Behavior. J Abnorm Child Psychol 27, 331–341 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021919716586
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021919716586