Abstract
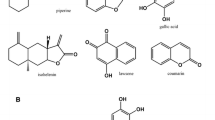
This study tests hypotheses on the biochemical functions of geophagy in parrots: mechanical enhancement of digestion, acid buffering capacity, mineral supplementation, adsorption of dietary toxins, and gastrointestinal cytoprotection. Parrots showed clear preferences for specific soil horizons. Comparisons of preferred and nonpreferred soils from several sites suggest that soils have little ability to enhance grinding and no measurable ability to buffer gastric pH. Soils offered insignificant mineral supplementation since most minerals occurred at similar levels in samples regardless of preference, and the minerals were generally more plentiful in the birds' diets. Sodium was available in moderate levels at some sites (>1000 ppm), but was well below sodium detection thresholds of parrots. X-ray diffraction, cation exchange capacity, and in vitro adsorptive trials showed that the preferred soils are capable of exchanging substantial quantities of cations and are capable of adsorbing low-molecular-weight secondary compounds. In captive Amazona parrots, orally administered clay reduced the bioavailability of the alkaloid quinidine by roughly 60%, demonstrating that in vivo adsorption of potentially toxic compounds may be a biologically important function of geophagy. Labeled clay remained in the lower gastrointestinal tract of captive parrots for >12 hr, which along with high adsorptive capacities, further suggests a potential role in protecting the gastrointestinal lining from various biological and chemical insults. Detoxification and cytoprotection are the most likely functions of geophagy for parrots and herbivores with similar ecologies. Given the variety of chemically defended seeds consumed by these herbivores, geophagy likely protects consumers from dietary toxins, allowing increased diet breadth and/or enhancing digestibility.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abrahams, P. W., and Parsons, J. A. 1996. Geophagy in the tropics—a literature review. Geogr. J. 162:63–72.
Acedo, V. 1992. Ecology of the Yellow-naped Amazon in Guatemala. AFA Watchbird 19:31–34.
Arms, K., Feeney, P., and Lederhouse, R. C. 1974. Sodium: Stimulus for puddling behavior by tiger swallowtail butterflies, Papilo glaucus. Science 185:372–374.
Berenbaum, M. R., and Zangerl, A. R. 1994. Costs of inducible defense: Protein limitation, growth, and detoxification in parsnip webworms. Ecology 75(8):2311–2317.
Best, L. B., and Gionfriddo, J. P. 1991. Characterization of grit use by cornfield birds. Wilson Bull. 103(1):68–82.
Blair-West, J. R., Coghlan, J. P., Denton, D. A., Nelson, J. F., Orchard, E., Scoggins, B. A., Wright, R. D., Myers, K., and Junqueira, C. L. 1968. Physiological morphological and behavioural adaptation to a sodium deficient environment by wild native Australian and introduced species of animals. Nature 217:922–928.
Brouillard, M. Y., and Rateau, J. G. 1989. Pouvoir d'adsorption de deux argiles, la smectite et le kaolin sur des entérotoxines bactériennes. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 13(1):18–24.
Burkitt, W. H. 1969. Sodium bentonite addition to high concentrate pelleted ratios self-fed to finishing yearling cattle. Feedstuffs 41(45):32, 39.
Cade, T. J. 1964. Water and salt balance in granivorous birds, pp. 237–255, in M. J. Wayner (eds.). Thirst. Pergamon Press, New York.
Cooper, M. 1957. Pica; a survey of the historical literature as well as reports from the fields of veterinary medicine and anthropology, the present study of pica in young children, and a discussion of its pediatric and psychological implications. Bannerstone House, Springfield, Illinois.
Diamond, J., Bishop, K. D., and Gilardi, J. D. 1999. Geophagy in New Guinea birds. Ibis. 141(2).
Dixon, W. J. 1992. BMDP Statistical Software Manual. BMDP Statistical Software, Inc., Los Angeles.
Droy-Lefaix, M. T., Drouet, Y., and Schatz, B. 1985. Sodium glycodeoxycholate and spinability of gastrointestinal mucus: protective effect of smectite. Gastroenterology 88:1369.
Dukes, G. E. 1990. Over-the-counter antidiarrheal medications used for the self-treatment of acute nonspecific diarrhea. Symposium on the management of acute nonspecific diarrhea, Innisbrook, Florida, February 6, 1988. Am. J. Med. 88(6 Part A):6A24S-6A26S.
Dumonceaux, G., and Harrison, G. J. 1994. Toxins, pp. 1030–1052, in B. W. Ritchie, G. J. Harrison, and L. R. Harrison (eds.). Avian Medicine: Principles and Application. Lake Worth, Florida.
Emmons, L. H., and Stark, N. M. 1979. Elemental composition of a natural mineral lick in Amazonia. Biotropica 11(4):311–313.
Fawcett, D. W. 1994. A Textbook of Histology, 12th ed. Chapman and Hall, New York.
Freeland, W. J., Calcott, P. H., and Geiss, D. P. 1985. Allelochemicals, minerals and herbivore population size. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 13(2):195–206.
Gardiner, K. R., Anderson, N. H., McCaigue, M. D., Erwin, P. J., Halliday, M. I., and Rowlands, B. J. 1993. Adsorbents as antiendotoxin agents in experimental colitis. Gut 34(1):51–55.
Gee, G. W., and Bauder, J. W. 1986. Particle size analysis, pp. 383–411, A. Klute (ed.). Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin.
Gee, J. M., and Johnson, I. T. 1988. Interactions between hemolytic saponins, bile salts, and small intestinal mucosa in the rat. J. Nutr. 118:1391–1397.
Gilardi, J. D., and Munn, C. A. 1998. Patterns of activity, flocking, and habitat use in parrots of the Peruvian Amazon. Condor 100(4):641–653.
Gionfriddo, J. P., and Best, L. B. 1995. Brit use by house sparrows: Effects of diet and grit size. Condor 97:57–67.
Goodman, L. S., Gilman, A., and Gilman, A. G. 1990. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed. Pergamon Press, New York.
Grandjean, D., CrÉpin, F., and Paragon, B. M. 1992. Intérêt de la smectite dans les diarrhées aiguës du chien de traîneau. Rec. Méd. Vét. 168(5):323–329.
Heimenz, P. C. 1986. Principles of Colloid and Surface Chemistry, 2nd ed. Marcel Dekker, New York.
Heymann, E. W., and Hartman, G. 1991. Geophagy in moustached tamarins, Saguinus mystax (Platyrrhini: Callitrichidae), at the Río Blanco, Peruvian amazonia. Primates 32(4):533.
Hladik, C. M., and Gueguen, L. 1974. Géophagie et nutrition minérale chez les primates sauvages. C. R. Acad. Sci. Ser. D. 279:1393–1396.
Holliman, A. 1985. Acorn poisoning in ruminants. Vet. Rec. 116:546.
Hunter, J. 1993. Macroterme geophagy and pregnancy clays in southern Africa. J. Cult. Geogr. 14(1):69–92.
Hunter, J. M. 1973. Geophagy in Africa and the United States: A culture-nutrition hypothesis. Geogr. Rev. 63:170–195.
Hunter, J. M., and De Kleine, R. 1984. Geophagy in Central America. Geogr. Rev. 74:157–169.
Huntington, G. B., Emerick, R. J., and Embry, L. B. 1977. Sodium bentonite or sodium bicarbonate as aids in feeding high-concentrate diets to lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 46(4):804–811.
Hwang, E. K., Kwon, Y. B., Jean, Y. H., Im, H. U., Hyun, K. J., Kim, K. S., Yang, C. B., and Bak, Y. K. 1991. Experimental studies on blue Japanese oak (Quercus glauca) poisoning in mixed beef cattle: 2. Pathological changes of cattle being fed a blue Japanese oak. Res. Rep. Rural Dev. Admin. (Suweon) 33(2 VET):35–40.
Izawa, K. 1993. Soil-eating in Aouatta and Ateles. Int. J. Primatol. 14(2):229–242.
Janitzky, P. 1986. Cation-exchange capacity. USGS Bull. 1648:21–23.
Johns, T. 1986. Detoxification function of geophagy and domestication of the potato. J. Chem. Ecol. 12(3):635–646.
Johns, T. 1990. With Bitter Herbs They Shall Eat It: Chemical Ecology and the Origins of Human Diet and Medicine. University of Arizona Press, Tuscon.
Johns, T., and Duquette, M. 1991. Traditional detoxification of acorn bread with clay. Ecol. Food Nutr. 25(3):221–228.
Jones, R. L., and Hanson, H. C. 1985. Mineral Licks, Geophagy, and Biogeochemistry of North American Ungulates. The Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa.
Kilham, L. 1960. Eating of sand by blue jays. Condor 62:295–296.
Kreulen, D. A. 1985. Lick use by large herbivores: A review of benefits and banes of soil consumption. Mammal Rev. 15(3):107–123.
Laufer, B. 1930. Geophagy. Field Mus. Nat. Hist. Anthropol. Ser. 28(2):1–198.
Leber, W. 1988. A new suspension form of smectite (liquid “Diasorb”) for the treatment of acute diarrhoea: a randomized comparative study. Pharmatherapeutica 5(4):256–260.
Leonard, A., Droy-Lefaix, M. T., and Allen, A. 1994. Pepsin hydrolysis of the adherent mucus barrier and subsequent gastric mucosal damage in the rat: effect of diosmectite and 16,16 dimethyl prostaglandin E2. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 18(6–7):609–616.
Lexomboon, U., Harikul, S., and Lortholary, O. 1994. Control randomized study of rehydration-rehydration with dioctahedral smectite in ambulatory Thai infants with acute diarrhea. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 25(1):157–162.
Lumeij, J. T. 1994. Gastroenterology, pp. 482–521, in B. W. Ritchie, G. J. Harrison, and L. R. Harrison (eds.). Avian Medicine: Principles and Application. Wingers, Lake Worth, Florida.
Mahaney, W. C., Hancock, R. G. V., Aufreiter, S., and Huffman, M. A. 1996. Geochemistry and clay mineralogy of termite mound soil and the role of geophagy in chimpanzees of the manhale mountains, Tanzania. Primates 37(2):121–134.
MacRoberts, M. H., and MacRoberts, B. R. 1976. Social organization and behavior of the Acorn Woodpecker in central coastal California. Ornithol. Monogr. 21:1.
Marlow, R. W., and Tollestrup, K. 1982. Mining and exploitation of natural mineral deposits by the desert tortoise, Gopherus agassizii. Anim. Behav. 30:475–478.
Martuscelli, P. 1995. Ecology and conservation of the Red-tailed Amazon Amazona brasiliensis in south-eastern brazil. Bird Conserv. Int. 5(2–3):405–420.
McIlhenny, E. A. 1932. The blue goose in its winter home. Auk 49:279–306.
McInnes, R. S., and Carne, P. B. 1978. Predation of cossid moth larvae by yellow-tailed black cockatoos causing losses in plantations of Eucalyptus grandis in north coastal New South Wales. Austr. Wildl. Res. 5:101–121.
Mendel, V. E. 1971. Montmorillonite clay in feed lot rations. J. Anim. Sci. 33(4):891–894.
Mitchell, D., Wells, C., Hoch, N., Lind, K., Woods, S. C., and Mitchell, L. K. 1976. Poison induced pica in rats. Physiol. Behav. 17:691–697.
Mitjavila, S., Lacombe, C., Carrera, G., and Derache, R. 1977. Tannic acid and oxidized tannic acid on the functional state of rat intestinal epithelium. J. Nutr. 107:2113–2121.
Mole, S., and Waterman, P. G. 1986. Tannins as antifeedants to mammalian herbivores—still an open Question? pp. 572–587, in G. R. Waller (ed.). Allelochemicals: Role in Agriculture and Forestry. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.
More, J., Penazet, F. Fioramonti, J., and Droy-Lefaix, M. T. 1987. Effects of treatment with smectite on gastric and intestinal glycoproteins in the rat a histochemical study. Histochem. J. 19(12):665–670.
Munn, C. A. 1988. Macaw biology in Manu National Park, Peru. Parrotletter 1:18–21.
Munn, C. A. 1992. Macaw biology and ecotourism, or “when a bird in the bush is worth two in the hand,” pp. 47–72, in S. R. Beissinger and N. F. R. Snyder (eds.). New World Parrots in Crisis: Solutions from Conservation Biology. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C.
Norconk, M. A., Wertis, C., and Kinzey, W. G. 1997. Seed predation by monkeys and macaws in eastern Venezuela: Preliminary Findings. Primates 38(2):177–184.
Oates, J. F. 1978. Water-plant and soil consumption by guerza mankeys (Colobus guereza): A relationship with minerals and toxins in the diet. Biotropica 10(4):241–253.
Ortiz, L. T., Alzueta, C., TreviÑo, J., and CastaÑo, M. 1994. Effects of faba bean tannins on the growth and histological structure of the intestinal tract and liver of chicks and rats. Br. Poult. Sci. 35:743–754.
Pendergast, B. A., and Boag, D. A. 1970. Seasonal changes in diet of spruce grouse in central Alberta. J. Wildl. Manage. 34(3):605–611.
Pryce, E. 1994. Grey Iouries Corythaixoides concolor feeding on clay. Babbler 26–27:23–24.
Rateau, J. G., Margant, G., Droy-Priot, M. T., and Parier, J. L. 1982. A histological enzymatic and water-electrolyte study of the action of smectite, a mucoprotective clay, on experimental infectious diarrhoea in the rabbit. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 8:233–241.
Robinson, S. K. 1994. Habitat selection and foraging ecology of raptors in Amazonian Peru. Biotropica 26(4):443–458.
Ronald, B. 1984. Comparison of quinidine assays on the TDx®, Optimate®, Cobas®, and Murtistat III®. Clin. Chem. 30(6):1020.
Roth, P. 1984. Repartição do habitat entre psitacídeos simpátricos no del sul da Amazonica. Acta Amazon. 14(1–2):175–221.
Sazima, I. 1989. Peach-fronted parakeet feeding on winged termites. Wilson Bull. 101(4):656–657.
Sick, H. 1993. Birds in Brazil: A Natural History. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey.
Smith, M. 1979. Behaviour of the koala, Phascolarctos cimereus Goldfuss, in captivity I. Non-social behaviour. Aust. Wildl. Res. 6:117–129.
Sokol, O. M. 1971. Lithophagy and geophagy in reptiles. J. Herpetol. 5:69–71.
Solis, P. N., Wright, C. W., Anderson, M. M., Gupta, M. P., and Phillipson, J. D. 1993. A microwell cytotoxicity assay using Artemia-Salina brine shrimp. Planta Med. 59(3):250–252.
Stahl, A. B. 1984. Hominid dietary selection before fire. Curr. Anthrpol. 25(2):151–168.
Struhsaker, T. T., Cooney, D. O., and Siex, K. S. 1997. Charcoal consumption by Zanzibar red colobus monkeys: Its function and its ecological and demographic consequences. Int. J. Primatol. 18(1):61–72.
Takeda, N., Hasegawa, S., Morita, M., and Matsunaga, T. 1993. Pica in rats is analogous to emesis: An animal model in emesis research. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 45(4):817–821.
Terborgh, J. 1983. Five New World primates: A Study in Comparative Ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey.
Terborgh, J. 1986. Community aspects of frugivory in tropical forests, pp. 371–384, in A. Estrada and T. H. Fleming (eds.). Frugivores and Seed Dispersal. Dr. W. Junk Publishers, Dordrecht.
Verbeek, N. A. M. 1995. The use of grit in pipits, especially the American pipit. J. Field Ornithol. 65(4):498–503.
Vermeer, D. E., and Ferrell, R. E. J. 1985. Nigerian geophagical clay: A traditional antidiarrheal pharmaceutical. Science 227:634–636.
Vivatvakin, B., Jongpipatvanich, S., Harikul, S., Eksaengri, P., and Lortholary, O. 1992. Control study of oral rehydration solution ors-ors plus dioctahedral smectite in hospitalized Thai infants with acute secretory diarrhea. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 23(3):414–419.
Watts, D. W. 1994. In vitro buffering capacities of proprietary non-particulate antacids available in New Zealand. Anaesth. Intens. Care 22(2):184–186.
Wang, X., LÁztity, A., VicziÁn, M., Isreal, Y., and Barnes, R. 1989. Inductively coupled plasma spectrometry in the study of childhood soil ingestion: part 1. methodology. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 4:727–735.
Whittig, L. D., and Allardice, W. R. 1986. X-ray diffraction techniques. In A. Klute (ed.). Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin.
Weisman, A., and Thompson, H. 1984. Acorn poisoning. Vet. Rec. 115:605.
Wyndham, E., and Cannon, C. E. 1985. Parrots of eastern Australian forests and woodlands: The genera Platycercus and Trichoglossus, pp. 141–150, in A. Keast, H. F. Recher, H. Ford, and D. A. Saunders (eds.). Birds of Eucalypt Forests and Woodlands: Ecology, Conservation and Management. Royal Australian Ornithologists Union and Surrey Beatty and Sons.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilardi, J.D., Duffey, S.S., Munn, C.A. et al. Biochemical Functions of Geophagy in Parrots: Detoxification of Dietary Toxins and Cytoprotective Effects. J Chem Ecol 25, 897–922 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020857120217
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020857120217