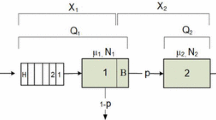
Abstract
Traditionally, studies on tandem queueing networks concentrate on systems with infinite buffers, exponential service times, and/or single servers where solutions are more tractable. Less research can be found on more general, less tractable systems. We examine multiple‐server systems with finite buffers and non‐exponential service times, studying the effects of coefficient of variation (cv) of the service‐time distribution on the throughput of these systems, where cv differs among stations.
Starting with the single station, we examine the effects of cv and the number of servers at the station on the distribution of interdeparture times. This insight helps explain the differences in throughput seen in the single (fast) server vs. multiple (slow) server problem. These results, in turn, shed light on the server allocation problem when cv differs among stations. We present some observations, as well as the intuition behind them.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.L. Albin, Approximating a point process by a renewal process, II: superposition arrival processes to queues, Operations Research 32 (1984) 1133–1162.
Y. Dallery and Y. Frein, On decomposition methods for tandem queueing networks with blocking, Operations Research 41 (1993) 386–399.
H. Damerdji and P.W. Glynn, Performance analysis of future event sets, Technical Report No. 95–2, Department of Operations Research, Stanford University (1995).
T.E. El-Rayah, The effect of inequality of interstage buffer capacities and operation time variability on the efficiency of production line systems, International Journal of Production Research 17 (1979) 77–89.
C. Heavy, H.T. Papadopoulos and J. Browne, The throughput rate of multistation unreliable production lines, European Journal of Operational Research 68 (1993) 69–89.
D.P. Heyman and M.J. Sobel, Stochastic Models in Operations Research, Vol. I: Stochastic Processes and Operating Characteristics (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1982) pp. 158–161.
F.S. Hillier and R.W. Boling, The effect of some design factors on the efficiency of production lines with variable operation times, Journal of Industrial Engineering 17 (1966) 651–658.
F.S. Hillier and R.W. Boling, Finite queues in series with exponential or Erlang service times-A numerical apporach, Operations Research 15 (1967) 286–303.
F.S. Hillier and R.W. Boling, Toward characterizing the optimal allocation of work in production line systems with variable operation times, in: Advances in Operations Research, Proceedings of EURO II, ed. M. Roubens (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1977) pp. 109–119.
F.S. Hillier and R.W. Boling, On the optimal allocation of work in symmetrically unbalanced production line systems with variable operations times, Management Science 25 (1979) 721–728.
F.S. Hillier and K.C. So, The assignment of extra servers to stations in tandem queueing systems with small or no buffers, Performance Evaluation 10 (1989) 219–231.
F.S. Hillier and K.C. So, Some data for applying the bowl phenomenon to large production line systems, International Journal of Production Research 31 (1993) 811–822.
F.S. Hillier and K.C. So, On the optimal design of tandem queueing systems with finite buffers, Queueing Systems 21 (1995) 245–266.
F.S. Hillier and K.C. So, On the simultaneous optimization of server and work allocations in production line systems with variable operation times, to appear in Operations Research.
G.C. Hunt, Sequential arrays of waiting lines, Operations Research 4 (1956) 674–683.
L. Kerbache and J.M. Smith, The generalized expansion method for open finite queueing networks, European Journal of Operational Research 32 (1987) 448–461.
H. Lau, On balancing variances of station processing times in unpaced lines, European Journal of Operational Research 56 (1992) 345–356.
M.J. Magazine and K.E. Stecke, Throughput for production lines with serial work stations and parallel service facilities, Performance Evaluation 25 (1996) 211–232.
E.J. Muth and A. Alkaff, The bowl phenomenon revisited, International Journal of Production Research 25 (1987) 161–173.
H.T. Papadopoulos, C. Heavy and M.E.J. O'Kelly, Throughput rate of multistation reliable production lines with inter station buffers: (I) Exponential case, Computers in Industry 13 (1989) 229–244.
H.T. Papadopoulos, C. Heavy and M.E.J. O'Kelly, Throughput rate of multistation reliable production lines with inter station buffers: (II) Erlang case, Computers in Industry 13 (1990) 317–335.
N.P. Rao, A generalization of the 'bowl phenomenon' in series production systems, International Journal of Production Research 14 (1976) 437–443.
A. Singh and J.M. Smith, Buffer allocation for an integer nonlinear network design problem, Computers Oper. Res. 24 (1997) 453–472.
D. Spinellis, H.T. Papadopoulos and J. MacGregor Smith, Large production line optimization using simulated annealing, to appear in International Journal of Production Research.
W. Whitt, Approximating a point process by a renewal process, I: Two basic methods, Operations Research 30 (1982) 125–147.
W. Whitt, Approximations for departure processes and queues in series, Naval Research Logistics Quarterly 31 (1984) 499–521.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Futamura, K. The multiple server effect: Optimal allocation of servers to stations with different service‐time distributions in tandem queueing networks. Annals of Operations Research 93, 71–90 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018948512499
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018948512499