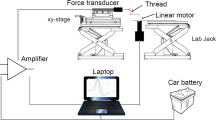
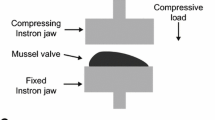
Abstract
Mechanical properties of the dragline and the capture thread for the spider Nephila clavata, called Jorougumo in Japan, were investigated and the effect of ultraviolet rays and acid rain on their strength was studied to consider the applicability to the environmental assessment of the habitat of the spider. It was shown that (1) the dragline, which has a fracture stress of about 1500 MPa, a fracture strain of about 0.3 and a modulus of about 10 GPa, is almost equivalent to the best man-made fibres such as aramid fibres, (2) the load-strain curve for the capture thread is J-shaped and its fracture strain amounts to more than 200%, whereas the endurance load is much smaller than that for the dragline, (3) a wonderful mechanism for the capture thread termed the “windlass system” by Vollrath and Edmonds, was reconfirmed, and (4) the irradiation by ultraviolet rays and exposure to quasi-acid rain induced degradation of the thread.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. M. GOSLINE, M. E. DEMONT and M. DENNY, Euroarticle 10 (1986) 37.
M. YOSHIKURA, “The Biology of Spiders” Gakkai shuppan Center, Tokyo 1987 (in Japanese).
M. DENNY, J. Exp. Biol. 65 (1976) 483.
R. W. WORK, Textile Res. J. 46 (1976) 485.
Idem, ibid. 47 (1977) 650
P. M. CUNNIF, S. A. FOSSEY, M. A. AUERBACH and J. W. SONG, in “Silk Polymers: Materials Science and Biotechnology“, ACS Symposium series, American Chemical Society, Washington, 544 (1993).
M. KITAGAWA, H. SASAGAWA and T. KITAYAMA, J. Soc Mater. Sci. Jpn. 44 (1995) 153.
M. KITAGAWA, H. SASAGAWA and M. KAWAGOE, ibid. 45 (1995) 1445.
D. V. MAHONEY, D. L. VESIE, R. K. EBY, W. W. ADAMS and D. L. KAPLAN, in “Silk Polymers: Material Science and Biotechnology”, ACS Symposium series, American Chemical Society, Washington, 544 (1993).
M. A. BECKER, D. V. MAHONEY, P. G. LENHERT, R. K. EBY, D. L. KAPLAN and W. W. ADAMS, in “Silk Polymers: Material Science and Biotechnology”, ACS Symposium series, American Chemical Society, Washington, 544 (1993).
S. J. LOMBARDI and D. L. KAPLAN, J. Arachnol. 18 (1990) 297
K. KERKAM, C. VINEY, D. L. KAPLAN and S. LOMBARDI, Nature 349 (1991) 596.
K. MURANO, “ Acid rain and acid mist” (Shoukabou, Tokyo 1993) (in Japanese).
J. HOJOU, “ Structure of silkworm silk” (Department of Textile Engineering, Tokyo 1980) (in Japanese).
P. CALVERT, Nature 340 (1989) 266
F. VOLLRATH and D. EDMONDS, ibid. 340 (1989) 305.
J. HAYAKAWA, “Life and its prediction of high polymers” (I.P.C., Tokyo 1989) (in Japanese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KITAGAWA, M., KITAYAMA, T. Mechanical properties of dragline and capture thread for the spider Nephila clavata. Journal of Materials Science 32, 2005–2012 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018550116930
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018550116930