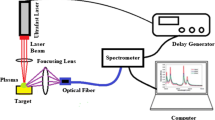
Abstract
A new all-spectroscopic method for depth-resolved thermal diffusivity measurement of metallic specimens has been demonstrated. The method entails measurement of the mass entrained into a laser-produced plasma (LPP) plume in such a manner that the plume is representative of the specimen in elemental composition. Both the abundance of matter and its elemental composition are measured by time-resolved spectroscopy for each LPP plume. In order to delineate the morphology versus composition basis of the depth dependence, a new study on a Nichrome ribbon specimen heated by ohmic heating in a vacuum is presented. A set of depth-resolved thermal diffusivity measurements is carried out, while noting the attendant changes in the spectral emissivity and elemental composition at succeeding ablation layers. Additional measurements are carried out after the specimen has been treated under varying heating conditions. Preferential diffusion of chromium at high temperatures has been found to contribute to the dynamics of surface thermophysical properties at high temperatures. Representative LPP ablation is well suited for removal of surface impurities prior to thermophysical property measurements by the pulse heating technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Y. W. Kim, in Laser-Induced Plasmasand Applications, L. J. Radziemski and D. A. Cremers, eds. (Marcell Dekker, New York, 1989), Chap. 8.
Y. W. Kim, High Temp. Sci. 26:57 (1990).
Y. W. Kim,in Intelligent Processing of Materials, H. G. N. Wadley and W. E. Eckhart, eds. (The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 1990), p. 317.
Y. W. Kim,in Advanced Sensing, Modeling, and Control of Materials Processing, E. F. Mattys and B. Kushner, eds. (TMS, Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 1992), p. 44.
Y. W. Kim and C. S. Park, Int. J. Thermophys. 17:713 (1996).
Y.W. Kim, and C. S. Park., Int. J. Thermophys. 17:1125 (1996).
Y. W. Kim, Int. J. Thermophys. 20:1315(1999).
Y. W. Kim, in Thermal Conductivity 25/ThermalExpansion 13, C. Uher and D. Morelli, eds. (Technomic Publishing, Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 2000), p. 15.
Y. W. Kim, Int. J. Thermophys. 14:397 (1993).
D. E. Gray, ed., AIP Handbook, 3rd Ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1972).
W. E. Forsythe, Smithsonian Physical Table, 9thEd. (The Smithsonian Institution, Washington, 1954).
W. M. Rohsenow, J. P. Hartnett, and Y. I. Cho, Handbook ofHeat Transfer, 3rd Ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1998), Chap. 16.
H. E. Boyer and T. L. Gall, eds. Metals Handbook(ASM, Metals Park, 1985).
D. L. Lide, ed.,Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 75th Ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 1994).
F. Righini, J. Spisiak, and G.C. Bussolino, Int. J. Thermophys. 20:1095 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.W. Effects of Surface Morphology and Composition Modification on Spectral Emissivity and Thermal Diffusivity Profile at High Temperatures. International Journal of Thermophysics 23, 1103–1113 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016398205153
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016398205153