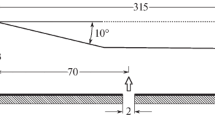
Abstract
2nd-order upwind TVD scheme was used to solve the laminar, fully Navier-Stokes equations. The numerical simulations were done on the propagation of a shock wave with Ma S = 2 and 4 into a hydrogen and air mixture in a duct and a duct with a rearward step. The results indicate that a swirling vortex may be generated in the lopsided interface behind the moving shock. Meanwhile, the complex shock system is also formed in this shear flow region. A large swirling vortex is produced and the fuel mixing can be enhanced by a shock wave at low Mach number. But in a duct with a rearward step, the shock almost disappears in hydrogen for Ma S = 2. The shock in hydrogen will become strong if Ma S is large. Similar to the condition of a shock moving in a duct full of hydrogen and air, a large vortex can be formed in the shear flow region. The large swirling vortex even gets through the reflected shock and impacts on the lower wall. Then, the distribution of hydrogen behind the rearward step is divided into two regions. The transition from regular reflection to Mach reflection was observed as well in case Ma S = 4.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drummond J P, Hussaini. Numerical simulation of a supersonic reacting mixing layer[A]. AIAA Paper, 87-1325,1987.
Roshko A. Structure of the turbulent shear flow: New Look[J]. AIAA J,1976,14(10):1349.
Guiguis R H, Grinstein F F, Young T R, et al. Mixing enhancement in supersonic shear layers[A] AIAA Paper, 87-0373,1987.
LIU Jun. GAO Shu-chun. Numerical study on supersonic free shear layers[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 1995,13(2):152-158. (in Chinese)
Yee H C, Klopeer G H, Montagne J L. High-Resolution Shock-capturing schemes for inviscid and viscous hypersonic flows[J]. J Comput Phys,1990,88:31-61.
Gordon S, McBride D J. Computer program for a calculation of complex chemical equilibrium compositions, rockets performance, incident and reflected shocks, Chapman-Joudguet detonations[A]. NASA SP-273,1971.
Eklund D R, Stouffer S D. A numerical and experimental study of a supersonic combustor employing swept ramp fuel injectors[A]. AIAA Paper 94-2819,1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Sl., Yue, Pt. & Han, Zy. Study on the Fuel Air Mixing Induced by a Shock Wave Propagating into a H2-Air Interface. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics 22, 460–467 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016353802422
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016353802422