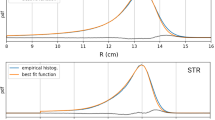
Abstract
Two colour laser ranging to artificial satellites is an attractivetechnique, which is capable to provide refraction corrected ranges without the need of an atmospheric model by measuring the dispersive delay of laser pulses of different wavelength. Although the required accuracy of the detection scheme is stringent, the technique has matured so far, that routine two colour observationsbecame feasible.The present paper describes a normal point procedure reducing two colour laser range observations with respect to the dispersive delay,exploiting the knowledge of satellite response signatures in conjunction with detector characteristics and the appropriate center of mass correction models.Moreover the dispersion model of the atmosphere is briefly reviewed, paying attention to the wavelength domains provided by modern twocolour ranging lasers, e.g., the Ti:SAP laser.Preliminary data is presented and compared to both, normal point data reduced with a standard procedure and zenith path equivalent meteorological parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrel, H. and Sears, J.E.: 1939, The refraction and dispersion of air for the visible spectrum, Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. London, Bd. A238, 6–62.
Edlen, B.: 1966, The refractive index of air, Metrologia 2, 71–80.
Fitzmaurice, M.W. et al.: 1977, Prelaunch Testing of the Laser Geodynamic Satellite (LAGEOS), NASA Technical Paper 1062.
Greene, B.A. and Herring, T.A.: 1986, Multiple Wavelength Laser Ranging, Sixth International Workshop on Laser Ranging Instrumentation, Antibes.
Lucchini, C.: 1995, Telemetrie laser deux couleurs, Ph.D. thesis, University of Nice, France.
Marini, J.W. and Murray, C.W., Jr: 1973, Correction of laser range tracking data for atmospheric refraction at elevations above 10 degrees, NASA–TM–X-70555.
Owens, J.C.: 1967, Optical refractive index of air: Dependence on pressure, temperature and composition, Appl. Opt. 6, 51–59.
Riepl, S. and Schreiber, U.: 1997, WLRS streak camera experiment, in U. Schreiber and C. Werner (eds.), Laser Radar Ranging and Atmospheric Lidar Techniques, Proc. SPIE 3218.
Schreiber, U., Maier, W., and Riepl, S.: 1994, Measuring atmospheric dispersion employing avalanche photodiodes, in C. Werner (ed.), Lidar Techiques for Remote Sensing, Proc. SPIE 2310, p. 2.
Zagwodzki, T.W., McGarry, J.F., and Degnan, J.J.: 1997, Two color SLR experiments at the GSFC 1.2-m telescope, in U. Schreiber and C. Werner (eds.), Laser Radar Ranging and Atmospheric Lidar Techniques, Proc. SPIE 3218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riepl, S., Schlüter, W. Normal Point Algorithm For Reduction Of Two Colour Slr Observations. Surveys in Geophysics 22, 581–588 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015696907252
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015696907252