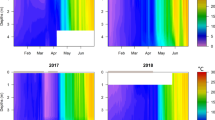
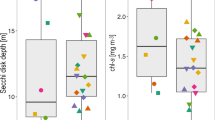
Abstract
The general model of seasonal phytoplankton succession in temperate lakes suggests that winter phytoplankton growth is minimal under ice-cover. However, some studies have found diverse phytoplankton communities during winter. The primary objectives of this study were to determine the species composition and the changes in the winter phytoplankton community structure under the ice. For 2 consecutive winters, phytoplankton samples were collected under ice-cover at 4 sites on 3 lakes in Arrowwood National Wildlife Refuge (ANWR), near Pingree, North Dakota. Ninety taxa were identified and enumerated. Densities of several of these taxa frequently exceeded 106 cells l−1. The winter phytoplankton communities in these lakes were dominated by flagellates, principally cryptomonads, a synurophyte (Synura uvella), small chrysophytes (Chrysococcus spp., Kephyrion spp.) and a dinoflagellate (Peridinium aciculiferum), as well as non-flagellate microchlorophytes (Monoraphidium spp., Ankistrodesmus spp., and Pseudodictyosphaerium sp.), a cyanobacterium (Gloeocapsa aeruginosa) and centric diatoms (Stephanodiscus minutulus, S. parvus and Cyclotella meneghiniana).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbeti, M. D. & J. P. Smol. 1995. Winter limnology: a comparison of physical, chemical and biological characteristics in two temperate lakes during ice cover. Hydrobiologia 304: 221–234.
Bolsenga, S. J. & H. A. Vanderploeg, 1992. Estimating photosynthesis available radiation into open and and ice-covered freshwater lakes from surface characteristics; a high transmittance case study. Hydrobiologia 243/244 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 79): 95–104.
Bourrelly, P., 1968. Les algues'eau douce. Tome 2. Les Algues jaunes and brunes. Chrysophycées, Phéophycées, Xanthophycées et Diatomées. Boubée et Cie, Paris: 438 pp.
Bourrelly, P., 1970. Les algues d'eau douce. Tome 3. Les Algues bleues et rouges. Les Eugléniens, Peridiniens et Cryptomonadines. Boubée et Cie, Paris: 512 pp.
Brunnthaler, J., 1900. Plankton-Studien. I. Das Phytoplankton des Donaustromes bei Wien. Verhandl. D. k. k. zool.-botan. Ges. Wien. 50: 308–311.
Clesceri, L. S., A. E. Greenberg & R. R. Trussell (eds), 1989. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association. Washington: 1193 pp.
Cloern, J. E., A. E Alpine, B. E. Cole & T. Heller, 1992. Seasonal changes in the spatial distribution of phytoplankton in small, temperate-zone lakes. J. Plankton Res. 14: 1017–1024.
Cox, E. J., 1996. Identification of Freshwater Diatoms from Live Material. Chapman & Hall, London: 158 pp.
Dodd, J. J., 1987. Diatoms. Southern Illinois University Press, Carbondale: 477 pp.
Ettl, H. & G. Gärtner, 1995. Syllabus der Boden-, Luft-, und Flechtenalgen. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart: 721 pp.
Gojdics, M., 1953. The Genus Euglena. University of Wisconsin, Madison: 268 pp.
Griffith, M. B. & S. A. Perry, 1995. Between-year variation of periphyton community structure in two Appalachian headwater streams. Hydrobiologia 302: 1–9.
Hanson, D. A., 1978. Chemical and physical characteristics of the James River from Arrowwood Refuge to the outflow of Jamestown Dam, North Dakota. M.S. thesis. North Dakota State University, Fargo: 77 pp.
Happey-Wood, C. M., 1991. Ecology of freshwater plankton green algae. In Sandgren, C. D. (ed.), Growth and Reproductive Strategies of Freshwater Phytoplankton, Cambridge University Press: 175–226.
Hasle, G. R., 1978. Using the inverted microscope. In Sornia, A. (ed.) Monographs on Oceanographic Methodology. no. 6. Phytoplankton Manual, Unesco Press: 194 pp.
Hindák, F., 1970. A contribution to the systematics of the family Ankistrodesmaceae (Chlorophyceae). Algol. Stud. (TÍeboá) 1: 7–32.
Hindák, F., 1988. Studies on the Chlorococcal Algae (Chlorophyceae) 4. VEDA, Bratislava, 263 pp.
Hutchinson, G. E. 1967. A Treatise on Limnology. 2. Introduction to Lake Biology and the Limnoplankton. John Wiley, New York: 1115 pp.
Jones, R. I. & V. Ilmavirta, 1978. Vertical and seasonal variation of phytoplankton photosynthesis in a brown-water lake with winter ice cover. Freshwat. Biol. 8: 561–572.
Kalff, J., H. J. Kling, S. H. Holmgren, & H. E. Welch, 1975. Phytoplankton, phytoplankton growth and biomoass cycles in an unpolluted and in a polluted polar lake. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 487–495.
Keefer, V. M. & R. W. Pennak, 1977. Plankton and seston of a Colorado (U.S.A.) alpine lake: the winter anomaly and the inlet-outlet budget. Int. Rev. ges. Hydrobiol. 62: 255–278.
Kofoid, C. A., 1908., The plankton of the Illinois River, 1894–1899, with introductory notes upon the hydrography of the Illinois River and its basin. Part 2. Constituent organisms and their seasonal distribution. Bull. Ill. State Lab. Nat. Hist. 8: 1–354.
Korshikov, O. A., 1987. The Freshwater Algae of the Ukranian SSR. V. Sub-Class Protococcineae, Vacuolales and Protococcales. Koeltz Scientific Books, Koenigstein, West Germany: 412 pp.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1991a. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Bacillariophyceae. 3. Teil: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart: 576 pp.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1991b. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Bacillariophyceae. 4. Teil: Achnanthaceae. Kritische Ergänzungen zu Navicula (Lineolatae) und Gomphonema. Gesamtliteraturerzeichnis für Teil 1–4). Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart: 437 pp.
Krammer, K. and H. Lange-Bertalot, 1997a. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Bacillariophyceae. 1. Teil: Naviculaceae. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart: 876 pp.
Krammer, K. and H. Lange-Bertalot,1997b. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa. Bacillariophyceae. 2. Teil: Bacillariaceae, Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart: 610 pp.
Komárková-Legnerová, J., 1969. The systematics and ontogenesis of the genera Ankistrodesmus Corda and Monoraphidium gen. nov. In Fott, B. (ed.), Studies in Phycology. Academia: 75–144.
Lecewicz, W., W. Sokotowska & I. Wojciechowski, 1973. The changes of winter phytoplankton in relation to the light climate in the lakes with various trophy. Ekol. Pol. 21: 193–208.
Marsson, M., 1900. Zur Kenntnis der Planktonverältnisse einiger Gewässer der Umgebung von Berlin. Forschungsber. aus der Biol. Station zu Plön 8: 86–119.
Nauwerck, A., 1963. Die beziehungen zwischen Zooplankton und Phytoplankton im See erken. Sym. Bot Upsalienses 17: 1–163.
Nebaeus, M., 1984. Algal water-blooms under ice-cover. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 22: 719–724.
Németh, J., 1997a. A Guide for the Identification of Euglenophyta occurring in Hungary, 1. K.G.I., Budapest: 352 pp.
Németh, J., 1997b. A Guide for the Identification of Euglenophyta occurring in Hungary, 2. K.G.I., Budapest: 254 pp.
Phillips, K. A., 1998. Phytoplankton community structure under ice in shallow North Dakota lakes. PhD thesis. North Dakota State University, Fargo 96 pp.
Phillips, K. A. & M. W. Fawley, 2001. Diversity of coccoid algae in shallow lakes during winter. Phycologia 39: 498–506.
Prescott, G. W., 1978. How to Know the Freshwater Algae. Wm. C. Brown, Dubuque: 293 pp.
Prescott, G. W., 1982. Algae of the Western Great Lakes Area. Koenigstein, West Germany: 977 pp.
Rengefors, K., Seasonal succession of dinoflagellates coupled to the benthic cyst dynamics in Lake Erken, Sweden. Arch. Hydrobiol. Spec. Issues Advanc. Limnol. 51: 123–141.
Round, F. E., R. M. Crawford & D. G. Mann, 1990. The Diatoms: Biology and Morphology of the Genera. Cambridge University Press, New York: 747 pp.
Skuja, H., 1948. Taxonomie des Phytoplanktons einiger Seen in Uppland, Schweden. Symbol. Bot. Upsal. 9: 1–399.
Spaulding, S. A., J. V. Ward & J. Baron, 1993.Winter phytoplankton dynamics in a subalpine lake, Colorado, U.S.A. Arch. Hydrobiol. 129: 179–198.
Starmach, K., 1985. Süßwasser von Mitteleuropa. Chrysophyceae und Haptophyceae. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart: 721 pp.
Stewart, A. J. & R. G. Wetzel, 1986. Cryptophytes and other micro-flagellates as couplers in planktonic community dynamics. Arch. Hydrobiol: 106: 1–19.
Taylor, F. J. R., 1987. Dinoflagellate morphology. In Taylor, F. J. R. (ed.), The Biology of Dinoflagellates. Blackwell Scientific Publ.: 24–91.
Throndsen, J., 1978. Preservation and storage. In Sornia, A. (ed.), Monographs on Oceanographic Methodology. No. 6. Phytoplankton Manual. Unesco Press: 69–71.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, 1997. Arrowwood National Wildlife Refuge, Pingree, North Dakota. http://www.r6.fws.gov/ REFUGES/ARROWWOO.HTM.
Verduin, J., 1959. Photosynthesis by aquatic communities in northwestern Ohio. Ecology 40: 377–383.
Wetzel, R. G., 1966. Variations in productivity of Goose and hypereutrophic Sylvan lakes, Indiana. Invest. Indiana Lakes & Streams 7: 147–184.
Wetzel, R. G., 1983. Limnology. Saunders, New York: 753 pp.
Wetzel, R. G. & G. E. Likens, 1991. Limnological Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York: 139–140.
Wiedner, C. & B. Nixdorf, 1998. Success of chrysophytes, cryptophytes and dinoflagellates over blue-greens (cyanobacteria) during an extreme winter (1995/96) in eutrophic shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 369/370: 229–235.
Wojciechowska, W., W. Pęczula & A. Zykubek, 1998. Eutrophication and winter-period structure of phytoplankton in three deep lakes in the Leczna-Włodawa Lakeland, Eastern Poland. Pol. J. Ecol. 46: 89–99.
Wright, R. T., 1964. The dynamics of a phytoplankton community in an ice-covered lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 9: 163–178.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phillips, K.A., Fawley, M.W. Winter phytoplankton community structure in three shallow temperate lakes during ice cover. Hydrobiologia 470, 97–113 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015667803372
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015667803372