Abstract
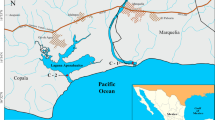
Studies on marine sediments are extremely important since they act as ultimate sink of anthropogenic pollutants. The present study was conducted near Mumbai city of India to understand andassess the behaviour and fluxes of trace and toxic elements increek sediment. Seven sediment core samples were collected andanalysed for trace and toxic elements such as Fe, Cu, Pb, Zn, Rb and Sr in different sections of the core using EDXRF technique. The fluxes of the elements in each section of the core were calculated using the mass sedimentation rates derivedfrom 210Pb dating technique and the sediment density at each location. The estimated depositional fluxes of Fe, Rb and Sr in Zone-1 and Zone-3 are in the ranges of 0.4–0.5% cm-2yr-1; 4–6 μg cm-2 yr-1 and 10–20 μg cm-2 yr-1 respectively, where as they were about 3–4 times higher in zone-2 for the same elements. The depositionalfluxes of elements Cu (40–60 μg cm-2 yr-1), Zn (35–43 μg cm-2 yr-1) and Pb (6–12 μg cm-2 yr-1) were also found to be higher in zone-2 compared tozone-1 and zone-3 which can be attributed to the release from thenewly developed chemical zone of Thane-Belapur industrial belt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhosale, U.: 1991, ‘Heavy metals pollution around the Island City of Bombay, India’, Chem. Geol. 90, 285–305.
Forstner U. and Wittmann G. Tt. W.: 1977, Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment, Springer, Berlin, pp. 486.
Forstner, U.: 1980, Inorganic Pollutants Particularly Heavy Metals In Estaurines:Chemistry and Bio-Chemistry of Estuaries, in: E. Olaussan and F. Cato (eds.), JohnWiley and Sons Ltd., pp 307–340.
Geostandards News Letter, Vol. XIII, Special issue July 1989. ISSN: 150–5505.
Jha S. K., Krishnamoorthy T. M., Pandit G. G. and Nambi K. S. V.: 1999, ‘History of accumulation of mercury and nickel in Thane Creek,Mumbai, using 210Pb dating technique’, Sci. Tot. Environ. 236, 91–99.
Mirajkar P., Moily R., Kulkarni V. V., Bhosale V. M. and Krishnamoorthy T. M.: 1995, Preliminary Studies on the Distribution of Heavy Metals in Thane Creek Ecosystem in Relation to Industrial Effluent Discharges, in Proceedings of 4th National Symposium on Environment, February 1995, Madras, India 7–10.
Patel B., Bangera V. S., Patel S. and Balani M. C.: 1985, ‘Heavy metals in the Bombay Harbour Area’, Marine Pollut. Bull. 16, 22–28.
Rath D. S. and Sahu B. K.: 1994, ‘Statistical assessment of geochemical variable and size distribution characteristics of sediment from two estuaries in Mumbai, India’, Int. J. Environ. Stud. 46, 115–142.
Salomons W., Van Driel W., Kerdijk H. and Boxma R.: 1982, ‘Effects of waste disposal on ground water’, Proc Exeter Symp IHAs 39: 255–269.
Suess E. and Erlenkenser H.: 1975, ‘History of metal pollution and carbon input in Baltic Sea sediments’, Meyniana 27, 63–75.
Turkian K. K. and Wedepohl K. H.: 1961, ‘Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth's crust’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 72, 175–192.
Wahlen M. and Thompson R. C.: 1980, ‘Pollution records from sediments of three lakes in New York State’, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 44, 333–339.
Wedepohl K. H. (Editor): 1969-1974, Handbook of Geochemistry, Springer, Berlin.
Wright P. and Mason C. F.: 1999, ‘Spatial and seasonal variation in heavy metals in the sediments and biota of two adjacent estuaries, the Orwell and Stour, in eastern England’, Sci. Tot. Environ. 226, 139–156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, S.K., Chavan, S.B., Pandit, G.G. et al. Behaviour and Fluxes of Trace and Toxic Elements in Creek Sediment Near Mumbai, India. Environ Monit Assess 76, 249–262 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015579913509
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015579913509