Abstract
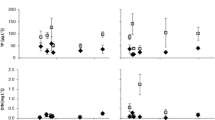
Loading, retention and release of nitrogen and phosphorus were studied for three growing seasons in experimental flow-through pond ecosystems, where impacts of rising temperature on the boreal zone were studied; one pond was under ambient temperature conditions and another was enclosed in a greenhouse with air temperature 2–3 °C higher than ambient. The ponds received a high load of nitrogen (14–18 g N m−2 in June–October) and a moderate load of phosphorus (0.2 g P m−2) from the nearby mesohumic Lake Pääjärvi. During the growing seasons, the ponds retained inorganic nitrogen (NO3–N), and the retention improved in the course of the experiment from 29% to 76% in the greenhouse pond and from 33% to 76% in the reference pond. For total nitrogen (totN), the retention was, however, lower (15–22% in the greenhouse pond and 16–33% in the reference pond). The ponds acted more as sources than sinks for P; with the exception of the greenhouse pond during the first growing season more P was released from than retained in the ponds. During the second and third growing seasons, the release of P exceeded the load of P in the inflow by 65% and 72% in the greenhouse pond and to a lesser extent (by 49% and 32%, respectively) in the reference pond. This was likely due to uptake of P by macrophytes from the sediment, and P released from decaying plants was later utilized by littoral algal communities. In a warmer climate, the uptake of P by macrophytes from sediment may be an important accelerator of eutrophication of lakes in the boreal zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auclair, A. N. D., 1979. Factors affecting tissue nutrient concentrations in a Scirpus-Equisetum wetland. Ecology 60: 337–348.
Balls, H., B. Moss & K. Irvine, 1989. The loss of submerged plants with eutrophication I. Experimental design, water chemistry, aquatic plant and phytoplankton biomass in experiments carried out in ponds in the Norfolk Broadland. Freshwat. Biol. 22: 71–87.
Barko, J. W. & R. M. Smart, 1980. Mobilization of sediment phosphorus by submersed freshwater macrophytes. Freshwat. Biol. 10: 229–238.
Bergström, S. & B. Carlsson, 1994. River runoff to the Baltic Sea: 1950–1990. Ambio 23: 280–287.
Boon, P. I. & B. K. Sorrell, 1991. Biogeochemistry of billabong sediments. I. The effect of macrophytes. Freshwat. Biol. 26: 209–226.
Brix, H. & H.-H. Schierup, 1989. The use of aquatic macrophytes in water-pollution control. Ambio 18: 100–107.
Carignan, R., 1982. An empirical model to estimate the relative importance of roots in phosphorus uptake by aquatic macrophytes. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 39: 234–247.
Carter, T., M. Posch & H. Tuomenvirta, 1995. SILMUSCEN and CLIGEN user's guide. Publications of the Academy of Finland 5/95: 1–62.
Dahlström, B., 1994. Short term fluctuations of temperature and precipitation in Western Europe. In Heino, R. (ed.), Proceedings of the European Workshop on Climate Variations held in Kirkkonummi (Majvik), Finland 15–18 May 1994 Publications of the Academy of Finland 3/94: 30–38.
Danell, K. & K. Sjöberg, 1979. Decomposition of Carex and Equisetum in a northern Swedish lake: dry weight loss and colonization by macro-invertebrates. J. Ecol. 67: 191–200.
Fleischer, S., A. Gustafson, A. Joelsson, J. Pansar & L. Stilbe, 1994. Nitrogen removal in created ponds. Ambio 23: 349–357.
Forsius, M., M. Johansson, M. Posch, M. Holmberg, J. Kämäri, A. Lepistö, J. Roos, S. Syri & M. Starr, 1997.Modelling the effects of climate change, acidic deposition and forest harvesting on the biogeochemistry of a boreal forested catchment in Finland. Boreal Env. Res. 2: 129–143.
Graneli, W., M. Enell & L. Unosson, 1982. Energivass — Rapport Etapp IV (Energy reeds — Report Part IV). Department of Lim76 nology, University of Lund, Sweden (in Swedish with English summary).
Grosse, W., J. Armstrong & W. Armstrong, 1996. A history of pressurised gas-flow studies in plants. Aquat. Bot. 54: 87–100.
Heino, R., H. Tuomenvirta & A. Drebs, 1996. Climatic changes in Northern Europe. In Roos, J. (ed.), The Finnish Research Programme on Climate Change. Final Report. Publications of the Academy of Finland 4/96: 35–40.
Houghton, J. T., L. G. M. Filho, B. A. Callander, N. Harris, A. Kattenberg & K. Maskell (eds), 1996. IPCC/WGI 1995. Climate Change 1995 — Contribution of Working Group I to the Second Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 584 pp.
Jansson, M., R. Andersson, H. Berggren & L. Leonardson, 1994. Wetlands and lakes as nitrogen traps. Ambio 23: 320–325.
Jensen, H. S. & F. Ø. Andersen, 1992. Importance of temperature, nitrate, and pH for phosphate release from aerobic sediments of four shallow, eutrophic lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37: 577–589.
Kairesalo, T., 1983. Photosynthesis and respiration within an Equisetum fluviatile L. stand in Lake Pääjärvi, southern Finland. Arch. Hydrobiol. 96: 317–328.
Kairesalo, T., I. Koskimies, A. Lehtovaara & I. Vähä-Piikkiö, 1985. Consequences of fertilization within a littoral Equisetum fluviatile L. stand in Lake Pääjärvi, southern Finland. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 2904–2908.
Kallio, K., S. Rekolainen, P. Ekholm, K. Granlund, Y. Laine, H. Johnsson & M. Hoffman, 1997. Impacts of climatic change on agricultural nutrient losses in Finland. Boreal Env. Res. 2: 33–52.
Kankaala, P., A. Ojala, T. Tulonen, J. Haapamäki & L. Arvola, 1997. Changes in water chemistry and macrophyte and algal communities in experimental ponds simulating climate warming in the boreal area. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 26: 496–501.
Kankaala, P., A. Ojala, T. Tulonen, J. Haapamäki & L. Arvola, 2000. Response of littoral vegetation on climate warming in the boreal zone; an experimental simulation. Aquat. Ecol. 34: 433–444.
Kistritz, R. U., 1978. Recycling of nutrients in an enclosed aquatic community of decomposing macrophytes (Myriophyllum spicatum). Oikos 30: 561–569.
Koroleff, F., 1979. Methods for the chemical analyses of seawater. In Meri, Vol 7. Institute of Marine Research, Helsinki (in Finnish): 1–60.
Landers, D. H., 1982. Effects of naturally senescing aquatic macrophytes on nutrient chemistry and chlorophyll a of surrounding waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 27: 428–439.
Leinonen, L. (ed.), 1996. Air Quality Measurements 1994. Finnish Meteorological Institute. Official Statistics of Finland: 236 pp.
Leinonen, L. (ed.), 1997. Air Quality Measurements 1995. Finnish Meteorological Institute. Official Statistics of Finland: 248 pp.
Madsen, T. V. & A. Baattrup-Pedersen, 1995. Regulation of growth and photosynthetic performance in Elodea canadensis in response to inorganic nitrogen. Funct. Ecol. 9: 239–247.
Malthus, T. J., E. P. H. Best & A. G. Dekker, 1990. An assessment of the importance of emergent and floating-leaved macrophytes to trophic status in the Loosdrecht lakes (The Netherlands). Hydrobiologia 191: 257–263.
Mjelde, M. & B. A. Faafeng, 1997. Ceratophyllum demersum hampers phytoplankton development in some small Norwegian lakes over a wide range of phosphorus concentrations and geographical latitude. Freshwat. Biol. 37: 355–365.
Moore, B. C., J. E. Lafer & W. H. Funk, 1994. Influence of aquatic macrophytes on phosphorus and sediment porewater chemistry in a freshwater wetland. Aquat. Bot. 49: 137–148.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1963. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 27: 31–36.
Ojala, A., P. Kankaala, J. Haapamäki & T. Tulonen, 1995. Immediate responses of photosynthesis and dark respiration of late summer stands of Equisetum fluviatile L. to increasing concentrations of atmospheric CO2. Angew. Bot. 69: 169–176.
Ojala, A., P. Kankaala & T. Tulonen, 2002. Growth response of Equisetum fluviatile to elevated CO2 and temperature. Environ. Exp. Bot. (in press)
Ozimek, T., E. Van Donk & R. G. Gulati, 1993. Growth and nutrient uptake by two species of Elodea in experimental conditions and their role in nutrient accumulation in a macrophyte-dominated lake. Hydrobiologia 251: 13–18.
Pelton, D. K., S. N. Levine & M. Braner, 1998. Measurements of phosphorus uptake by macrophytes and epiphytes from the LaPlatte River (VT) using 32P in stream microcosms. Freshwat. Biol. 39: 285–299.
Sarvala, J., T. Kairesalo, I. Koskimies, A. Lehtovaara, J. Ruuhijärvi & I. Vähä–Piikkiö, 1982. Carbon, phosphorus and nitrogen budgets of the littoral Equisetum belt in an oligotrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 86: 41–53.
Schindler, D. W., S. E. Bayley, B. R. Parker, K. G. Beaty, D. R. Cruikshank, E. J. Fee, E. U. Schindler & M. P. Stainton, 1996. The effects of climatic warming on the properties of boreal lakes and streams at the Experimental Lakes Area, northwestern Ontario. Limnol. Oceanogr. 41: 1004–1017.
Schindler, D. W., 1997 Widespread effects of climatic warming on freshwater ecosystems in North America. In Cushing, C. E. (ed.), Freshwater Ecosystems and Climate Change in North America. Advances in Hydrological Processes. John Wiley & Sons. Chichester: 225–249.
Schlott, G. & G. Malicky, 1984. Biomasse und Phosphorgehalt der Makrophyten in der NO-Bucht des Lunzer Untersees (Austria) in Abhängigkeit von nährstoffreichen Zuflüssen und vom Sediment. Arch. Hydrobiol. 101: 265–277.
Shaver, G. R. & J. M. Melillo, 1984. Nutrient budgets of marsh plants: efficiency concepts and relation to availability. Ecology 65: 1491–1510.
Smith, C. S. & M. S. Adams, 1986. Phosphorus transfer from sediments by Myriophyllum spicatum. Limnol. Oceanogr. 31: 1312–1321.
Solorzano, L., 1969. Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14: 799–801.
Tulonen, T., P. Kankaala & A. Ojala, 1996. Production of bacteria in the littoral zone of two experimental mesohumic ponds. Arch. Hydrobiol. Spec. Issues Advanc. Limnol. 48: 217–225.
Weisner, S. E. B., P. G. Eriksson, W. Graneli & L. Leonardson, 1994. Influence of macrophytes on nitrate removal in wetlands. Ambio 23: 363–366.
Weisner, S. E. B., J. A. Strand & H. Sandsten, 1997. Mechanisms regulating abundance of submerged vegetation in shallow eutrophic lakes. Oecologia (Berl.) 109: 592–599.
Wood, E. D., F. A. J. Armstrong & F. A. Richards, 1967. Determination of nitrate in sea water by cadmium copper reduction to nitrite. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 47: 23–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kankaala, P., Ojala, A., Tulonen, T. et al. Changes in nutrient retention capacity of boreal aquatic ecosystems under climate warming: a simulation study. Hydrobiologia 469, 67–76 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015563224554
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015563224554