Abstract
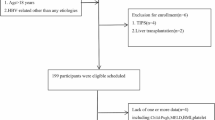
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide, especially in Asia. Gastrointestinal bleeding due to esophagogastric variceal hemorrhage is one of the leading causes of death in HCC patients. The aim of study was to determine whether clinical variables were predictive of the presence of large esophagogastric varices (EGV) before performing endoscopy. Three hundred and four HCC patients who received endoscopy were enrolled and studied retrospectively. Univariate and stepwise logistic regression analysis were used to evaluate associations between the presence of large EGV and patient characteristics. There were 248 patients with small or no EGV and 56 patients with large EGV. The optimal critical values determined by a receiver operating characteristic curve for platelet count and albumin level were 135,000/mm3 and 3.5 g/dl, respectively. Stepwise logistic regression analysis demonstrated that splenomegaly [odds ratio (OR): 9.72; confidence interval (CI): 3.75–25.17], portal vein thrombosis (OR: 2.73; CI: 1.50–4.97), low platelet count (<135,000/mm3) (OR: 3.78; CI: 2.07–6.90) and low albumin level (<3.5 g/dl) (OR: 3.44; CI: 1.73–6.82) were significant, independent predictors for large EGV. Large EGV also could be independently predicted by Child-Pugh classification, splenomegaly (OR: 4.93; CI: 1.87–13.01), or portal vein thrombosis (OR: 2.37; CI: 1.28–4.39) while excluding the non-cirrhotic patients. In conclusion, splenomegaly, low platelet count (<135,000/mm3), and low albumin level (<3.5 g/dl) are clinical predictors to stratify HCC patients at risk of developing large EGV. Besides factors related to liver cirrhosis, portal vein thrombosis is also an important predictor for HCC patients with large EGV.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Whang-Peng J, Chao Y: Clinical trials of HCC in Taiwan. Hepatogastroenterology 45:1937–1943, 1998
Llovet JM, Bustamante J, Castells A, Vilana R, AyusoMdel C, Sala M, Bru C, Rodes J, Bruix J: Natural history of untreated non-surgical hepatocellular carcinoma: Rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology 29:62–67, 1999
Nagasue N, Yukaya H, Hamada T, Hirose S, Kanashima R, Inokuchi K: The natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. A study of 100 untreated cases. Cancer 54:1461–1465, 1984
Nakashima T: Esophageal varices (in Japanese). Acta Hepat Jpn 15:254, 1974
Hashizume M, Inokuchi K, Beppu K, Koyanagi N, Nagamine K, Sugimachi K, Hirose S: The natural history of non-alcoholic cirrhosis. Gastroenterol Jpn 19:430–435, 1984
Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 19-1980. N Engl J Med 302:1132–1140, 1980
D'Amico G, Pagliaro L, Bosch J: The treatment of portal hypertension: A meta-analytic review. Hepatology 22:332–354, 1995
Lay CS, Tsao YT, Teg CY, Shyu WS, Guo WS, Wu KL, Lo KJ: Endoscopic variceal ligation in prophylaxis of first variceal bleeding in cirrhotic patients with high risk esophageal varices. Hepatology 25:1346–1350, 1997
Ng FH, Wong SY, Loo CK, Lam KM, Lai CW, Cheng CS: Prediction of oesophagogastric varices in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:785–790, 1999
Zaman A, Hapke R, Flora K, Rosen HR, Benner K: Factors predicting the presence of esophageal or gastric varices in patients with advanced liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 94:3292–3296, 1999
Chalasani N, Imperiale Thomas F, Ismail A, Sood G, Carey M, Wilcox M, Madichetty H, Kwo Paul Y, Boyer Thomas D: Predictors of large esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 94:3285–3291, 1999
Maratka Z: Terminology, Definitions, and Diagnostic Criteria in Digestive Endoscopy. Englewood, New Jersey, Normed Verlag, 1994
Hashizume M, Kitano S, Yamaga H, Koyanagi N, Sugimachi K: Endoscopic classification of gastric varices. Gastrointest Endosc 36:276–280, 1990
Pugh RN, Murray Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R: Transection of esophagus for bleeding esophageal varices. Br J Surg 60:646–649, 1973
Loftus WK, Metreweli C: Normal splenic size in a Chinese population. J Ultrasound Med 16:345–347, 1997
Weinreb J, Kumari S, Phillips G, Pochaczevsky R: Portal vein measurements by real-time sonography. Am J Roentgenol 139:497–499, 1982
Bolondi L, Gandolfi L, Arienti V, Caletti GC, Gasbarrini G, Labo G: Ultrasonography in the diagnosis of portal hypertension: Diminished response of portal vessels to respiration. Radiology 142:167–172, 1982
Itai Y, Furui S, Ohtomo K, Kokubo T, Minami M, Yashiro N: Dynamic CT features of arterioportal shunts in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Roentgenol 146:723–727, 1986
North Italian Endoscopic Club for the Study and Treatment of Esophageal Varices: Prediction of the first variceal hemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis of the liver and esophageal varices. A prospective multicenter study. N Engl J Med 319:983–989, 1988
Lai CL, Lam KC, Wong KP, Wu PC, Todd D: Clinical features of hepatocellular carcinoma: Review of 211 patients in Hong Kong. Cancer 47:2746–2755, 1981
Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H, Tomimatsu M, Okazaki N, Hasegawa H, Nakajima Y, Ohnishi K: Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Study of 850 patients. Cancer 56:918–928, 1985
De Franchis R: Updating consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno III Consensus Workshop on Definitions, Methodology and Therapeutic Strategies in Portal Hypertension. J Hepatol 33:846–852, 2000
Grace N: Diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding secondary to portal hypertension. Am J Gastroenterol 92:1081–1091, 1997
Cales P, Zabotto B, Meskens C, Caucanas JP, Vinel JP, Desmorat H, Fermanian J, Pascal JP: Gastroesophageal endoscopic features in cirrhosis observer variability, interassociations, and relationship to hepatic dysfunction. Gastroenterology 98:156–162, 1990
Witzel L, Wolbergs E, Merki H: Prophylactic endoscopic sclerotherapy of oesophageal varices: A prospective controlled study. Lancet i(8432):773–775, 1985
Toghill P, Green S, Ferguson R: Platelet dynamics in liver disease with special reference to the role of the spleen. J Clin Pathol 30:367–371, 1977
Tumen HJ: Hypersplenism and portal hypertension. Ann NY Acad Sci 170:332–337, 1970
Peck-Radosavljevic M, Zacherl J, Meng YG, Pidlich J, Lipinski E, Langle F, Steininger R, Muhlbacher F, Gangl A: Is inadequate thrombopoietin production a major cause of thrombocytopenia in cirrhosis of the liver? J Hepatol 27:127–131, 1997
Martin TG, Somberg KA, Meng YG, Cohen RL, Heid CA, de Sauvage FJ, Shuman MA: Thrombopoietin levels in patients with cirrhosis before and after orthotopic liver transplantation. Ann Intern Med 127:285–288, 1997
Webb LJ, Sherlock S: The aetiology, presentation and natural history of extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Q J Med 48:627–639, 1979
Pande GK, Sahni P, Nundy S: Extraphepatic obstruction causing portal hypertension. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:99–107, 1988
Okuda K, Ohnishi K, Kimura K, Matsutani S, Sumida M, Goto N, Musha H, Takashi M, Suzuki N, Shinagawa T, Suzuki N, Ohtsuki T, Arakawa M, Nakashima T: Incidence of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis: An angiographic study in 708 patients. Gastroenterology 89:279–286, 1985
Gaiani S, Bolondi L, Li Bassi S, Zironi G, Siringo S, Barbara L: Prevalence of spontaneous heptatofugal portal flow in liver cirrhosis. Clinical and endoscopic correlation in 228 patients. Gastroenterology 100:160–167, 1991
Albalete RA, Matthews MJ, Saini N: Portal vein thrombosis in malignant hepatoma. Ann Intern Med 67:337–348, 1967
Price J, Chan M, Hamilton-Wood C, Chronos NA, Mok SD, Metreweli C: Sonographic diagnosis of portal vein invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with arterial portography. Clin Radiol 41:9–12, 1990
Okuda K, Musha H, Yamasaki T, Jinnouchi S, Nagasaki Y, Shimokawa Y, Nakayama T, Kojiro M, Sakamoto K, Nakashima T: Angiographic demonstration of intrahepatic arterio-portal anastomosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 122:53–58, 1977
Takayasu K, Shima Y, Muramatsu Y, Goto H, Moriyama N, Yamada T, Makuuchi M, Yamasaki S, Hasegawa H, Okazaki N, Hirohasi S, Kishi K: Angiography of small hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of 105 resected tumors. Am J Roentgenol 147:525–529, 1986
Okuda K, Moriyama M, Yasumoto M, Jinnouchi S, Shimokawa Y: Roenterologic demonstration of spontaneous reversal of portal blood flow in cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Roentgenol 119:419–428, 1973
Okuda K, Obata H, Jinnouchi S, Kubo Y, Nagasaki Y: Angiographic assessment of gross anatomy of hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of celiac angiograms and liver pathology in 100 cases. Radiology 123:21–29, 1977
Nagasue N, Inokuchi K, Kobayashi M, Ogawa Y, Saku M: Angiographic evaluation of hepatoma for surgical treatment. Surg Gynecol Obstet 143:84–90, 1976
Schmidt B, Bhatt GM, Abo MN: Management of post-traumatic vascular malformations of the liver by catheter embolization. Am J Surg 140:332–335, 1980
Okuda K, Musha H, Nakajima Y, Takayasu K, Suzuki Y, Morita M, Yamasaki T: Frequency of intrahepatic arteriovenous fistula as a sequela to percutaneous needle puncture of the liver. Gastroenterology 74:1204–1207, 1978
Nagasue N, Inokudi K, Kobayashi M, Saku M: Hepatoportal arteriovenous fistula in primary carcinoma of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet 145:504–508, 1977
Nakashima T, Kojiro M: Hepatocellular Carcinoma, an Atlas of its Pathology, 1st ed. Tokyo, Springer-Verlag, 1987, pp 3–135
Lladó L, Virgili J, Figueras J, Valls C, Dominguez J, Rafecas A, Torras J, Fabregat J, Guardiola J, Jaurrieta E: A prognostic index of the survival of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cancer 88:50–57, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, JL., Peng, YC., Tung, CF. et al. Clinical Predictors of Large Esophagogastric Varices in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 47, 723–729 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014719428637
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014719428637