Abstract
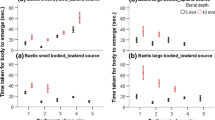
The larvae of Melampophylax mucoreus were buried with either 5 mm or 10 mm of four sediment size classes and their response recorded. The majority of individuals (63.8%) were able to extract themselves from the sediment within the 900 second (15 minute) experimental period. Body length was significantly greater in those larvae which excavated themselves compared to those that did not. Sedimentation/burial with finer sediment size classes to a greater depth significantly increased the escape time of larvae. The results are discussed in relation to the impact of sedimentation on larval trichopterans and other benthic organisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage, P. D., J. H. Blackburn, J. M. Winder and J. F. Wright, 1994. Impact of vegetation management on macroinvertebrates in chalk streams. Aquat. Conserv.4: 95–104.
Armitage, P. & A. Davies, 1989. A versatile laboratory stream with examples of its use in the investigation of invertebrate behaviour. Hydrobiol. Bull. 23: 151–160.
Bergy, E. A. and V. H. Resh, 1994. Effects of burrowing by a stream caddisfly on case-associated algae. J. n. am. Benthol. Soc. 13: 379–390.
Boulton, A. J., M. R. Scarsbrook, J. M. Quinn & G. P. Burrell, 1997. Land-use effects on the hyporheic ecology of five small streams near Hamilton, New Zealand. N. Z. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 31: 609–622.
Brookes, A., 1986. Response of aquatic vegetation to sedimentation downstream from river channelisation works in England and Wales. Biol. Conserv. 38: 352–367.
Chapman, D. W., 1988. Critical review of variables used to define effects of fines in redds of large Salmonids. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 117: 1–21.
Dobson, M., K. Poynter & H. Cariss, 2000. Case abandonment as a response to burial by Potamophylax cingulatus (Trichoptera: Limnephilidae) larvae. Aquat. Insect. 22: 99–107.
Doeg, T. J. and J. D. Koehn, 1994. Effects of draining and desilting a small weir on downstream fish and macroinvertebrates. Regul. Riv. 9: 263–278.
Frochot, B., 1963. Trois nouvelles larves du genre Halesus (s.l.) (Trichoptera: Limnephilidae). Trav. Lab. Zool., Stn. Aquic. Grimaldi, Dijon. 49: 1–36.
Higler, L. W. G., 1975. Reactions of some caddis larvae (Trichoptera) to different types of substrate in an experimental stream. Freshwat. Biol. 5: 151–158.
Hiley, P. D., 1976. The identification of British Limnephilidae larvae (Trichoptera). Syst. Entomol. 1: 147–167.
Johansson, A. & G. England, 1995. A predator-prey game between bullheads and case-making caddis larvae. Anim. Behav. 50: 785–792.
Murphy, M. L. and A. M. Milner, 1997. Timber harvest and fish habitat. In Milner, A. M. & M. W. Oswood (eds), Alaska Fresh Waters. Springer, New York: 229–263.
Nislow, K. H. and M. C. Molles, 1993. The influence of larval case design on vulnerability of Limnephilus frijole (Trichoptera) to predation. Freshwat. Biol. 29: 411–417.
Orth, D. J. and O. E. Maughan, 1983. Microhabitat preferences of benthic fauna in a woodland stream. Hydrobiologia 106: 157–168.
Otto, C. & A. Johansson, 1995. Why do dome caddis larvae in running water construct heavy, bulk cases? Amin. Behav. 49: 473–478.
Peterson, N. P. & T. P. Quinn, 1996, Persistence of egg pocket architecture in redds of chum salmon, Oncorhynchus keta. Envir. Biol. Fishes. 46: 243–253.
Quinn, J. M., R. J. Davies-Colley, C. W. Hickey, M. L. Vickers & P. A. Ryan, 1992. Effects of clay discharge on streams: 2. Benthic invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 248: 235–247.
Richards, C., G. H. Host & J. W. Arthur, 1993. Identification of predominant environmental factors structuring stream macroinvertebrate communities within a large agricultural catchment. Freshwat. Biol. 29: 285–294.
Rier, S. T. & D. K. King, 1996. Effects of inorganic sedimentation and riparian clearing on benthic community metabolism in an agriculturally-disturbed stream. Hydrobiologia 339: 111–121.
Ryan, P. A., 1991. Environmental effects of sediment on New Zealand streams: a review. N. Z. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 25: 207–221.
Sand-Jensen, K. & J. P. Mebus, 1996. Fine-scale patterns of water velocity within macrophyte patches in streams. Oikos 76: 169–180.
Wallace, I. D., 1980. The identification of British limnephilid larvae (Trichoptera: Limnephilidae) which have single-filament gills. Freshwat. Biol. 10: 171–189.
Wallace, I. D., 1991. A review of the Trichoptera of Great Britain. Nature Conservany Council, Peterborough: 61 pp.
Wallace, I. D., B. Wallace & G. N. Philipson, 1990. A Key to the Case-Bearing Caddis Larvae of Britain and Ireland. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication No. 51. Ambleside: 237 pp.
Wood, P. J. & P. D. Armitage, 1997. Biological effects of fine sediment in the lotic environment. Envir. Mgmt: 21: 203–217.
Wood, P. J. & P. D. Armitage, 1999. Sediment deposition in a small lowland stream – management implications. Regul. Riv. 15: 199–210.
Zeh, M. & W. Donni, 1994. Restoration of spawning grounds for trout and grayling in the river High-Rhine. Aquat. Sci. 56: 59–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wood, P.J., Vann, A.R. & Wanless, P.J. The response of Melampophylax mucoreus (Hagen) (Trichoptera: Limnephilidae) to rapid sedimentation. Hydrobiologia 455, 183–188 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011985403744
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011985403744