Abstract
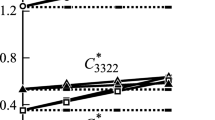
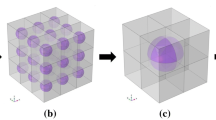
Most piezocomposites, which have been widely used in engineering, consist of piezoelectric inclusions and a non-piezoelectric matrix. Due to the limits of fabrication technology, it is hard to avoid the matrix intermingling with other non-piezoelectric inclusions, such as cavities. The non-piezoelectric inclusions can substantially affect performance of piezocomposites. In this paper we study the electromechanical fields in piezocomposites which are composed of a non-piezoelectric matrix embedded with both piezoelectric and non-piezoelectric inclusions. Closed-form relations are obtained for the effective electroelastic moduli of a piezocomposite with both piezoelectric and non-piezoelectric inclusions. The effective properties of a 1-3 type piezocomposite with non-piezoelectric spherical inclusions are analyzed carefully and explicit formulae for the effective electroelastic properties of a 1-3-0 piezocomposite are also obtained. The analysis shows that the effect of non-piezoelectric inclusions on the electroelastic properties of piezocomposites is significant and should not be neglected. The model proposed in this paper is expected to be useful for predicting and analyzing the overall electromechanical properties of piezocomposites with a non-piezoelectric matrix containing both piezoelectric and non-piezoelectric inclusions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.E. Newnham, D.P. Skinner and L.E. Cross, Connectivity and piezoelectric pyroelectric composites. Mat. Res. Bull. 13 (1978) 525–536.
S.S. Rao and M. Sunar, Piezoelectricity and its use in disturbance sensing and control of flexible structures: A survey. Appl. Mech. Rev. 47 (1994) 113–123
C.J. Disa and D.K. Das-Gupta, Inorganic ceramic/polymer ferroelectric composite electrets. IEEE Trans. Dielectrics and Electric Inclusion 3 (1996) 706–734.
W.A. Smith and A.A. Shaulov, Composite piezoelectrics: Basic research to a practical device. Ferroelectrics 87 (1988) 307–320.
W.A. Smith, Modeling 1–3 composite piezoelectric: hydrostatic response. IEEE Ultrasonic Ferroelec. Freq. Contr. 40 (1993) 41–48.
P.F. Gobin, G. Guenin, M. Morin, M. Salvia and J. Tatibouet, Smart materials: A future for composites. J. Intelligent Material Systems Struct. 7 (1996) 353–357.
Y. Ohara, M. Miyayama, K. Koumoto and H. Yanagida, PZT-polymer piezoelectric composites: A design for an acceleration sensor. Sensors and Acruators A 26 (1993) 121–126.
A. Egusa and N. Iwasawa, Piezoelectric pints: preparation and applications as bulit-in vibration sensors of structural materials. J. Mater. Sci. 28 (1993) 1667–1672.
B.A. Auld and Y. Wang, Acoustic wave vibrations in periodic composite plates. In: IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Texas, USA (1984) pp. 528–532.
H. Banno, Theoretical equations for the dielectric and piezoelectric properties of ferroelectric composites based on modified cubes model. Japan J. Appl. Phys. 24 (1985) 445–447.
H.L.W. Chan and J. Unsworth, Simple model for piezoelectric ceramic/polymer 1–3 composites used in ultrasonic transducer applications. IEEE Ultrasonics Ferroelec. Freq. Contr. 36 (1989) 434–441.
A.A. Grekov, S.O. Kramarov and A.A. Kuprienko, Effective properties of transversely isotropic piezocomposite with cylindrical inclusions. Ferroelectrics 99 (1989) 115–126.
J.A. Hossack and R.L. Bedi, Design of composite piezoelectric transducers. In: K. Das-Gupta (ed.), Ferroelectric Polymers and Ceramic-polymer composites, Trans-Tech Pub., Switzerland (1994).
W.A. Smith, Modeling 1–3 composite piezoelectrics: Thickness-mode oscillations. IEEE Ultrasonics Ferroelec. Freq. Contr. 38 (1991) 40–47.
Y. Benveniste and G.J. Dovrak, On uniform fields and universal relations in piezoelectric composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 40 (1992) 1295–1312.
Y. Benveniste, The determination of the elastic and electric fields in a piezoelectric inhomogeneity. J. Appl. Phys. 72 (1992) 1086–1095.
Y. Benveniste, Universal relations in piezoelectric composites with eigenstress and polarization fields, I: Binary media: Local fields and effective behavior. II, multiphase media: effective behavior. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 60 (1993) 265–270.
Y. Benveniste, Exact results concerning the local fields and effective properties in piezoelectric composites. Trans. ASME J. Engng. Mater. Tech. 116 (1994) 260–267.
C.J. Disa and D.K. Das-Gupta, Piezoelectric properties of 0–3 ceramic-polar polymer composites. In: Materials Research Society Symposium Proc., Vol.276 (1992) pp. 25–29.
B. Wang, Three dimensional analysis of an ellipsoidal inclusion in a piezoelectric material. Internat. J. Solid Struct. 29 (1992) 313–318.
D.K. Das-Gupta and M.J. Abdullah, Electroactive properties of polymer-ceramic composites. Ferroelectrics 87 (1993) 2462–2466.
M.L. Dunn and M. Taya, An analysis of piezoelectric composite materials containing ellipsoidal inhomogeneities. Internat. J. Solids. Struct. 30 (1993) 161–175.
M.L. Dunn and M. Taya, Micromechanics predictions of the effective electroelastic moduli of piezoelectric composites. Proc. Roy. Soc. London A 443 (1993) 265–287.
R.E. Newnham and G.R. Ruschau, Electromechanical properties of smart materials. J. Intelligent Mater. System and Struct. 4 (1993) 289–294.
B. Jiang, D.N. Fang and K.C. Hwang, The effective properties of piezocomposites, Part I: Single inclusion problem. Acta Mechanica Sinica 13 (1997) 339–346.
B. Jiang, D.N. Fang and K.C. Hwang, A unified model for piezocomposites with nonpiezoelectric matrix and piezoelectric ellipsoidal inclusions. Internat. J. Solids Struct. 36 (1999) 2707–2733.
M. Avellaneda and P.J. Swart, Calculating the performance of 1–3 piezoelectric composite for hydrophone applications: An effective medium approach. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103 (1998) 1449–1467.
T. Furukawa, K. Fujino and E. Fukasa, Electromechanical properties in the composites of epoxy resin and PZT ceramics. Japan J. Appl. Phys. 15 (1976) 2119–2129.
A. Safari, R.E. Newnham, L.E. Cross and W.A. Schulze, Perforated PZT-polymer composites for piezoelectric transducer applications. Ferroelectrics 41 (1982) 197–202.
K. Hikita, K. Yamada, M. Nishioka and M. Ono, Effect of porous structure to piezoelectric properties of PZT ceramics. Japan J. Appl. Phys. 22 (1983) 64–66.
R.E. Newnham, Ferroelectric composites. Japan J. Appl. Phys. 24 (1985) 16–17.
S.M. Pilgrimand and R.E. Newnham, 3–0 a new composite connectivity. Mater. Res. Bull. 21 (1986) 1447–1454.
R.Y. Ting, The hydroacoustic behavior of piezoelectric composite materials. Ferroelectrics 102 (1990) 215–224.
H.S. Paul and V.K. Nelson, Flexural vibration of piezoelectric composite hollow cylinder. J. Acoust. Soc. Amer. 99 (1996) 309–313.
Q.M. Zhang, H. Wang, J. Zhao, J.T. Fielding, R.E. Newnham and L.E. Cross, A high sensitivity hydrostatic piezoelectric transducer based on transverse piezoelectric mode honeycomb ceramic composites. IEEE Ultrasonic Ferroelec. Freq. Contr. 43 (1996) 36–43.
H.G. Lee and H.G. Kim, Influence of microstructures on the dielectric and piezoelectric properties of lead zirconate titanate-polymer composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 72 (1989) 938–942.
B. Budiansky, On the elastic moduli of some heterogeneous materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 13 (1965) 223–227.
T. Mori and T. Tanaka, Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusion. Acta Metallurgica 21 (1973) 517–574.
W.F. Deeg, The analysis of dislocation, crack and inclusion problems in piezoelectric solids. PhD Thesis of Stanford University, USA (1980).
T.Y. Chen, Green function and the non-uniform transformation problem in a piezoelectric medium. Mech. Res. Comm. 20 (1993) 271–278.
T.Y. Chen, Some exact relations of inclusions in piezoelectric media. Internat. J. Engng. Sci. 32 (1994) 553–556.
J.H. Huang and J.S. Yu, Electroelastic Eshelby tensors for an ellipsoidal piezoelectric inclusion. Composites Engineering 4 (1994) 1169–1182.
H.J. Bunge, Texture Analysis in Materials Science. Butterworth, London (1982).
B. Jaff, W.R. Cook and H. Jaff, Piezoelectric Ceramics. Academic Press, New York (1971).
M.E. Lines and A.M. Glass, Principles and Applications of Ferroelectrics and Related Materials. Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford (1977).
T. Mura, Micromechanics of Defects in Solids. Martinus Nijhoff, The Hague (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, DN., Jiang, B. & Hwang, KC. A Model for Predicting Effective Properties of Piezocomposites with Non-piezoelectric Inclusions. Journal of Elasticity 62, 95–118 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011690908826
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011690908826