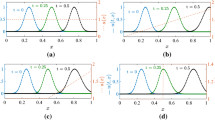
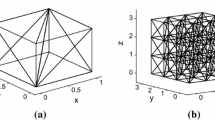
Abstract
Given a precision threshold to be imposed on the group velocity error and a finite difference scheme for the acoustic wave equation, it is possible to determine time-step and grid-spacing in an optimal manner, i.e., so as to minimize the computational cost. Using this optimal cost as a criterion, it becomes easy to compare schemes for efficiency in homogeneous media.
Heterogeneous media with constant density can be accommodated to a certain extent by minimizing the cost over a range of Courant numbers. Such analysis shows that, amongst the second-order Taylor series schemes in time, higher-order schemes are generally more efficient than lower-order schemes. However, this result does not extend to very high order schemes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. M. Alford, K. R. Kelly and D. M. Boore, Accuracy of finite-difference modeling of the acoustic wave equation, Geophysics 39 (1974) 834–842.
A. Bamberger, G. Chavent and P. Lailly, Etude des schémas numériques pour l'équation des ondes, Technical Report INRIA No. 41 (1980).
L. Brillouin, Wave Propagation and Group Velocity (Academic Press, New York, 1960).
G. Cohen and P. Joly, Fourth order schemes for the heterogeneous acoustic equation, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 80 (1990) 397–407.
M. A. Dablain, The application of high-order differencing to the scalar wave equations, Geophysics 51 (1986) 54–66.
K. R. Kelly, R. W. Ward, S. Treitel and R. M. Alford, Synthetic seismograms: a finite-difference approach, Geophysics 41 (1976) 2–27.
M. Kern and W. W. Symes, Loop level parallelisation of a seismic inversion code, in: Proceedings of the 63rd SEG Annual Meeting, Washington DC (1993).
I. Mufti, Large-scale three-dimensional seismic models and their interpretative significance, Geophysics 55 (1990) 1166–1182.
E. Piault, P. Duclos and A. Sei, Gigaflops performance for 2-D/3-D heterogeneous acoustic modelling on a massively parallel computer, in: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Mathematical and Numerical Aspects of Wave Propagation Phenomena (SIAM, 1991).
R. Richtmyer and K. Morton, Difference Methods for Initial-Value Problems (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1967).
A. Sei, Étude de schémas numériques pour les modèles de propagation d'ondes en milieux hétérognes, Thèse de doctorat de l'Université de Paris-Dauphine (1991).
A. Sei, Computational cost of finite difference elastic waves modelling, in: Proceedings of the 63rd SEG Annual Meeting, Washington DC (1993).
L. Trefethen, Group velocity in finite difference schemes, SIAM Review 24 (1982) 113–136.
R. Vichnevetsky and J. B. Bowles, Fourier Analysis of Numerical Approximation of Hyperbolic Equations (SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, 1982).
G. B. Whitham, Linear and Nonlinear Waves (Wiley, New York, 1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anné, L., Tran, Q.H. & Symes, W.W. Dispersion and cost analysis of some finite difference schemes in one-parameter acoustic wave modeling. Computational Geosciences 1, 1–33 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011576309523
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011576309523